Im Living With Hiv Is It Safe For Me To Get Shingrix
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention hasnt made a recommendation about the use of Shingrix in people living with HIV.
However, one study looked at healthy adults ages 18 and older who were living with HIV and had an HIV dosing schedule that was customized to their needs. These people received the Shingrix vaccine, and the study results did not report any safety issues.
If youre living with HIV, talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of getting Shingrix.
How Do You Get Immunised Against Shingles
You can only get the shingles vaccine on its own, not as a combination vaccine. It is given as a needle.
Shingles vaccines include:
Note the Zostavax vaccine contains a small amount of the live virus. Some people may not be able to receive a live vaccine for medical reasons, please discuss with your doctor or immunisation provider for further information.
More Common Side Effects
The more common side effects of Shingrix can include:
- pain, redness, and swelling at site of injection*
- dizziness or fainting
- flu-like symptoms, including fever, shivering, and tiredness
Most of these side effects may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. If theyre more severe or dont go away, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
* For more information about this side effect, see Side effect details below.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles And Not Have A Rash
Administering And Storing Shingrix
- Adults 50 years and older should receive 2 doses of Shingrix. Give the second dose 2 to 6 months after the first.
- Administer Shingrix intramuscularly in the deltoid region of the upper arm with a 1- to 1.5-inch needle.
- Both vials of Shingrix must be refrigerated at a temperature of 36-46° F. Do not use if exposed to temperatures below 36° F.
Side Effects Of Herpes Zoster Vaccine
The most common side effects of the recombinant vaccine are pain, soreness, redness, and swelling at the injection site and headache, fatigue, muscle pain, shivering, fever, and digestive upset.
The most common side effects of the live-attenuated vaccine are soreness, redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site and headache.
Also Check: Are There Foods To Avoid When You Have Shingles
Shingles Disease And How To Protect Against It
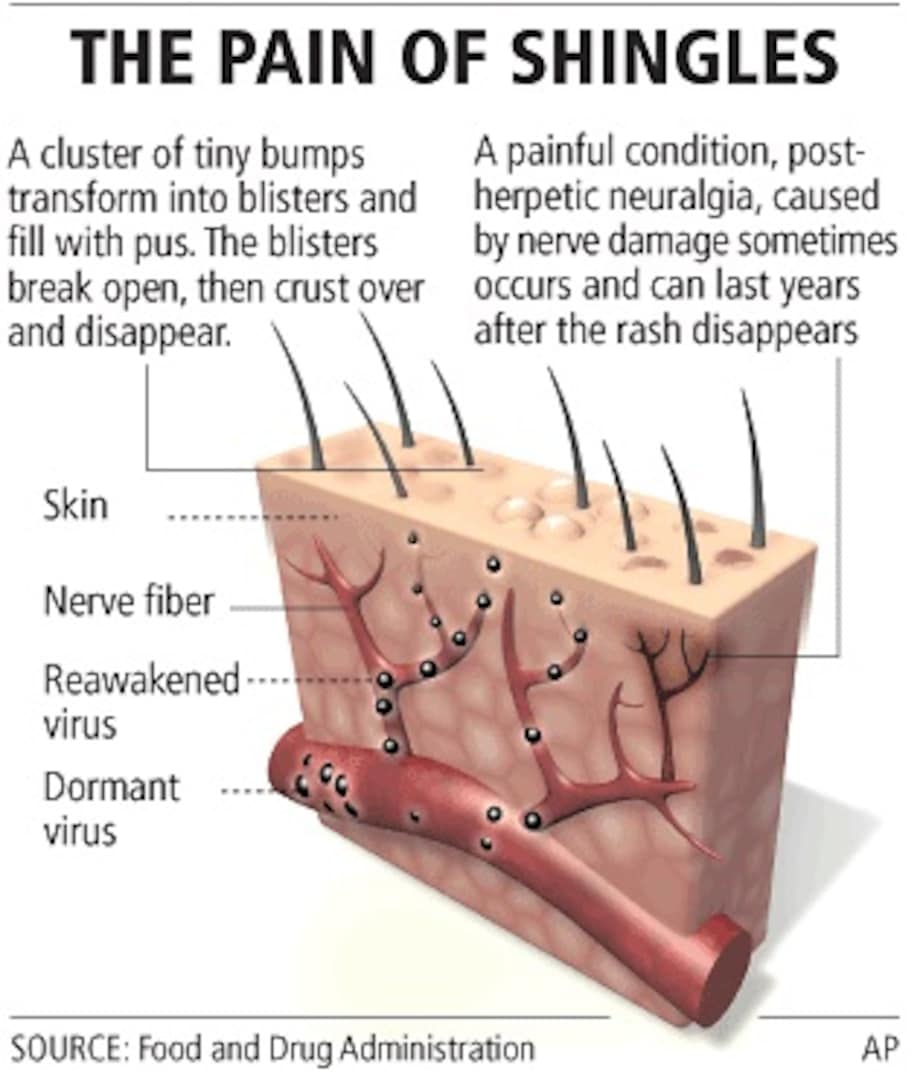
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash that develops on one side of the face or body. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus , the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who has had chickenpox in the past can get shingles because VZV remains in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. VZV can reactivate many years later, causing shingles.
Shingles is more common in older adults, people who have medical conditions that weaken the immune system, and people who take medications that suppress their immune systems. Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles.
