Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, zoster vaccine, inactivated may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking zoster vaccine, inactivated:
Rare
- Ankle, knee, or great toe joint pain
- fever greater than 39 degree Celsius
- joint stiffness or swelling
- lower back or side pain
- swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin
Incidence not known
- Hives, welts, or itching
- inability to move the arms and legs
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- redness of the skin
- sudden numbness and weakness in the arms and legs
When Should You Get Immunised Against Shingles
Anyone aged 60 years and over who wants to protect themselves against shingles can talk to their doctor about getting immunised.
Shingles immunisation is recommended for:
- adults aged 60 years and over who have not previously received zoster vaccine
- adults aged 70 years to 79 years, for free under the National Immunisation Program
- adults aged 50 or over who live in the same household as someone who has a weakened immune system.
Who Should Not Get Shingrix
You should not get Shingrix if you:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix.
- Currently have shingles.
- Currently are pregnant. Women who are pregnant should wait to get Shingrix.
If you have a minor illness, such as a cold, you may get Shingrix. But if you have a moderate or severe illness, with or without fever, you should usually wait until you recover before getting the vaccine.
Read Also: Shingles On Eye And Face
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
Who Shouldn’t Get A Shingles Vaccine
The CDC says some people shouldn’t get the shingles vaccine. That includes those who:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix
- Tested negative for VZV immunity
- Currently have shingles
- Have a severe or moderate acute illness, such as a respiratory infection
Your healthcare provider can answer any questions you have about whether the vaccine is safe for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Shingle Shot
How Long After Ive Received The Shingles Vaccine Am I Contagious
With the currently authorized shingles vaccine, Shingrix, you wont be contagious. The old vaccine, Zostavax, used a weakened form of the live varicella-zoster virus. Therefore, people worried about spreading the disease to the people around them.
Shingrix doesnt use a live version of the varicella-zoster virus. It is inactivated, which means it uses a dead version of the virus. Therefore, you have no risk of transmitting the disease to anyone.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
No one likes to get shots, especially for something youve already been vaccinated for. But the newer version of the shingles vaccine is one youll want to offer up your arm for. The Shingrix vaccine is more than 90% effective at helping you prevent shingles. Since most of us have had chickenpox in the past, the shingles vaccine is an easy way to prevent the dormant chickenpox virus from creeping up and hitting you again with shingles.
Vaccine Side Effects & Injury Lawyers
If you or a loved one has been the victim of a vaccine side effect, you should contact a vaccine lawyer with experience in this type of complex litigation.
We have recently partnered with Schmidt & Clark, LLP a Nationally recognized law firm who handles vaccine lawsuits in all 50 states.
The lawyers at the firm offer a Free Confidential Case Evaluation and may be able to obtain financial compensation for you or a loved one by filing a vaccine lawsuit or claim with The National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. Contact Schmidt & Clark today by using the form below or by calling them directly at .
Also Check: Is New Shingles Shot Covered By Medicare
Why Is The Shingles Vaccine Important
Shingles causes a painful rash and blisters and it can lead to serious complications. The most common complication is post-herpetic neuralgia , a condition that causes burning pain that can last long after the shingles rash and blisters go away. The older you are when you get shingles, the more likely you are to develop PHN.
Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles and PHN.
Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you have chickenpox, the chickenpox virus stays dormant in your body. The virus can activate years later and cause shingles.
Symptoms of shingles include:
Shingles cant spread from person to person like chickenpox. But if you have shingles, you can spread the virus to someone who isnt immune to chickenpox meaning someone who hasnt had chickenpox and isnt vaccinated against it. If that happened, the person might get chickenpox but not shingles. Learn more about shingles.
- Adults age 50 and older
- Adults 19 years and older who have a weakened immune system because of disease or treatments
You need to get 2 doses of Shingrix. Youll need the second dose 2 to 6 months after the first dose. You need to get Shingrix even if you:
- Have already had shingles
- Have been vaccinated against shingles with Zostavax
- Are not sure if youve had chickenpox
What Are The Side Effects
Shingrix can make the area where you get the shot swell or feel sore. Other effects include:
- Many people who get the vaccine have muscle aches, headaches, or feel tired.
