How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.
Read Also: Where To Buy Tamko Heritage Shingles
Another Jab At Shingles
In October 2018, the FDA approved Shingrix, a two-shot shingles vaccine for patients 50 and older. To be the most effective, patients must get the second shot between two to six months after the first. Clinical trials demonstrated that it was 91% to 97% effective in preventing shingles, and that protection seems to stay strong, at least for the first four years in the patients who were tracked.
There has slowly been uptick, but still very large group of those aged 50 and older who have not received it, saysNatalie Baker, DNP, president of the gerontological advanced practice nursing association .
Given its improved efficacy and the fact that the efficacy of Zostavaxwanes over the course of a few years, regulators recommended getting the Shingrix shots even if you already received Zostavax, which was discontinued in 2020. A lot of our older adults have received Zostavax, but, unfortunately, it just does not continue to be effective, she says, explaining that even those patients should get the Shingrix vaccine.
Who Should Get The Shingles Vaccine
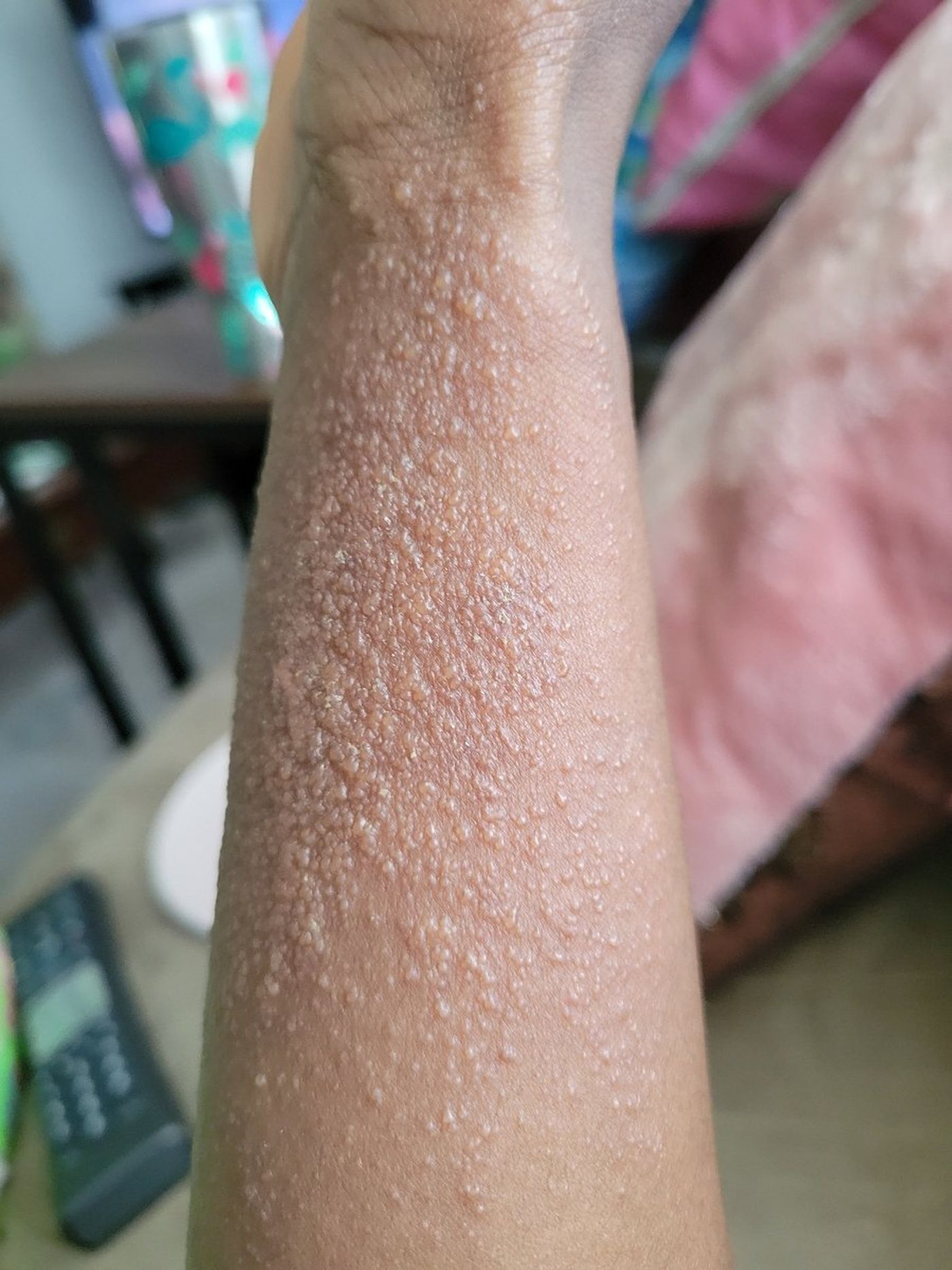
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says you should get a shingles vaccine if you:
- Are an adult aged 50 and older
- Have never had shingles
- Have had shingles before
- Aren’t sure whether you’ve had chickenpox
- Have been previously vaccinated with the Zostavax shingles vaccine
- Are age 19 or older and are immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy
You May Like: Chronic Nerve Pain From Shingles
What Are Side Effects Of Inactivated Viral Vaccines
Side effects of inactivated viral vaccines may include the following:
- Injection site reactions include:
Information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible side effects, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to make sure these drugs do not cause any harm when you take them along with other medicines. Never stop taking your medication and never change your dose or frequency without consulting your doctor.
What Everyone Should Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Shingles vaccination is the only way to protect against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication from shingles.
CDC recommends that adults 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine called Shingrix to prevent shingles and the complications from the disease. Adults 19 years and older who have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and related complications.
Your doctor or pharmacist can give you Shingrix as a shot in your upper arm.
Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and PHN. In adults 50 years and older who have healthy immune systems, Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and PHN. Immunity stays strong for at least the first 7 years after vaccination. In adults with weakened immune systems, studies show that Shingrix is 68%-91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on the condition that affects the immune system.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Internal Shingles
Considerations For Patients Who Previously Received Zostavax
Studies have not examined the safety and immunogenicity of Shingrix administered less than 5 years following Zostavax vaccination. However, there are no data or theoretical concerns to indicate that Shingrix would be less safe or less effective when given at an interval shorter than 5 years following Zostavax. Since the risk of herpes zoster increases with age, providers should weigh a patients risk of herpes zoster with the age-specific protection expected from Zostavax to determine when to vaccinate with Shingrix.
When They Start How Long They Last
The shingles vaccine is given in a two-shot series. You may experience side effects after the first, second, or both shots. Most of the time, these symptoms are mild and occur immediately following vaccination. They typically only last for two or three days.
Side effects of the shingles vaccine are more common in younger people, and might interrupt your normal daily activities for a few days.
This may seem like a downside of the shingles vaccine, but remember that these symptoms are a result of the creation of a strong shingles defense within your body.
It is OK to take Tylenol or Advil after a shingles vaccine to relieve symptoms. Rest and plenty of fluids may help, too.
Read Also: Does Medicare Cover Shingles Shots For Seniors
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccines
What patients can expect after Shingrix or Zostavax injections.
Any medicine, including vaccines, carries a risk of adverse events or side effects. The CDC estimates that vaccine-related reactions occur once in a million doses, usually within a few minutes or hours of the injection. Generally they are minor and subside within a day or two.
The two available vaccines for shingles-Shingrix and Zostavax-each has its own associated side effects. Patients should be informed about what to expect prior to vaccination to help them manage their expectations.
Shingrix
GSK, the manufacturer of Shingrix, says its most common side effects include pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site muscle pain tiredness headache shivering fever and upset stomach. While severe allergic reactions are less common, they may range from hives, swelling of the face and throat, and difficulty breathing to a fast heartbeat, dizziness, and weakness.
