What Are Risk Factors For Shingles
Shingles can only occur in individuals who have previously been exposed to the varicella-zoster virus. Risk factors for the development of shingles include the following:
- Increasing age: Though shingles can rarely occur in children, it is much more common in older adults, with the incidence increasing with age. This is thought to be in large part due to waning immunity as people age. Approximately 50% of all cases of shingles occur in adults 60 years of age or older.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with impaired immune systems have a higher probability of developing shingles. This can be seen in diseases such as cancer and HIV/AIDS, or in individuals taking certain medications. Patients taking steroids or other immunosuppressive medications, such as people who have undergone organ transplants, and individuals with certain autoimmune diseases are at increased risk for developing shingles.
- Psychological and emotional stressors are also thought to possibly contribute to the development of shingles, perhaps from the detrimental effects of stress on the immune system and the persons health.
- By Kelly Bilodeau, Executive Editor, Harvard Womens Health Watch
If youre like 95% of American adults, you had chickenpox as a kid. Before the United States started its widespread vaccination program in 1995, there were roughly four million cases of chickenpox every year. So, most people suffered through an infection with this highly contagious virus and its itchy, whole-body rash.
Shingles Linked To Stroke Heart Attack
Not only do shingles flare-ups hurt, research says they can increase your short-term risk of heart attack and stroke following the virus outbreak.
Shingles was found to raise the risk of stroke by 35% and the risk of heart attack by nearly 60%, according to a study of more than half a million people. The risk of stroke was highest in those under age 40.
Its been known for a while now that zoster causes stroke, said Dr. Gwen Wigand-Bolling, an internist at . The inflammation it creates causes heart attack and stroke, and shingles causes increased blood clotting in the arteries, she added.
The risks of both stroke and heart attack were highest in the first year after the onset of shingles and decreases with time, researchers said.
What Is Postherpetic Neuralgia
In some instances, people whove had shingles may experience postherpetic neuralgia , in which pain persists well after the blisters go away. This happens because the shingles-damaged nerves continue to send pain signals to the brain.
Neurology
There are several factors that can lead to postherpetic neuralgia. Anything that depresses immunity can increase your risk, says Dr. Oaklander.
She adds: The severity of postherpetic neuralgia gradually eases over time in everyone, but the rate of resolution can vary. As you get older, your postherpetic neuralgia typically lasts longer and longer. Senior citizens, who are the most at risk for zoster, have substantial risk of postherpetic neuralgia lasting over a year, and sometimes for the rest of their lives.
If you have a lot of pain before the rash, it puts you at much higher risk for postherpetic neuralgia, adds Joseph Safdieh, MD, professor of neurology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City.
Pain
- Personality disorder
Don’t Miss: What Medication To Use For Shingles
What Problems Can Happen
Most cases of shingles heal on their own, with or without treatment, and won’t lead to any other problems. In rare cases, shingles can lead to complications, including:
- Ongoing pain : Damaged nerve fibers in the skin send confused messages to the brain, leading to pain. Pain can go on for a long time after the shingles rash is gone. This is the most common shingles complication.
- Vision problems: Shingles near or in an eye can lead to vision loss.
- Skin infections: A shingles rash can become infected with bacteria, leading to impetigo or cellulitis.
- Nervous system problems: Shingles on the face can involve different nerves that connect to the brain. This can lead to nerve-related problems such as facial paralysis, hearing problems, and problems with balance. In very rare cases, shingles can lead to encephalitis .
How Long Does It Take For Shingles To Progress
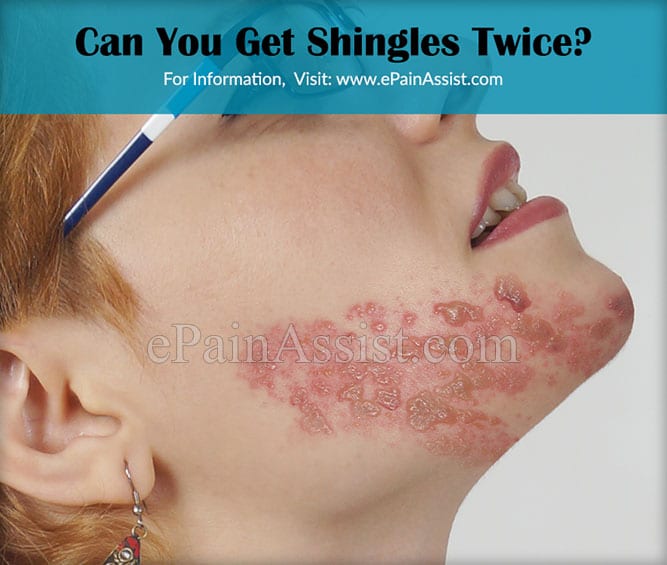
Shingles progresses into blisters over three to five days and begins to crust over after seven to ten days. The rash is preceded by a prodromal phase lasting 48-72 hours or longer, consisting of throbbing pain and numbness in the area affecting the nerve. Once the rash blisters, it can last another three to five days before the lesions scab over.
