Skipping The Second Dose Of The Shingles Vaccine Might Mean You Have Less Protection Against This Painful Rash
Medically reviewed in March 2021
Shingles is a painful condition, and the effects of it can last for months or even years in some cases. Although there is no cure for shingles once you have it, there is a vaccine that prevents shingles in the first place.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that healthy adults over the age of 50 get the shingles vaccine. This is true even if youve had shingles in the past, or if you were previously vaccinated with the older shingles vaccine.
The shingles vaccine is administered in two separate dosesonce you receive the first dose, the second should be given 2 to 6 months later. After the second dose, the vaccine is more than 90 percent effective at preventing shingles, according to the CDC.
Why the second dose matters The shingles vaccine is designed to be given as two doses, not as one. Despite the effectiveness of the vaccine, some people skip their second dose. Some simply forget to follow up and lose track of the appointment date. Others may skip the second dose due to costdepending on your insurance plan, you may be responsible for a co-pay or deductible fee, or you may need to pay for the second dose out of pocket.
Getting the second dose gives you the full protection the vaccine offers. Below are some ways to make sure you get your second dose.
Swelling Around The Injection Site
Swelling around the injection site is another common side effect of Shingrix. Like pain and redness, minor swelling can usually result from a localized immune system response, which isnt necessarily dangerous.
You can apply hydrocortisone cream on or around the injection site to reduce redness and swelling. However, if you experience severe swelling that doesnt go away, or the swelling accompanies other symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention right away.
Shingrix: Dont Miss Your Second Dose
If you received one dose of the Shingrix® vaccine but a shortage kept you from getting your second dose a painful case of shingles still could be in your future.
The makers of Shingrix claim its protection is sustained at a high level for at least four years but only if you get both doses two to six months apart. Many people rushed to get the Shingrix vaccine after it was introduced in 2017. But, shortages left some people without the crucial second dose. Supplies have rebounded, and the vaccine is now widely available.
Shingles is a painful rash that follows nerve pathways. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus . The virus can lie dormant in the nerves for many years. People older than age 50 have a greater risk of developing shingles.
Who should get vaccinated?
Shingrix is recommended for adults age 50 and older who have normal immune systems. The Centers for Disease Control & Prevention recommends that people previously vaccinated with the less-effective Zostavax® vaccine, be revaccinated with Shingrix even if they have never had chickenpox. Many patients who could not take Zostavax may be able to receive Shingrix.
Because the vaccine is preventive, health plans often fully cover the cost for members who fit the CDC prescribing guidelines .
If you have questions or need help locating a pharmacy or clinic with the Shingrix vaccine, call the customer service number on the back of your ID card or on page 23 of Blue & You.
Don’t Miss: What Can Ease The Pain Of Shingles
Fever And Feelings Of Malaise
Fever is one of the most common side effects of many vaccines, including Shingrix. This symptom often accompanies other feelings of malaise, such as muscle pains, chills, and headaches. A fever indicates that the bodys immune system is doing its job of responding to the vaccine.
Ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and other OTC fever reducers can help keep a fever and many accompanying symptoms at bay. However, if you develop a high-grade fever of 103°F or higher, reach out to your doctor immediately.
