Shingles Vaccine Side Effects
Like all vaccines, the shingles vaccines can cause side effects, but they’re generally mild and do not last long.
Common side effects that occur in at least 1 in 10 people are:
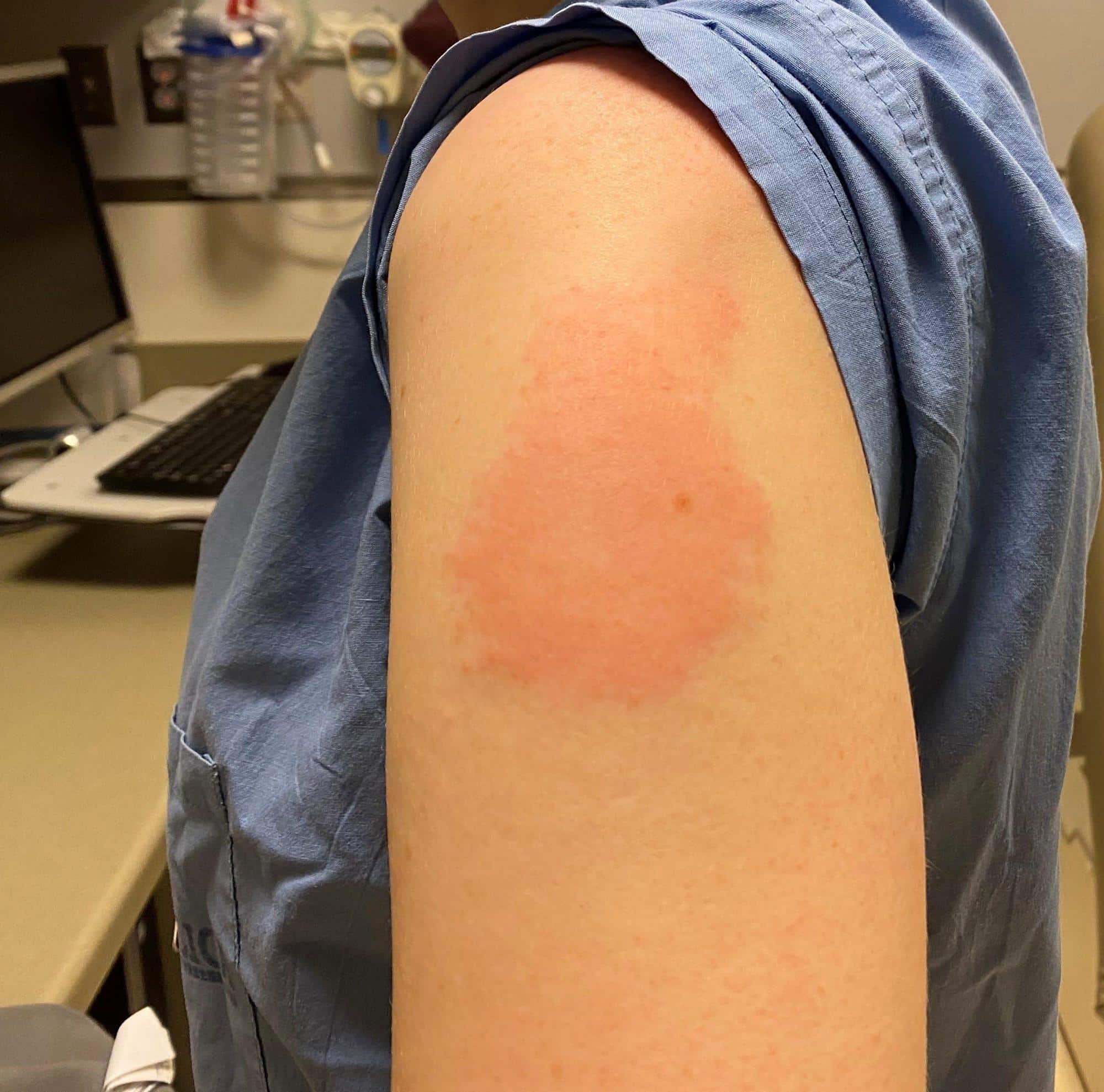
- redness, pain, swelling, itching and warmth at the injection site
If any side effects carry on for longer than a few days, speak to your GP or practice nurse.
Tell your GP if you develop a rash after having the shingles vaccination.