After the lesions crust over, it may take two to four weeks to heal completely. At this time, pain may still be present. The most painful stage of shingles is when you have fluid-filled blisters. This usually occurs three to five days after the rash first appears.
You May Like: How To Treat Shingles In The Eye
Should You Get The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine is safe and easy, and it may keep you from getting shingles and PHN. Healthy adults age 50 and older should get vaccinated with a shingles vaccine called Shingrix, which is given in two doses. Zostavax, a previous shingles vaccine, is no longer available in the United States.
You should try to get the second dose of Shingrix between two and six months after you get the first dose. If your doctor or pharmacist is out of Shingrix, you can use the Vaccine Finder to help find other providers who have Shingrix. You can also contact pharmacies in your area and ask to be put on a waiting list for Shingrix. If its been more than six months since you got the first dose, you should get the second dose as soon as possible. You dont need to get a first dose again.
You should get Shingrix even if you have already had shingles, received Zostavax, or dont remember having had chickenpox. However, you should not get a vaccine if you have a fever or illness, have a weakened immune system, or have had an allergic reaction to Shingrix. Check with your doctor if you are not sure what to do.
You can get the shingles vaccine at your doctors office and at some pharmacies. Medicare Part D and private health insurance plans may cover some or all of the cost. Check with Medicare or your health plan to find out if it is covered.
You May Like: Shingles Vaccine Walgreens Cost
Could It Be Shingles
If youre an older adult and experiencing a blistery rash, the most likely answer is that youve got shingles, a.k.a. herpes zoster, which affects one in three people in their lifetime, according to the CDC. Shingles is whats known as a reactivation virus that usually affects older adults, says Dr. Jones Lopez. Basically, once youve had chickenpox, the varicella zoster virus stays in your body. After the initial infection, the virus goes into dormant state for potentially decades, he says. Much later in life, when your immunity goes down, it can reactivate as shingles.
Unlike a chickenpox rash, the shingles rash is usually confined to a specific area of the body and appears in a single band, rather than spreading indiscriminately. It typically happens somewhere on the chest or back, says Dr. Jones-Lopez, although the head and other parts of the body can sometimes be affected. The key thing that distinguishes the shingles rash is that it doesnt cross the midline. If it spreads across your body, its not shingles. For example, if youve got a rash on left side of your face but another on the right side of your back, you can probably rule out this illness.
In addition to a rash , you may have some pain, itching, or tingling on your skin. You may also have flu-like symptoms . Like chickenpox, shingles rashes may itchbut they are mostly known for causing pain.
You May Like: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Neck
What Are The Complications Associated With Shingles
Shingles is not usually dangerous to healthy individuals although it can cause great misery during an attack. Anyone with shingles on the upper half of their face, no matter how mild, should seek medical care at once because of the risk of damage to the eye. Very rarely, shingles can lead to pneumonia, hearing problems, blindness, brain inflammation or death. For about one person in five, severe pain can continue even after the rash clears up. This pain is called post-herpetic neuralgia. As people get older, they are more likely to develop post-herpetic neuralgia, and it is more likely to be severe.
Treatments For Other Problems Caused By Shingles
In some cases, shingles causes long-term problems. Treatment depends on what the problem is.
- Disseminated zoster. This is a blistery rash over a large portion of the body. It may affect the heart, lungs, liver, pancreas, joints, and intestinal tract. Treatment is done in the hospital. It may include antiviral medicines to prevent the virus from multiplying and antibiotics to stop infection.
- Herpes zoster ophthalmicus. This is a rash on the forehead, cheek, nose, and around one eye. It could threaten your sight. Get treatment from an ophthalmologist right away. Treatment may include antiviral medicines and steroid eye drops.
- If the shingles virus affects the nerves that begin in the brain , serious problems involving the face, eyes, nose, and brain can occur. Treatment depends on what the problem is and where it is.
Don’t Miss: Does Health Insurance Cover Shingles Vaccine
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Shingles
Often the first shingles symptoms happen in the area where the rash will appear. A person may have tingling, itching, or pain in this area. When the rash shows up, the pain may be mild or severe.
The rash starts as groups of tiny pimples on one side of the body or the face. Its often in the shape of a band or belt. The pimples change to pus-filled blisters that break open and scab over in about 710 days. The scabs usually heal and fall off about 24 weeks after the rash starts.