Will There Be Any Side Effects From The Shingles Vaccination
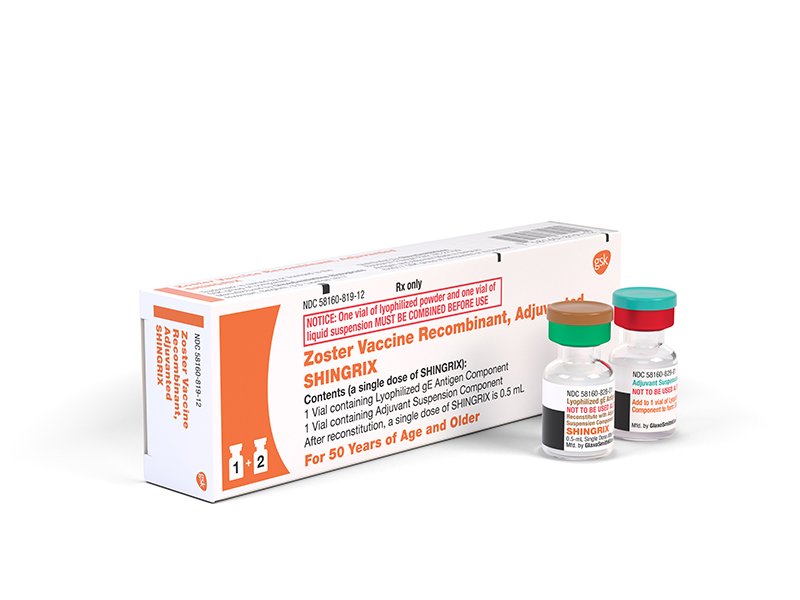
There are 2 shingles vaccines: Zostavax and Shingrix .
With both vaccines it’s quite common to get redness and discomfort at the vaccination site, headaches and fatigue, but these side effects should not last more than a few days. See a GP if you have side effects that last longer than a few days, or if you develop a rash after having the shingles vaccination.
Read more about the shingles vaccine side effects.
Also Check: Can The Shingles Vaccine Cause Eye Problems
What Else To Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Ready to get vaccinated? This is the essential info on how the shots are given, what to expect with side effects, and more.
You need two doses of Shingrix to get full protection from shingles. You should get your second dose 2 to 6 months after the first. Your doctor or pharmacist will inject the vaccine into the muscle of your upper arm, so wear clothes that give easy access to that area.
If it has been more than 6 months since you got your first dose, go ahead and get your second dose. You donât need to start over, Dooling says.
Because Shingrix is so new, experts arenât sure whether youâll eventually need another shot, or a booster, years down the road.
âThe CDC is actively following how protected people remain after the two-dose series,â she says. We know that after 4 years, protection remains above 85%. Only time will tell how durable that protection is.â
You do not have to wait between Shingrix and COVID-19 vaccination. The CDC has determined its safe to get the COVID-19 vaccine at the same time as Shingrex, but recommends they be given in different arms. You should not get eithe vaccine if you have COVID.
Side effects are fairly common. You may have heard that people sometimes have unpleasant side effects soon after they get the shingles vaccine.
âShingrix tends to have has more side effects than some vaccines, like those for the seasonal flu,â says Kistler. The shingles vaccine may cause:
Shingles Vaccine Side Effects
Like all vaccines, the shingles vaccines can cause side effects, but theyre generally mild and do not last long.
Common side effects that occur in at least 1 in 10 people are:
- redness, pain, swelling, itching and warmth at the injection site
If any side effects carry on for longer than a few days, speak to your GP or practice nurse.
Tell your GP if you develop a rash after having the shingles vaccination.
Read Also: How To Treat Shingles At Home
Can I Get Shingrix If Ive Never Had Chickenpox
If youve never had chickenpox , the CDC recommends that you get the chickenpox vaccine instead of Shingrix. Researchers havent studied Shingrix in people who have never had chickenpox. And Shingrix is not approved for preventing chickenpox.
If you cant recall whether youve had chickenpox, you may need to be screened for it. But this will depend on your age.
Its assumed that people born in the United States and elsewhere before 1980 have been exposed to chickenpox. Therefore, you may be able to receive Shingrix. You should check with your doctor first to make sure.
Who Shouldnt Get A Shingles Vaccine
The CDC says some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. That includes those who:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix
- Tested negative for VZV immunity
- Currently have shingles
- Have a severe or moderate acute illness, such as a respiratory infection
Your healthcare provider can answer any questions you have about whether the vaccine is safe for you.
Also Check: Shingles Nerve Pain Without Rash
Who Is A Candidate For The Shingles Vaccine
Healthy adults aged 50 years and older are candidates for the shingles vaccine Shingrix. There is no age limit, and you can get the Shingrix vaccine even if you have already had shingles, have had the Zostavax vaccine, or do not remember whether you have had chickenpox in the past.