In Shingrix clinical trials, the majority of people complained of mild to moderate pain in their arm, as well as redness and swelling at the injection site. About one in six people experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities for two to three days. These side effects were reportedly more common in younger people.
Zostavax
Both Merck, which manufacturers Zostavax, and GSK acknowledge that their vaccines may not protect all individuals, so some people who get shingles vaccine may still develop shingles.
Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, zoster vaccine, inactivated may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking zoster vaccine, inactivated:
Rare
- Ankle, knee, or great toe joint pain
- fever greater than 39 degree Celsius
- joint stiffness or swelling
- lower back or side pain
- swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin
Incidence not known
- Hives, welts, or itching
- inability to move the arms and legs
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- redness of the skin
- sudden numbness and weakness in the arms and legs
You May Like: Is A Prescription Required For Shingles Vaccine
Weighing The Risks Vs Benefits
The vaccine to prevent shingles will help you to avoid shingles symptoms, which in most cases are quite mild but may cause intense pain in some people.
Shingles symptoms come in two stages: the prodromal stage and the eruptive stage. In the first stage, your symptoms may include:
About three to five days later, you develop a prickly and painful pimple-like rash. These pimples turn into blisters during this eruptive stage, and your skin may be red and swollen. Shingles sores also can affect your mouth, which is another symptom the vaccine can prevent.
Shingles isn’t generally life-threatening. It can be, though, if your immune system is compromised. During an outbreak and after the rash clears up, some people may experience complications that require immediate medical attention.
Common ones include:
- Postherpetic neuralgia : Damaged nerves cause lingering pain for three months or more.
- Bacterial skin infections: When shingles blisters pop, bacteria can get in.
- Eye damage: One branch of the trigeminal nerve goes to the eye. Damage there can lead to eye damage, which can be severe.
While you may experience side effects with the vaccine, the benefits outweigh the risks of shingles symptoms and complications in most people.
If you were vaccinated with Zostavaxa shingles vaccine that is no longer being givenask your healthcare provider about getting the Shingrix vaccine.
Who Should Get Shingrix
Adults 50 years and older should get two doses of Shingrix, separated by 2 to 6 months. Adults 19 years and older who have or will have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix. If needed, people with weakened immune systems can get the second dose 1 to 2 months after the first.
You should get Shingrix even if in the past you:
- Received varicella vaccine
There is no maximum age for getting Shingrix.
If you had shingles in the past, Shingrix can help prevent future occurrences of the disease. There is no specific length of time that you need to wait after having shingles before you can receive Shingrix, but generally you should make sure the shingles rash has gone away before getting vaccinated.
Chickenpox and shingles are related because they are caused by the same virus . After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus stays dormant in the body. It can reactivate years later and cause shingles.
Shingrix is available in doctors offices and pharmacies.
If you have questions about Shingrix, talk with your healthcare provider.
* A shingles vaccine called zoster vaccine live is no longer available for use in the United States, as of November 18, 2020. If you had Zostavax in the past, you should still get Shingrix. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine the best time to get Shingrix.
Also Check: Does Cvs Caremark Cover Shingles Vaccine
Should I Get A Vaccine
Doctors say most healthy people over 50 should get Shingrix, as well as anyone 19 or older who are immunocompromised. Itâs available at pharmacies as well as doctorsâ offices. Most people have been exposed to the chickenpox even if they didnât actually develop symptoms.
You should get the Shingrix vaccine unless:
- You are allergic to any part of the vaccine
- Had a blood test that proves you never had chicken pox
- Have shingles now
- Are breastfeeding or nursing.
Side Effects And Counseling For Reactogenicity
In eight clinical trials of more than 10,000 immunocompetent participants 50 years or older, grade 3 reactions were common after patients received Shingrix. About 1 out of 10 adults who received Shingrix reported grade 3 injection-site symptoms such as pain, redness, and swelling. Also, about 1 out of 10 reported grade 3 systemic reactions such as myalgia, fatigue, headache, shivering, fever, and gastrointestinal illness. Most people who got Shingrix reported at least some pain at the injection site.