Some kids with shingles also may have a fever and a headache, and might feel tired and achy. Rarely, a child has the pain of shingles without the rash. More severe symptoms can happen, but usually in people over age 50.
How Can I Prevent The Spread Of The Shingles Virus
The virus can be passed to a person who has never had chickenpox. This usually happens if the other person comes in contact with your open sores. This person may get chickenpox, but not shingles. You are contagious until your blisters scab over. Stay away from people who have not had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine. Avoid pregnant women, newborns, and people with weak immune systems. They have a higher risk of infection.
- Wash your hands often. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child’s diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Use soap and water every time. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Wash the front and back of your hands, and in between your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available. Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth without washing your hands first.
- Cover a sneeze or cough. Use a tissue that covers your mouth and nose. Throw the tissue away in a trash can right away. Use the bend of your arm if a tissue is not available. Wash your hands well with soap and water or use a hand sanitizer.
Read Also: Can You Run A Fever With Shingles
Rebooting The Nervous System
Its like restarting a computer, Dr. Rosenquist says. When its running slowly or acting weird, you restart it. We are trying to turn that nerve off. When it comes back on, hopefully, it will send an appropriate transmission as opposed to a pain transmission.
Treatmentoptions for PHN patients include:
Patientswith refractory PHN rarely need opioid pain medication. However,you should be evaluated by a physician. We cant make a blanket statement abouttreatment. It is individualized, she says.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Shingles
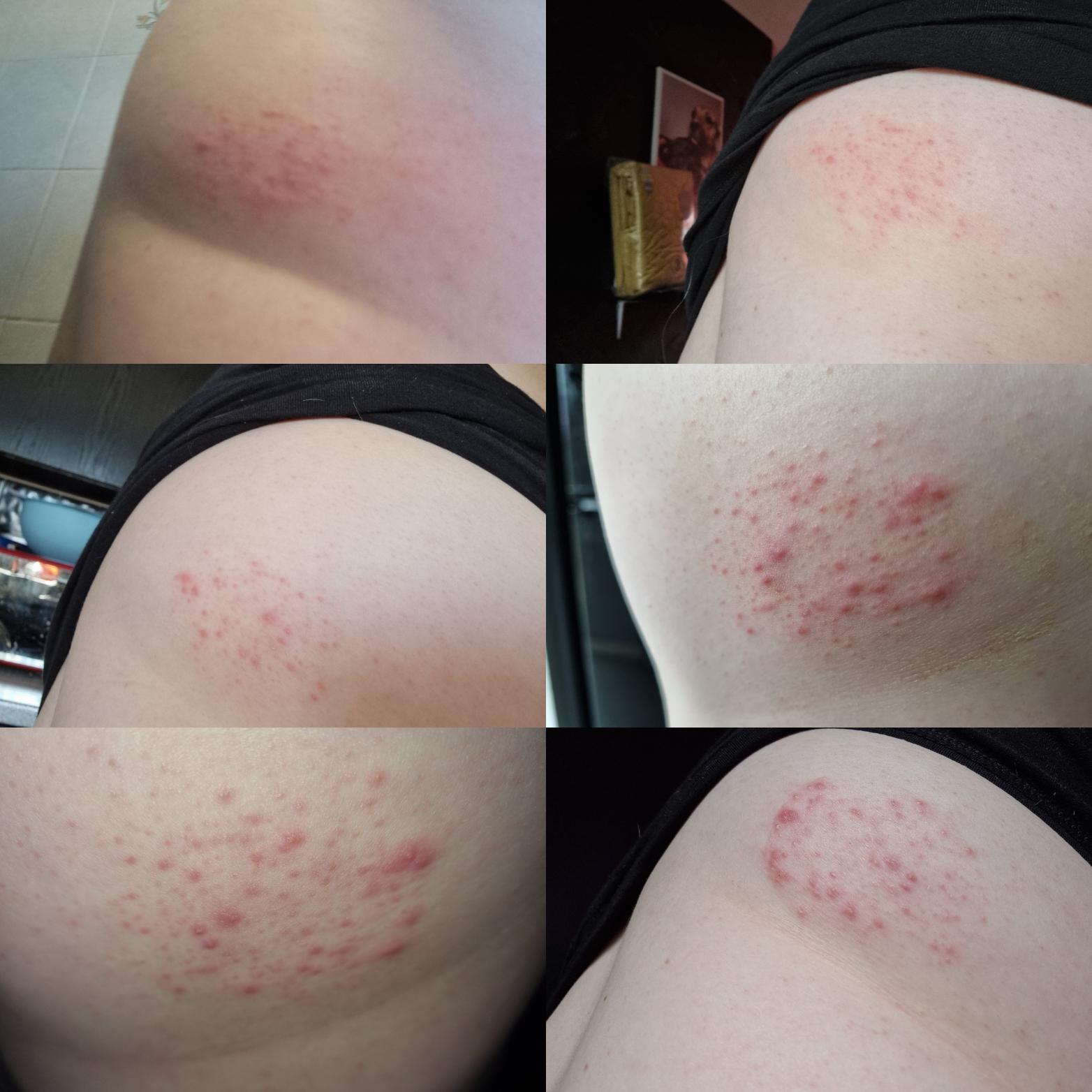
Shingles can appear anywhere on your body, but it is most common on your torso. A line of painful blisters develops on the left or right side of your torso. The rash starts as red dots that become blisters filled with fluid. The blisters usually grow bigger, become filled with pus, and then crust over after a few days. You may also have any of the following:
- Severe tiredness and muscle weakness
- Pain when your skin is lightly touched
- Eye pain when exposed to light
You May Like: How To Soothe Shingles Rash
What Are Vaccine Side Effects
There are two vaccinations for shingles to prevent an outbreak: Zoster vaccine live and Recombinant zoster vaccine are both legitimate shots to protect the at-risk population. Brand name Shingrix is one of the latter and the top recommendation from the CDC for shingles vaccines. The CDC recommends the vaccine for adults over the age of 50 that have had chickenpox at some time in their lifetime. The organization estimates that 99% of elderly adults have had a chickenpox outbreak in their childhood, even if they dont remember.
