What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Its normal to have questions before you get a vaccine. Some common questions you may want to discuss with your healthcare provider include:
- When should I get the shingles vaccine?
- What side effects should I expect?
- How does the shingles vaccine work?
- When should I schedule each dose of the shingles vaccine?
- How effective is the shingles vaccine?
- Is there any reason I shouldnt get the shingles vaccine?
- What could happen if I dont get the shingles vaccine?
Should You Get Shingrix If You Had The Zostavax Shingles Vaccine
It is recommended that you get two doses of Shingrix even if you got a different shingles vaccine in the past. Before Shingrix was approved, the Zostavax shingles vaccine was available. It was discontinued in November 2020 as Shingrix is much more effective. If you had the Zostavax vaccine, talk to your healthcare provider about getting Shingrix.
When They Start How Long They Last
The shingles vaccine is given in a two-shot series. You may experience side effects after the first, second, or both shots. Most of the time, these symptoms are mild and occur immediately following vaccination. They typically only last for two or three days.
Side effects of the shingles vaccine are more common in younger people, and might interrupt your normal daily activities for a few days.
This may seem like a downside of the shingles vaccine, but remember that these symptoms are a result of the creation of a strong shingles defense within your body.
It is OK to take Tylenol or Advil after a shingles vaccine to relieve symptoms. Rest and plenty of fluids may help, too.
Read Also: Can Shingles Cause Hair Loss
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Where Does Shingles Come From
When you have chickenpox as a child, your body fights off the varicella-zoster virus and the physical signs of chickenpox fade away, but the virus always remains in your body. In adulthood, sometimes the virus becomes active again. This time, the varicella-zoster virus makes its second appearance in the form of shingles.
Also Check: What’s The Best Medicine For Shingles
Summary And Quick Facts For Herpes And Shingles
- Herpes and shingles are both caused by members of the Herpesviridae family of viruses, which can establish latent infections that remain dormant before reactivating at a later time under certain conditions. Herpes simplex virus-1 and herpes simplex virus-2 cause oral and genital herpes, and varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children and shingles later in life.
- In this protocol, you will learn about the viruses that cause herpes and shingles, and how these infections are conventionally treated. Several natural ingredients that may help ease the symptoms of herpes and shingles will also be discussed, and important lifestyle and dietary considerations that can help prevent outbreaks will be examined as well.
- Antiviral medication is the standard treatment for both shingles and herpes. Although there is no effective cure for herpes virus infections, several natural interventions may help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Herpes and shingles are both caused by members of the Herpesviridae family of viruses, which can establish latent infections that remain dormant and then reactivate under certain conditions. Herpes simplex virus-1 and herpes simplex virus-2 cause oral and genital herpes, and varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children and shingles later in life.
Dont Miss: How Long Does An Initial Herpes Outbreak Last
More Information On Side Effects
Reactions listed under possible side effects or adverse events on vaccine product information sheets may not all be directly linked to the vaccine. See Vaccine side effects and adverse reactions for more information on why this is the case.
If you are concerned about any reactions that occur after vaccination, consult your doctor. In the UK you can report suspected vaccine side effects to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency through the Yellow Card Scheme . See more information on the Yellow Card scheme and monitoring of vaccine safety.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Not To Eat With Shingles
Is The Shingles Vaccine Safe
The FDA have approved the use of both shingles vaccines in healthy adults over the age of 50.
However, there are some instances in which a person should not get either vaccine â if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, allergic to any ingredient in the vaccine, or have a weakened immune system, for example.
What Are The Side Effects
Shingrix can make the area where you get the shot swell or feel sore. Other effects include:
- Many people who get the vaccine have muscle aches, headaches, or feel tired.
- About 1 in 4 people have a fever or an upset stomach.
Younger people are more likely to have these side effects, and they typically last 2 or 3 days.
Itâs also possible to have an allergic reaction to an ingredient in the vaccine. If you have problems breathing, feel your face or throat swelling, or feel weak or dizzy after the shot, call 911 and get medical help right away.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Take For Shingles
How Are Shingles And Herpes Treated
Neither condition can be cured, but treatments are available.
Shingles is treated with both antiviral prescription medications that can speed up your healing and with medications that can help with your pain. Your exact treatment plan will depend on:
- how severe your case is
- your overall health
- the medications you already take
Antiviral options include:
Herpes is also treated with antiviral medication.
Antivirals can help you heal first and reduce your symptoms. Depending on your case and your overall health, you might take these medications during an outbreak or daily.