Who Shouldnt Get The Shingles Vaccine
There are a few situations in which shingles vaccination may not be right for you. You should not get Shingrix if youâve ever had a severe reaction to a vaccine. This means you had trouble breathing or swelling in your mouth or airway, a life-threatening condition called anaphylaxis.
You should also skip Shingrix if:
- You have allergies to any parts of the vaccine. These include gelatin and the antibiotic neomycin. If you have other allergies, tell your doctor or pharmacist about them before you get Shingrix.
- You currently have shingles or another illness. You can get the vaccine when youâre well.
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding. You should wait until youâve stopped breastfeeding to get vaccinated.
- You happened to test negative for VZV, the virus that causes chickenpox. If youâre older than 50, you probably had chickenpox even if you donât remember it. The CDC does not recommend testing for this. However, if a blood test shows youâve never had the childhood illness, you should get the chickenpox vaccine instead.
If you have a disease or take medications that affect your immune system, talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of Shingrix.
âItâs an individualized decision based on factors such as the specific medications and conditions of the person sitting in front of you,â Kistler says. She often consults with her patientsâ specialist doctors to make decisions about Shingrix.
What Are The Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
Just like with any other medication or vaccine, there is always a risk of potential side effects or allergic reactions. The shingles vaccine, however, is considered to be safe and poses a small risk of side effects.
- The Zostavax shingles vaccine may cause:
- Redness, soreness, swelling, or itching at the site of the injection, or
Read Also: Who Can Have Shingles Vaccine
Who Should Not Get The Vaccine
It is safe for most people to get two doses of Shingrix. However, you should talk to your healthcare provider before getting the shingles vaccine if:
- You are pregnant
- You have severe allergies to any of the Shingrix ingredients
- You have ever experienced a severe allergic reaction to Shingrix
If you have a mild sickness, such as a cold, its usually safe to get the shingles vaccine. If you are moderately or severely ill, you should wait until you feel better to get your next dose of Shingrix.
You should still get the shingles vaccine if you dont remember having the chickenpox virus in the past and if youve had shingles previously. Shingrix can protect you against developing shingles again in the future.
Can Zostavax Cause Shingles
Yes. Shingles is a side effect of Zostavax that Merck & Co. added to the label at the request of the FDA in . The FDA also strengthened warnings about serious infections and infestations with the virus in the vaccine.
In Australia, safety officials have reported the death of sick patients who were given Zostavax and warned that it should not be given to patients with compromised immune systems due to the risk of death from serious infections with the vaccine virus.
Recommended Reading: How To Handle Shingles Pain
Is The Shingles Vaccine Safe
The FDA have approved the use of both shingles vaccines in healthy adults over the age of 50.
However, there are some instances in which a person should not get either vaccine â if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, allergic to any ingredient in the vaccine, or have a weakened immune system, for example.
Allergic Reaction To Shingles Vaccination
There is a very small chance of a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine, as there is with other vaccines.
Anaphylaxis is very serious and potentially life-threatening, but it can be treated. All healthcare staff that deliver vaccinations are trained in this. With prompt treatment, people fully recover from anaphylaxis.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles Multiple Times
Fever And Feelings Of Malaise
Fever is one of the most common side effects of many vaccines, including Shingrix. This symptom often accompanies other feelings of malaise, such as muscle pains, chills, and headaches. A fever indicates that the bodys immune system is doing its job of responding to the vaccine.
Ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and other OTC fever reducers can help keep a fever and many accompanying symptoms at bay. However, if you develop a high-grade fever of 103°F or higher, reach out to your doctor immediately.
Can You Get Shingles After Youve Been Vaccinated
While the shingles vaccine is highly effective, some people can still get shingles. However, people who do get shingles after getting the shingles vaccine usually have milder symptoms and a shorter illness. Youll also be less likely to have complications from shingles, including postherpetic neuralgia.
Recommended Reading: Is Shingles An Autoimmune Disease
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
Shingles is a common disease, affecting about 1 out of 3 adults during their lifetime.
Shingles is most common among older adults. However, shingles can also occur in healthy younger adults and in children. Those with immune systems that have been weakened by HIV, AIDS, cancer or treatment with certain drugs are also at an increased risk of getting shingles. Shingles causes a painful rash and blisters and can lead to serious complications, including post-herpetic neuralgia.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
For most people, the effects of Shingrix are mild and short-term. In very rare cases, Shingrix can cause more serious side effects.