The vaccine side effects are mild for most patients and include:
- Soreness and redness at the injection site
For most people, the after-effects of the vaccine cleared up in 2 to 3 days from the booster. The formula does not include the preservative thimerosal, for those concerned with mercury poisoning.
Who Shouldn’t Get A Shingles Vaccine
The CDC says some people shouldn’t get the shingles vaccine. That includes those who:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix
- Tested negative for VZV immunity
- Currently have shingles
- Have a severe or moderate acute illness, such as a respiratory infection
Your healthcare provider can answer any questions you have about whether the vaccine is safe for you.
You May Like: What Causes Shingles To Break Out
Facial Pain And Eye Damage
Between 10% and 15% of the time, shingles affects the trigeminal gangliona triple-branched nerve that provides sensation to structures in the face. The medical term for head or facial pain due to shingles is “painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to herpes zoster.”
Specifically, the trigeminal ganglion involves the eye the cheek and the mandibular branch . Of these, the ophthalmic branch is the one most commonly affected by herpes zoster.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology , 25% of the 300,000 to 500,000 cases of shingles that occur each year are herpes zoster ophthalmicus .
HZO can affect any part of the eye, from the optic nerve to the conjunctiva . Without antiviral treatment, almost half of people who have shingles near the eye will experience eye damage or even lose an eye, so it’s vital to see an ophthalmologist immediately.
What Can You Do To Prevent Shingles
While you may not be able to control certain factors that might trigger shingles, there are strategies you can use to prevent shingles. The most important is vaccination. Research shows that the shingles vaccine Shingrix is 90% effective in preventing an outbreak of shingles. Even if you do get shingles after being vaccinated, Shingrix greatly reduces your risk of developing persistent pain in the affected area, known as post-herpetic neuralgia.
In addition to getting vaccinated, its always a good idea to take steps to keep your body healthy, such as choosing healthy foods, staying active, and getting sufficient sleep. Its not clear if healthy lifestyle habits like these can prevent shingles, but even if they dont, theyre worthwhile because they will benefit your body in many other ways.
Dont Miss: Rite Aid Shingles Shot Cost
Recommended Reading: What Can You Use For Shingles Pain
What Are Complications Of Shingles
Though shingles often resolve without any major problems, several potential complications can arise from shingles.
- Postherpetic neuralgia : This is the most common complication of shingles. PHN is characterized by persistent pain and discomfort in the area affected by shingles. The pain can last for months to several years after the rash has cleared up. This complication is thought to occur because of damage to the affected nerves. The pain can sometimes be severe and difficult to control, and the likelihood of developing postherpetic neuralgia increases with age. This chronic post-herpetic pain can sometimes lead to depression and disability. In people 60 years of age and older with shingles, postherpetic neuralgia will develop in approximately 15%-25% of cases. It rarely occurs in people under 40 years of age. Timely treatment with antiviral medication during a shingles outbreak may help reduce the incidence of developing postherpetic neuralgia. If postherpetic neuralgia develops, there are various treatment options available including topical creams such as capsaicin , topical anesthetic lidocaine patches , antiseizure medications such as gabapentin , pregabalin , tricyclic antidepressant medications, and opioid pain medications. Intrathecal glucocorticoid injections may be useful for select patients with postherpetic neuralgia who do not respond to conventional medications and treatment measures.