What Is Brain Damage
Brain damage involves the destruction or deterioration of a persons brain cells.5
Most Zostavax cases involving brain damage pertain to acquired brain injuries. These injuries are associated with pressure on the brain and may result from a neurological illness .6
Symptoms of brain damage can include:
- difficulty processing information,
- sensory problems, and
- bladder or bowel dysfunction.10
Treatment typically involves medications and rehabilitative therapy. Most people that suffer from the condition recover at least partially. Severe cases of myelitis can lead to major disabilities.11
Also Check: How Do You Treat Shingles On The Hands
What Else To Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Ready to get vaccinated? This is the essential info on how the shots are given, what to expect with side effects, and more.
You need two doses of Shingrix to get full protection from shingles. You should get your second dose 2 to 6 months after the first. Your doctor or pharmacist will inject the vaccine into the muscle of your upper arm, so wear clothes that give easy access to that area.
If it has been more than 6 months since you got your first dose, go ahead and get your second dose. You donât need to start over, Dooling says.
Because Shingrix is so new, experts arenât sure whether youâll eventually need another shot, or a booster, years down the road.
âThe CDC is actively following how protected people remain after the two-dose series,â she says. We know that after 4 years, protection remains above 85%. Only time will tell how durable that protection is.â
You do not have to wait between Shingrix and COVID-19 vaccination. The CDC has determined its safe to get the COVID-19 vaccine at the same time as Shingrex, but recommends they be given in different arms. You should not get eithe vaccine if you have COVID.
Side effects are fairly common. You may have heard that people sometimes have unpleasant side effects soon after they get the shingles vaccine.
âShingrix tends to have has more side effects than some vaccines, like those for the seasonal flu,â says Kistler. The shingles vaccine may cause:
I Got The Shingles Shot And Still Got Shingles How Come
Reader Question 741 votes
A
Its not really surprising that you got shingles after being vaccinated. No vaccine is 100 percent effective and whilechildhood vaccinations get close, the shingles vaccine only cuts the risk of shingles by half for people who receive it at age 60 or older. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a single dose for those 60 or older, though the vaccine is approved for use starting at age 50.
Even though the vaccine is not always effective, it still protects a lot of people, since nearly one in three adults develops shingles during their lifetime. And if you do get shingles, you may have a milder episode because you were vaccinated. A large clinical trial found that the vaccine reduces the risk of having very severe, long-lasting pain, a syndrome called postherpetic neuralgia.