Local and systemic grade 3 reactions among immunocompromised adults were evaluated in six studies in five immunocompromised groups. Local grade 3 reactions occurred in 10.7% to 14.2% of RZV recipients, and systemic grade 3 reactions occurred in 9.9% to 22.3% of RZV recipients, compared with 0% to 0.3% and 6.0% to 15.5%, respectively, among placebo recipients. The most commonly reported systemic symptoms were fatigue and myalgia.
Healthcare providers should counsel patients about expected reactogenicity before administering Shingrix.
What to tell patients about the side effects of Shingrix:
Most people have a sore arm after they get Shingrix. Many people have redness and swelling on their arm spanning several inches where they got the shot. Many people also feel tired or have muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea.
Also Check: Are 50 Year Shingles Worth It
What Are The Side Effects
Shingrix can make the area where you get the shot swell or feel sore. Other effects include:
- Many people who get the vaccine have muscle aches, headaches, or feel tired.
- About 1 in 4 people have a fever or an upset stomach.
Younger people are more likely to have these side effects, and they typically last 2 or 3 days.
Itâs also possible to have an allergic reaction to an ingredient in the vaccine. If you have problems breathing, feel your face or throat swelling, or feel weak or dizzy after the shot, call 911 and get medical help right away.
A New Shingles Vaccine: Prepare For Harsher Side Effects
If you’re 50 or older, you’re advised to get immunized to protect yourself from shingles. If the new shingles vaccine made you feel worse than you expected, you’re not alone. Skin rash, joint pain, flu-like symptoms, headaches and fatigue are some complaints from patients who’ve had the recently approved Shingrix vaccine. Side effects can last two or three days, and the injection site in the upper arm can hurt.
The upside is Shingrix provides stronger protection against shingles — a painful condition that wreaks havoc on the nervous system — than previous vaccines. As people get older, they become increasingly vulnerable to developing shingles. Temporary vaccine side effects pale in comparison to shingles’ long-lasting effects on the body, experts says.
One of every three people in the U.S. will eventually develop shingles, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Caused by the varicella zoster virus — also responsible for chickenpox — shingles is notoriously painful. Once someone has chickenpox, the inactive virus dwells in the body. Decades later, the virus can become active again, now causing shingles.
Early shingles symptoms include numbness, tingling or burning and touch sensitivity. A red rash, usually affecting just one side the body, and itching come next. People may develop blisters that fill with fluid, burst open and crust over. Fever and problems such as headache, fatigue and light sensitivity can also occur.
Weighing Vaccination
Also Check: What Can You Put On Shingles
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
For most people, the effects of Shingrix are mild and short-term. In very rare cases, Shingrix can cause more serious side effects.
Seek urgent medical care if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction a few minutes or hours after your second dose of Shingrix, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Facial swelling
- Swelling in the throat or mouth
You should also let your healthcare provider know if your Shingrix side effects are severe or arent going away on their own.
Recommended Reading: Why Do You Get The Shingles
Can The Shingles Shot Cause Guillain
Though rare, but Guillain-Barré syndrome can occur with both the shingles vaccine and the shingles virus itself.
Symptoms of this serious autoimmune disorder include a loss of sensation and muscle paralysis that tends to come on quickly, typically spreading up from your lower extremities.
It can be life-threatening, so contact a healthcare provider immediately if you think you may have symptoms.