If you have already had shingles, getting the Shingrix can help protect you from the disease coming back. Studies have reported that almost every American aged 40 years and older have more than a 99% chance of having had chickenpox, and people who have had chickenpox are more likely to develop shingles in the future because both are caused by the same virusthe varicella-zoster virus.
After having shingles, there is no duration that you need to wait before getting vaccinated, although you should wait until the rash has completely disappeared. Shringrix is given in 2 doses 2-6 months apart.
Side effects are usually mild and may last for two to three days. No severe side effects for Shingrix have been reported so far.
Is The Shingles Vaccine Covered By Insurance
The shingles vaccine may be covered by insurance depending upon the insurance program:
- Medicare: Medicare Part D covers shingles vaccine expenses, but it depends on the plan. You may need to pay either in part or full and then get it reimbursed. Medicare part B does not cover the vaccine.
- Medicaid: Medicaid may or may not cover the vaccine. You can find out by contacting your insurer.
- Private health insurance: Most private health insurance programs cover the shingles vaccine, but you may need to pay some part of the expenses depending on your plan.
- Vaccine assistance program: Check with the Shingrix manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline, if they have a Shingrix vaccine assistance program. Through vaccine assistance programs, people who cannot afford the vaccine can get help in the form of free vaccination.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Determine If You Have Shingles
Is It Possible To Get Shingles Twice
Most people who get shingles only experience it one time in their lives. However, it is possible to get shingles more than once . This is known as recurrent shingles. Getting vaccinated can help minimize the chance that this will happen.
These are only a few of the many questions people may have about Shingrix. To learn more about the vaccine and shingles, individuals can consult a medical professional.
New Shingles Vaccine Changes Recommendations For Adults

The pain associated with shingles can be unbearable. It can last for months and be so debilitating that even routine tasks become too difficult to bear. The single dose Zostavax® vaccine had been recommended since 2006, and it is about 50 percent effective at protecting against a shingles rash and about 75-80 percent effective at protecting against pain.
Fortunately, a new shingles vaccine, called Shingrix®, offers improved protection not only from developing the disease, but also against the severe pain associated with shingles. Shingrix is 95 percent effective at protecting against both the rash and associated pain. It is given as two doses separated by two to six months.
In this video, Dr. Offit discusses the differences between the two shingles vaccines and updated recommendations for adults. These include getting the vaccine at 50 years of age instead of 60 and being revaccinated if youve previously received the older version .
Read Also: What Prescription Cream Is Used For Shingles
Shingrix Is Not A Live Vaccine
A live vaccine is one that contains a weakened form of a germ. Shingrix is not a live vaccine. Its an inactive vaccine, which is a vaccine thats made from a germ thats been killed.
Because Shingrix is inactive, more people can receive it. This includes people with a weakened immune system .
People with weakened immune systems are typically advised against receiving live vaccines. This is because on very rare occasions, live vaccines can mutate back to the full-strength germ that causes a disease.
If this happens, people with weakened immune systems would have a much higher risk for developing the disease that the vaccine is meant to prevent.
Shingrix is also a recombinant vaccine. This means that its made of parts of the shingles virus, such as protein, sugar, or capsid .
There used to be an alternative shingles vaccine to Shingrix. This other vaccine was called Zostavax.
Like Shingrix, it was approved to prevent shingles . However, Zostavax is
Below, we briefly describe the similarities and differences between these two vaccines.
Contraindications And Precautions For Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Shingrix should not be administered to:
- A person with a history of severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, to any component of this vaccine.
- A person experiencing an acute episode of herpes zoster. Shingrix is not a treatment for herpes zoster or postherpetic neuralgia . The general guidance for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
There is currently no CDC recommendation for Shingrix use in pregnancy therefore, providers should consider delaying vaccination until after pregnancy. There is no recommendation for pregnancy testing before vaccination with Shingrix. Recombinant vaccines such as Shingrix pose no known risk to people who are breastfeeding or to their infants. Providers may consider vaccination without regard to breastfeeding status if Shingrix is otherwise indicated.