Its these extreme, prolonged painful episodes that the vaccine works better at preventing, said Dr. Rafael Harpaz, a medical epidemiologist in the division of viral diseases at the C.D.C.What would motivate me to run out and get the vaccine, he said, would be to protect myself from being that rare person who gets 10 years of life-shattering pain.
The vaccine may be most effective at younger ages. If you get it in your 60s, it reduces cases by nearly two thirds, or 64 percent it reduces risk by 41 percent if you are in your 70s when vaccinated and by 18 percent if you are in your 80s.
Do you have a health question? Submit your question to Ask Well.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Shingles Pain Last After Medication
Drug Interactions Of Shingrix Vs Zostavax
Immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus can decrease the effectiveness of vaccines. Steroids, like prednisone, and chemotherapy can also have immunosuppressive effects that can alter how vaccines work.
Those who are on immunosuppressive therapy should avoid Zostavax altogether Zostavax contains the live virus, which could result in an infection.
Antiviral drugs such as acyclovir and famciclovir can interfere with the effects of the Zostavax vaccine. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that people who are on antiviral drugs stop taking antiviral medications 24 hours before getting a Zostavax vaccine. Treatment with antiviral drugs should not be resumed for at least 14 days after vaccination with Zostavax.
| Drug |
Consult a healthcare professional for other possible drug interactions
Is Shingrix Or Zostavax Better
Shingrix is more effective than Zostavax. Shingrix is 97% effective at preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old whereas Zostavax is only 70% effective at preventing shingles in the same age group. Shingrix consistently prevents shingles in older adults while the effectiveness of Zostavax decreases with increasing age. However, Shingrix has more systemic side effects than Zostavax.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Shingles To Break Out
What Are The Main Differences Between Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix is a recombinant, adjuvanted zoster vaccine that was first FDA-approved in 2017. It uses the varicella-zoster glycoprotein E antigen to produce an immune response in the body. An adjuvant, or added ingredient, helps boost the bodys immune response to the virus. Because Shingrix is an inactivated vaccine, it can be used in immunocompromised patients or those with a weakened immune system.
Shingrix is administered as an injection into the muscle . It is given in two separate doses with a period of two to six months in between. The second dose is necessary to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Zostavax, approved in 2006, is a live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine. In other words, Zostavax contains a weakened version of the actual virus to produce an immune response. For this reason, it is not recommended for those who are immunocompromised. Or else, the vaccine itself could cause an infection.
Zostavax is administered as a single injection underneath the skin . It comes in a frozen version and a refrigerator-stable version. The frozen version must be kept frozen during transport and storage to ensure its effectiveness while the refrigerator-stable Zostavax can be kept in a refrigerator until it needs to be used.
How Long Does It Take To Work
It takes time for your body to make enough antibodies to fight off germs and protect you from certain diseases.
Results from clinical studies of Shingrix showed that the recommended dosing schedule for Shingrix does cause an immune response.
How long Shingrix takes to work may not be the same for everyone. The timing for you will depend on your body chemistry. In general, you should be protected from shingles soon after the second dose.
Studies in animals showed that there was no risk with Shingrix during pregnancy. However, animal studies dont always predict the way humans would respond.
If youre pregnant or planning to become pregnant, wait until after youve had your baby to get the Shingrix vaccine. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
There havent been enough studies to show whether Shingrix appears in breast milk.
Until more is known, its best to wait until youve finished breastfeeding before getting Shingrix.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take To Cure Shingles
Shingrix Vaccine For People With Weakened Immune Systems
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/shingrix-vaccine-for-people-with-weakened-immune-systems/shingrix-vaccine-for-people-with-weakened-immune-systems
From 1 September 2021, people who are 70 to 79 years of age with weakened immune systems will be offered the Shingrix vaccine to help protect them against shingles.
Is The Vaccine Safe
The vaccine can be given to people with a previous history of shingles infection. It should not be given to anyone who currently has shingles. As stated above, the vaccine should not be given to people who are clinically immunosuppressed because the vaccine strain could replicate too much and cause a serious infection. For more information see the MHRA’s Drug Safety Update .