Options for herpes treatment include both acyclovir and valacyclovir.
Some other pain management options may include:
- numbing patches, gels, or creams you can apply to your skin
- codeine or other narcotic medications
- steroid injections
- anticonvulsants or antidepressants that can control pain
Talk with a doctor before using any of the treatments above. These treatments should not be used without guidance from a medical professional. A medical professional can help you avoid any unintended side effects, such as allergic reactions.
You May Like: What Causes Herpes Flare Ups
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Also Check: How Long Does Shingles Take To Heal
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of zoster vaccine, inactivated may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- itching at the injection site
Why Is Shingrix Administered In Two Doses
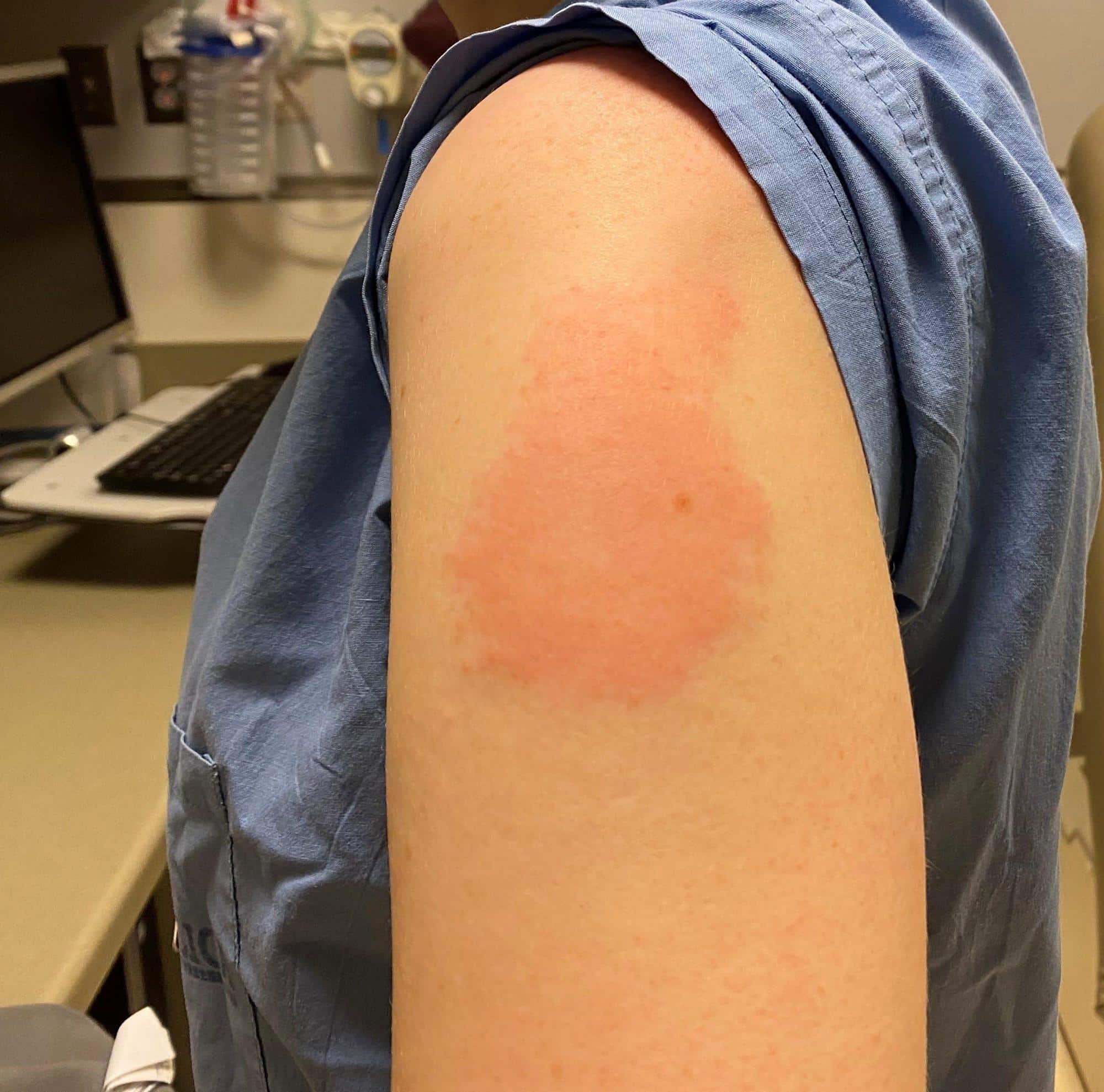
Shingrix is typically given in two doses, usually as a shot to the upper arm.