- About 1 in 4 people have a fever or an upset stomach.
Younger people are more likely to have these side effects, and they typically last 2 or 3 days.
Itâs also possible to have an allergic reaction to an ingredient in the vaccine. If you have problems breathing, feel your face or throat swelling, or feel weak or dizzy after the shot, call 911 and get medical help right away.
Also Check: What Antiviral Drugs Are Used To Treat Shingles
When To See A Healthcare Provider
For most people, the effects of Shingrix are mild and short-term. In very rare cases, Shingrix can cause more serious side effects.
Seek urgent medical care if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction a few minutes or hours after your second dose of Shingrix, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Facial swelling
- Swelling in the throat or mouth
You should also let your healthcare provider know if your Shingrix side effects are severe or arent going away on their own.
Who Should Get Shingrix
Adults 50 years and older should get two doses of Shingrix, separated by 2 to 6 months. Adults 19 years and older who have or will have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix. If needed, people with weakened immune systems can get the second dose 1 to 2 months after the first.
You should get Shingrix even if in the past you:
- Received varicella vaccine
There is no maximum age for getting Shingrix.
If you had shingles in the past, Shingrix can help prevent future occurrences of the disease. There is no specific length of time that you need to wait after having shingles before you can receive Shingrix, but generally you should make sure the shingles rash has gone away before getting vaccinated.
Chickenpox and shingles are related because they are caused by the same virus . After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus stays dormant in the body. It can reactivate years later and cause shingles.
Shingrix is available in doctors offices and pharmacies.
If you have questions about Shingrix, talk with your healthcare provider.
* A shingles vaccine called zoster vaccine live is no longer available for use in the United States, as of November 18, 2020. If you had Zostavax in the past, you should still get Shingrix. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine the best time to get Shingrix.
Also Check: Shingles Nerve Pain Without Rash
Can My Grandfather With Shingles Give My Baby Daughter Chickenpox
Yes, although people with shingles cannot pass shingles to someone else, they can pass chickenpox virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If your baby has not yet had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine, she could become infected with the virus and develop chickenpox.
Unlike chickenpox that can be passed to others through coughs or sneezes, people with shingles can only pass the virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If the rash has yet to develop or has crusted, the patient cannot transmit the virus. Similarly, people who still have pain without the rash are no longer able to transmit the virus.
Pain At Injection Site
Pain at the injection site is a common side effect of many vaccines, including Shingrix. This pain is generally mild but can feel like anything from slight discomfort to deep bruising. In some cases, injection site pain can be severe enough to limit arm movement.
To ease this discomfort, you can apply cold packs to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time.
If these arent effective, over-the-counter pain remedies may help. However, if you have injection site pain that is severe or lasts longer than 2 to 3 days, follow up with your doctor.
You May Like: What Should You Do When You Have Shingles
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of zoster vaccine, inactivated may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- itching at the injection site
What Everyone Should Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Shingles vaccination is the only way to protect against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication from shingles.
CDC recommends that adults 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine called Shingrix to prevent shingles and the complications from the disease. Adults 19 years and older who have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and related complications.
Your doctor or pharmacist can give you Shingrix as a shot in your upper arm.
Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and PHN. In adults 50 years and older who have healthy immune systems, Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and PHN. Immunity stays strong for at least the first 7 years after vaccination. In adults with weakened immune systems, studies show that Shingrix is 68%-91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on the condition that affects the immune system.
Recommended Reading: Lifetime Shingles Vs 30 Year
Can The Shingles Shot Cause Guillain
Though rare, but Guillain-Barré syndrome can occur with both the shingles vaccine and the shingles virus itself.
Symptoms of this serious autoimmune disorder include a loss of sensation and muscle paralysis that tends to come on quickly, typically spreading up from your lower extremities.
It can be life-threatening, so contact a healthcare provider immediately if you think you may have symptoms.