In clinical trials of the vaccine, there have been no reports of someone who was vaccinated passing the virus on to anyone else. However, because the shingles vaccine is a live vaccine, it is thought that this may be possible in rare cases.
There is thought to be a very small risk that someone who has been vaccinated could pass on the virus to someone who is not immune to chickenpox. This is only thought to be a risk if the person who has been vaccinated develops a shingles type rash at the injection site or elsewhere on the body.
The shingles vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women as a matter of caution. However, studies have been carried out on pregnant women who have accidentally received chickenpox or shingles vaccines. These have not shown any link between the weakened virus in the vaccine and any specific problems in babies born to these women. See this Public Health England statement for more information.
Read Also: Pre Stained White Cedar Shingles
Conditions Treated By Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix and Zostavax are FDA approved to prevent shingles . Both vaccines are indicated to prevent shingles in adults aged 50 years and older. Shingrix and Zostavax are not used to prevent primary varicella infection, also known as chickenpox.
Postherpetic neuralgia is a common type of nerve pain that arises with shingles. Because Shingrix and Zostavax can prevent shingles, they can also prevent postherpetic neuralgia and other painful complications from shingles. However, these vaccines are not labeled to treat PHN.
| Condition |
| Yes |
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Signs Of Having Shingles
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Its normal to have questions before you get a vaccine. Some common questions you may want to discuss with your healthcare provider include:
- When should I get the shingles vaccine?
- What side effects should I expect?
- How does the shingles vaccine work?
- When should I schedule each dose of the shingles vaccine?
- How effective is the shingles vaccine?
- Is there any reason I shouldnt get the shingles vaccine?
- What could happen if I dont get the shingles vaccine?
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Determine If You Have Shingles
What Vaccines Can Help Prevent Shingles
There is currently one vaccine available in the U.S. to prevent shingles. Shingrix was approved in 2017 and it is more than 90% effective in preventing shingles. With Shingrix, you get two shots between 2 and 6 months apart and protection lasts an estimated 4-5 years. Doctors recommend it for healthy people over 50 as well as those 19 years of age and older who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to disease or therapy..
An earlier vaccine called Zostavax was removed from the market in 2020. That vaccine used a weak form of the chickenpox virus to send your bodyâs immune system into action to fight the disease. Shingrix does not. If you received the Zostavax vaccine, it is recommended that you also receive Shingrix.
Dont Miss: What Cancers Does Hpv Vaccine Prevent
Shingrix Vs Zostavax: Differences Similarities And Which Is Better For You
Drug overview & main differences | Conditions treated | Efficacy | Insurance coverage and cost comparison | Side effects | Drug interactions | Warnings | FAQ
There are currently two vaccines that can be given to prevent herpes zoster, more commonly known as shingles: Shingrix and Zostavax. A shingles vaccine is recommended for adults once they turn 50.
Most people have been infected with the varicella zoster virus if theyve ever had chickenpox. After chickenpox resolves, the varicella zoster virus lies dormant in the body for years, if not forever. Later in life, the virus can reactivate as shingles and cause a painful rash that usually wraps around the face or torso.
Although Shingrix and Zostavax work in similar ways to prevent shingles, there are some important differences between the two.
Recommended Reading: What Over The Counter Medicine Can I Use For Shingles
Shingrix And Other Medications
Below are medications that can interact with Shingrix. These are not all the drugs that may interact with Shingrix.
Before taking Shingrix, be sure to tell your doctor and pharmacist about all prescription, over-the-counter, and other drugs you take. Also tell them about any vitamins, herbs, and supplements you use. Sharing this information can help you avoid potential interactions.
If you have questions about drug interactions that may affect you, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Immunosuppressive drugs such as prednisone
Taking Shingrix with drugs that suppress your immune system can cause problems with the way your body responds to Shingrix. Examples of immunosuppressive medications include:
- corticosteroids, such as:
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about Shingrix.