Who Shouldnt Receive Shringrix
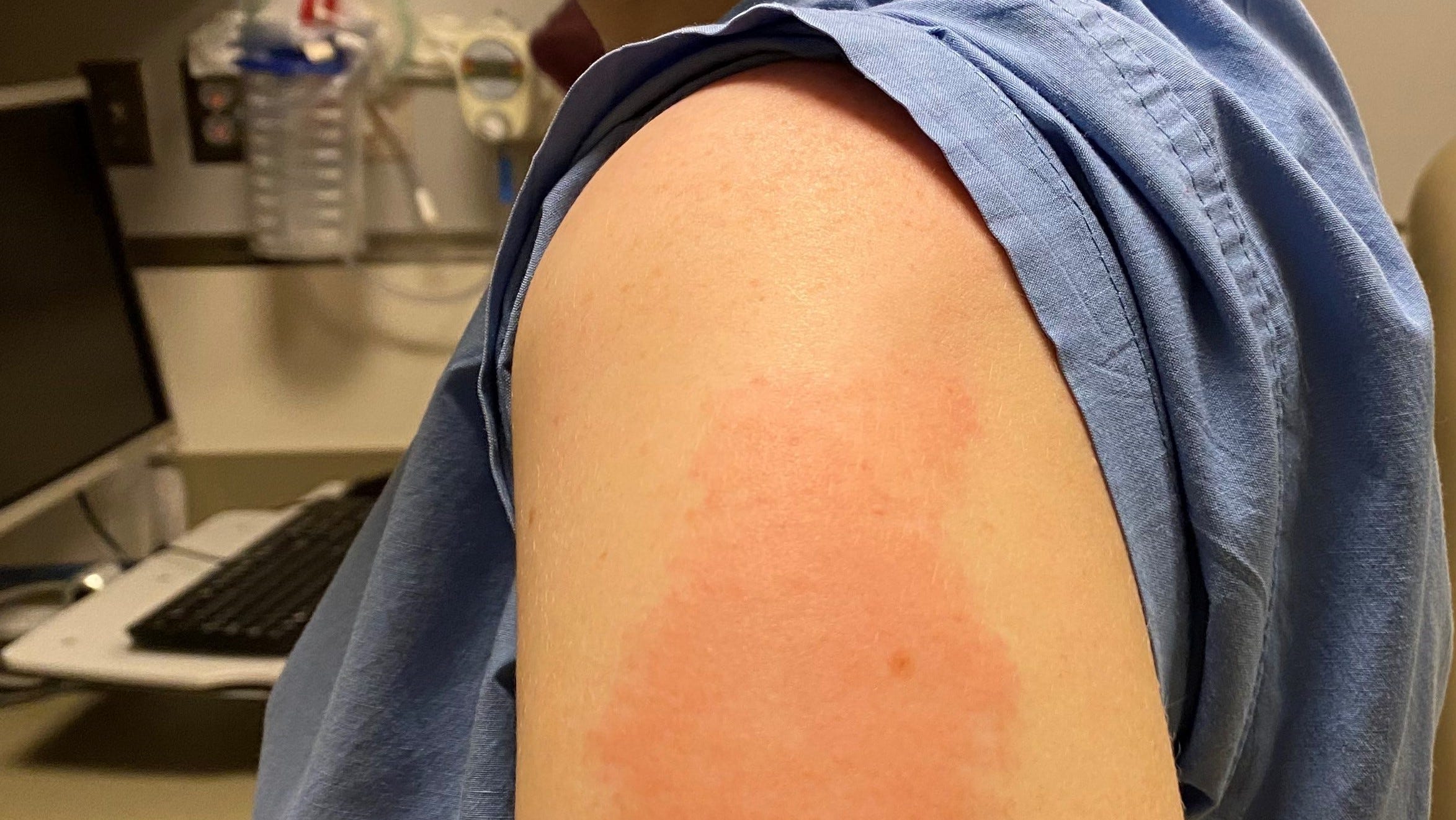
Although vaccines go through rigorous safety testing to ensure they are safe, they arent suitable for everyone. You shouldnt receive Shingrix if you:
- have an active shingles infection
- have a severe illness or a fever of 101.3°F or higher
- have had a severe allergic reaction to Shingrix or any ingredient in the vaccine
- have no immunity to varicella based on a blood test carried out for other reasons
- are pregnant or breastfeeding
If you currently have shingles, another serious illness, or a fever of 101.3°F , wait until these issues have resolved to receive a Shingrix vaccination.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does 1 Pack Of Shingles Cover