Adults with a minor acute illness, such as a cold, can receive Shingrix. Adults with a moderate or severe acute illness should usually wait until they recover before getting the vaccine.
To learn more, see Contraindications and Precautions, General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices .
You May Like: How Do Adults Get Shingles
Redness At Injection Site
Redness at and around the injection site is common and may appear immediately or some days after receiving Shingrix. This redness commonly develops due to a localized immune system response, which shouldnt cause further concern.
Arm redness should disappear within a few days after receiving the vaccine. However, if you experience redness with a rash or severe pain, let your doctor know as soon as possible.
If Youre 50 Or Older Get Shingrix
- Shingrix provides strong protection from shingles and long-term nerve pain.
- Get Shingrix even if you already had shingles, because you can get the disease more than once.
- Your risk of shingles and complications increases as you age.
- You need 2 doses of Shingrix. Get the second dose 2 to 6 months after you get the first dose.
Recommended Reading: What Causes The Disease Shingles
Reasons To Get The Shingles Vaccine
Once a person develops chickenpox after contracting the varicella-zoster virus, the virus never leaves the body. It remains dormant in the nerve roots and can reappear as shingles later in life.
The primary symptom of shingles is a painful rash on one side of the body, most often on the torso or face. People initially have pain or a burning sensation on the skin without a rash, and then painful blisters develop. The rash lasts approximately seven to 10 days and fully clears within two to four weeks.
The likelihood of developing shingles increases dramatically after age 50. Therefore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all adults age 50 and over receive two doses of Shingrix to prevent shingles. The vaccine is recommended even if a person is unsure if they have ever had chickenpox.
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for shingles. Therefore, the Food and Drug Administration also recently approved Shingrix vaccination for adults age 18 and older who are at risk for shingles due to immunodeficiency or immunosuppression caused by an underlying disease or medication.
Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, zoster vaccine, inactivated may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking zoster vaccine, inactivated:
Rare
- sudden numbness and weakness in the arms and legs
You May Like: How Do Shingles Go Away
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Why Do I Need Two Doses Of Shingrix
In addition to a painful rash, shingles can lead to serious health complications like PHN, pneumonia, vision loss, hearing problems, and encephalitis . Research indicates that about 1% to 4% of people with shingles will be hospitalized.
Two doses of Shingrix offer effective protection against shingles and related complications for at least seven years. Among healthy adults ages 50-69, Shingrix is more than 90% effective in preventing PHN when two doses are administered. Among adults ages 70 and older, it is 89% effective.
Also Check: How Do You Develop Shingles
Itchy Skin Near The Injection Site
Itchy skin, also called pruritus, can potentially occur near the injection site after receiving Shingrix. Itching, swelling, and redness arent usually a huge cause for concern, as they often occur together as a localized reaction.
Applying Benadryl gel or hydrocortisone cream around the injection area can help reduce itchy, swollen, or red skin. If the itching worsens or spreads away from the injection site, get in touch with your doctor.
Shingrix Vaccine Efficacy And Duration Of Protection
Among immunocompetent adults 50 years and older, the efficacy of two doses of Shingrix for the prevention of herpes zoster was high among all age groups. In a clinical trial of more than 30,000 participants, vaccine efficacy was 96.6% in adults aged 50 to 59 years, 97.4% in adults aged 60 to 69 years, and 91.3% in adults aged 70 years and older.
The efficacy of two doses of Shingrix for the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia was high: 91.2% in adults aged 50 years and older, and 88.8% in adults aged 70 years and older.
Vaccine efficacy was estimated among several immunocompromised groups:
- 68.2% among adult autologous hematopoietic cell transplant recipients.
- 87.2% in a post hoc efficacy analysis of adult patients with hematologic malignancies.
- 90.5% in a post hoc efficacy analysis of adult patients with immune-mediated diseases who were not taking immunosuppressive medication.
In immunocompetent adults 70 years and older, vaccine efficacy remained high, at or above 84% in all 7 years after vaccination.
Also Check: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Face