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Don’t Miss: How To Keep From Getting Shingles
Itchy Skin Near The Injection Site
Itchy skin, also called pruritus, can potentially occur near the injection site after receiving Shingrix. Itching, swelling, and redness arent usually a huge cause for concern, as they often occur together as a localized reaction.
Applying Benadryl gel or hydrocortisone cream around the injection area can help reduce itchy, swollen, or red skin. If the itching worsens or spreads away from the injection site, get in touch with your doctor.
What Are The Advantages Of Getting The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine reduces your risk of getting shingles. Shingles causes a painful rash that usually develops on one side of your body or face. Some people describe the pain as an intense burning or shooting sensation. The rash is often a single strip that wraps around one side of your body or is on one side of your face. It consists of blisters that normally crust over in seven to 10 days. The rash generally clears up within a month.
Some people with shingles also experience additional symptoms including fever, headache, chills or upset stomach.
For some people, the pain from the rash can last for months or even years after the rash goes away. This long-term pain is called postherpetic neuralgia , and it is the most common complication of shingles.
Read Also: How To Stop Shingles Early
Are There Any Reasons I Shouldn’t Have The Shingles Vaccine
You shouldn’t have the shingles vaccine if:
- you’ve had a severe reaction to any of the ingredients in the vaccine
- you’ve had a severe reaction to a previous dose of the chickenpox vaccine
If you don’t have a severely weakened immune system, the shingles vaccine you’ll be offered contains a small trace of pork gelatine.
Gelatine is a common and essential ingredient in many medicines, including some vaccines.
Many faith groups, including Muslim and Jewish communities, have approved the use of gelatine-containing vaccines. It is, however, an individual choice whether or not to receive the shingles vaccine.
What Are Common Side Effects Of Zostavax
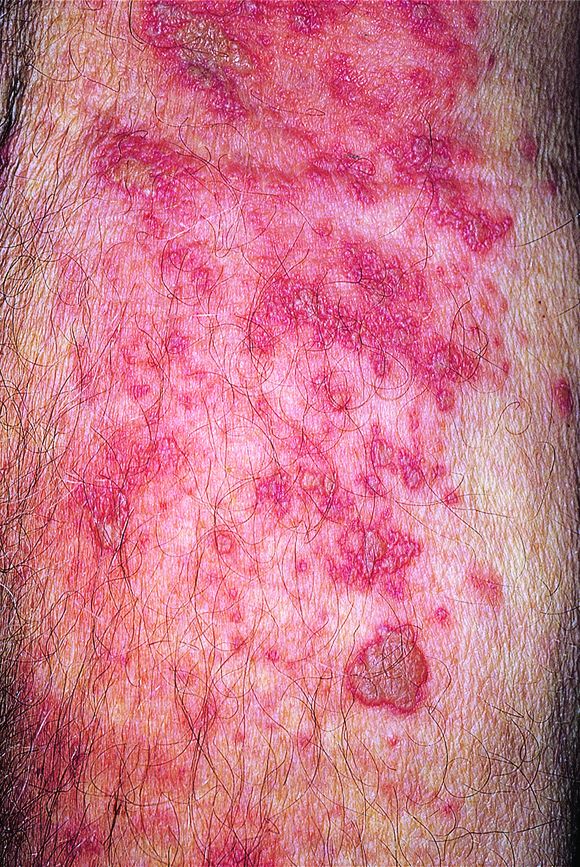
About 1 in 3 people suffer injection suffer redness, soreness, swelling, or itching at the site of the injection. About 1 in 70 people experience a headache.
Some people who get the shingles vaccine develop a chickenpox-like rash near the place where they were vaccinated. This rash is potentially contagious and it should be covered to avoid transmission of the varicella zoster virus to young children, pregnant women, or people with weakened immune systems.
The most common side effects of the shingles vaccine include:
- Injection-site reactions
Tags: Chickenpoxshingleszostavax
Don’t Miss: How Contagious Is Shingles Virus
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.