A 2021 study found that adults over 65 were significantly less likely to develop either shingles or PHN after getting two doses of Shingrix than they were after one dose. Two doses of Shingrix also offered better protection against shingles complications to adults over 80 and immunocompromised adults.
Previously, Zostavax was offered to older and immunocompromised adults to prevent shingles, PHN, and other shingles-related health problems. Zostavax is a live vaccine, which means it contains a weakened version of the herpes zoster virus. Shingrix is a recombinant vaccine, meaning that it uses only a small piece of the virus.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. Zostavax is no longer available in the U.S. People who have gotten Zostavax in the past should now get Shingrix.
Studies have shown that Zostavaxa one-dose vaccineis generally less effective than two doses of Shingrix in preventing shingles complications among older and immunocompromised adults. Shingrix currently offers the best chance of protection against shingles, PHN, and shingles-related hospitalization.
Recommended Reading: How To Handle Shingles Pain
How Long Does A Shingles Outbreak Last
It can take three to five weeks from the time you begin to feel symptoms until the rash totally disappears.
Who Shouldn’t Get It
A person should not get Shingrix if:
- They have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or the first dose of the vaccine.
- They test negative for immunity to varicella-zoster virus.
- They currently have shingles.
- They are pregnant.
If you are experiencing a moderate to severe illness, with a fever or not, you should consider waiting until you are better before getting the vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Does Shingles Affect The Eyes
Side Effects Of Shingles Vaccine
The most common shingles shot side effects include pain and soreness at the injection site. Some people also notice a bit of redness, swelling or itching at the site of the shot. Other side effects of the shingles vaccine may include fatigue, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. According to the CDC, side effects are more common in younger people than older people.
Most people can resume their regular activities immediately after vaccination. However, about 1 out of 6 people develop flu-like symptoms that last anywhere from 1 to 3 days.
Side effects can occur after the first, second, or both doses of Shingrix vaccine. If possible, it is a good idea to schedule vaccination the day before some downtime, so you can rest if you develop side effects.
If you develop flu-like symptoms after shingles vaccination, you can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to control your fever and improve comfort. Those who develop flu-like symptoms after their first dose of vaccine may want to pre-medicate with ibuprofen or acetaminophen an hour or so before their second dose. Your healthcare provider can answer your questions about shingles vaccine side effects and pre-medication for vaccination.
Serious side effects are rare, but not impossible, after shingles vaccination. If you develop hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, a rapid heartbeat, or sudden dizziness or weakness, and seek medical care immediately.
Redness At Injection Site
Redness at and around the injection site is common and may appear immediately or some days after receiving Shingrix. This redness commonly develops due to a localized immune system response, which shouldnt cause further concern.
Arm redness should disappear within a few days after receiving the vaccine. However, if you experience redness with a rash or severe pain, let your doctor know as soon as possible.
You May Like: Stone Coated Steel Shingles Cost
Swelling Around The Injection Site
Swelling around the injection site is another common side effect of Shingrix. Like pain and redness, minor swelling can usually result from a localized immune system response, which isnt necessarily dangerous.
You can apply hydrocortisone cream on or around the injection site to reduce redness and swelling. However, if you experience severe swelling that doesnt go away, or the swelling accompanies other symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention right away.
What Does The Shingles Vaccine Do
The shingles vaccine can prevent shingles. Every year, about 1 million people in the United States get shingles. Anyone whos had chickenpox can get shingles. Thats because the varicella-zoster virus lives silently in your nervous system after you’ve had chickenpox. The virus can reactivate later in your life if your immune system is weakened. Your risk of getting shingles goes up as you get older. In the United States, 1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Shingles On Your Chest
Do I Need To Pay For Shingles Immunisation
Vaccines covered by the NIP are free for people who are eligible. See the NIP Schedule to find out which vaccines you or your family are eligible to receive.
Eligible people get the vaccine for free, but your health care provider may charge a consultation fee for the visit. You can check this when you make your appointment.
If you are not eligible for free vaccine, you may need to pay for it. The cost depends on the type of vaccine, the formula and where you buy it from. Your immunisation provider can give you more information.
Shingles Vaccine Side Effects
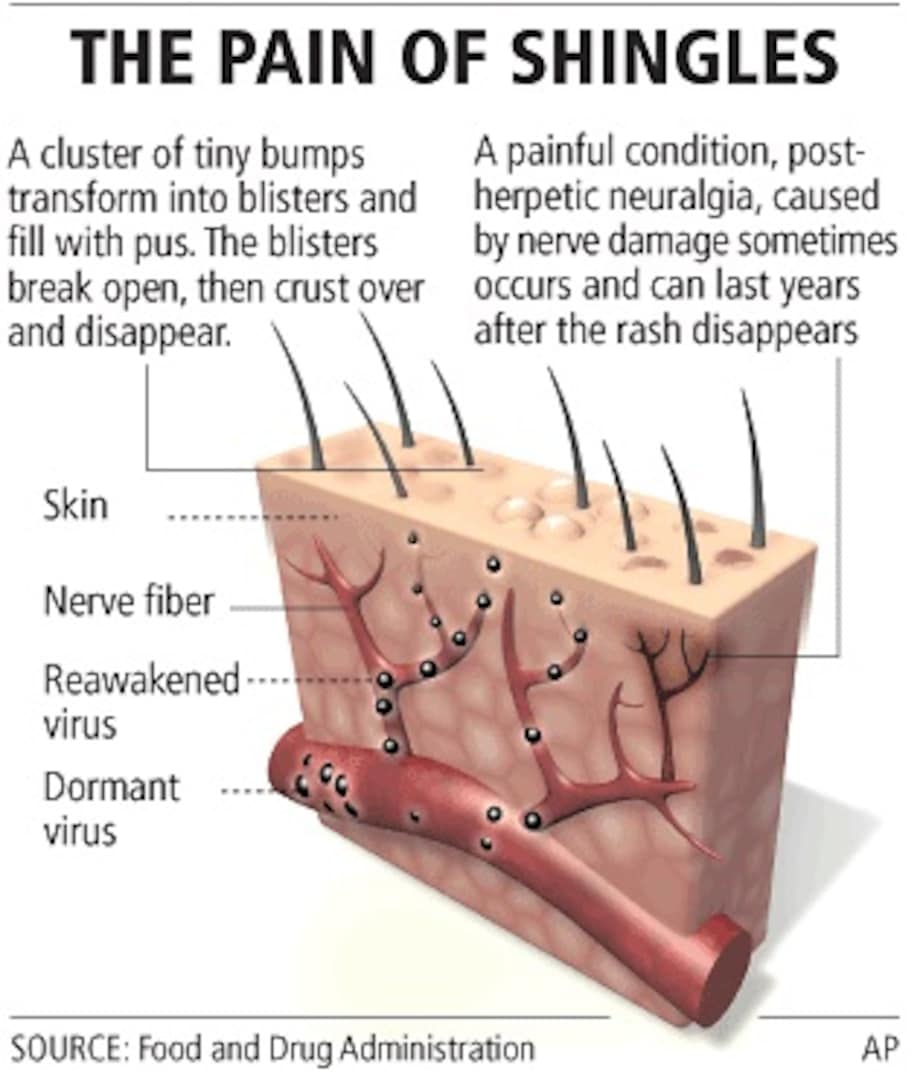
Like all vaccines, the shingles vaccines can cause side effects, but they’re generally mild and do not last long.
Common side effects that occur in at least 1 in 10 people are:
- redness, pain, swelling, itching and warmth at the injection site
If any side effects carry on for longer than a few days, speak to your GP or practice nurse.
Tell your GP if you develop a rash after having the shingles vaccination.
Read Also: Can You Get A Shingles Shot At Cvs
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Recommended Reading: How Many Times Can You Get Shingles
Who Shouldn’t Get A Shingles Vaccine
The CDC says some people shouldn’t get the shingles vaccine. That includes those who:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix
- Tested negative for VZV immunity
- Currently have shingles
- Have a severe or moderate acute illness, such as a respiratory infection
Your healthcare provider can answer any questions you have about whether the vaccine is safe for you.
Talk With Your Health Care Provider
Tell your vaccine provider if the person getting the vaccine:
- Has had an allergic reaction after a previous dose of live shingles vaccine or varicella vaccine, or has any severe, life-threatening allergies.
- Has a weakened immune system.
- Is pregnant or thinks she might be pregnant.
- Is currently experiencing an episode of shingles.
In some cases, your health care provider may decide to postpone shingles vaccination to a future visit.
People with minor illnesses, such as a cold, may be vaccinated. People who are moderately or severely ill should usually wait until they recover before getting live shingles vaccine.
Your health care provider can give you more information.
You May Like: How Many Shingles Vaccines Do I Need