Seek urgent medical care if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction a few minutes or hours after your second dose of Shingrix, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Facial swelling
- Swelling in the throat or mouth
You should also let your healthcare provider know if your Shingrix side effects are severe or arent going away on their own.
You May Like: What Are The Side Effects Of Having Shingles
Side Effects Of Shingles Vaccine
The most common shingles shot side effects include pain and soreness at the injection site. Some people also notice a bit of redness, swelling or itching at the site of the shot. Other side effects of the shingles vaccine may include fatigue, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. According to the CDC, side effects are more common in younger people than older people.
Most people can resume their regular activities immediately after vaccination. However, about 1 out of 6 people develop flu-like symptoms that last anywhere from 1 to 3 days.
Side effects can occur after the first, second, or both doses of Shingrix vaccine. If possible, it is a good idea to schedule vaccination the day before some downtime, so you can rest if you develop side effects.
If you develop flu-like symptoms after shingles vaccination, you can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to control your fever and improve comfort. Those who develop flu-like symptoms after their first dose of vaccine may want to pre-medicate with ibuprofen or acetaminophen an hour or so before their second dose. Your healthcare provider can answer your questions about shingles vaccine side effects and pre-medication for vaccination.
Serious side effects are rare, but not impossible, after shingles vaccination. If you develop hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, a rapid heartbeat, or sudden dizziness or weakness, and seek medical care immediately.
Rare Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
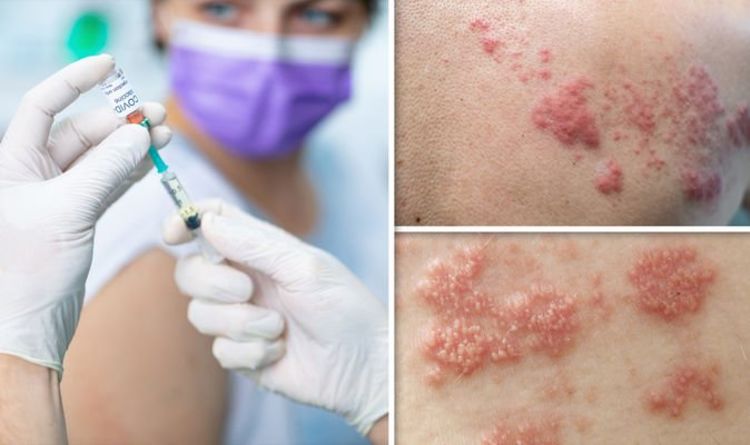
In rare cases, a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis may occur. This can be a life-threatening emergency and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis after receiving the shingles vaccine include:
Typically, these side effects appear immediately or within a few minutes of vaccination your vaccination provider may be present. If you experience them after leaving the office, call 911.
Recommended Reading: How To Fix Loose Shingles
Considerations For Patients Who Previously Received Zostavax
Studies have not examined the safety and immunogenicity of Shingrix administered less than 5 years following Zostavax vaccination. However, there are no data or theoretical concerns to indicate that Shingrix would be less safe or less effective when given at an interval shorter than 5 years following Zostavax. Since the risk of herpes zoster increases with age, providers should weigh a patients risk of herpes zoster with the age-specific protection expected from Zostavax to determine when to vaccinate with Shingrix.
Why Do I Need Two Doses Of Shingrix
In addition to a painful rash, shingles can lead to serious health complications like PHN, pneumonia, vision loss, hearing problems, and encephalitis . Research indicates that about 1% to 4% of people with shingles will be hospitalized.
Two doses of Shingrix offer effective protection against shingles and related complications for at least seven years. Among healthy adults ages 50-69, Shingrix is more than 90% effective in preventing PHN when two doses are administered. Among adults ages 70 and older, it is 89% effective.
You May Like: Can The Shingles Vaccine Help With Genital Herpes
What Does The Shingles Vaccine Do
The shingles vaccine can prevent shingles. Every year, about 1 million people in the United States get shingles. Anyone whos had chickenpox can get shingles. Thats because the varicella-zoster virus lives silently in your nervous system after you’ve had chickenpox. The virus can reactivate later in your life if your immune system is weakened. Your risk of getting shingles goes up as you get older. In the United States, 1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.
Another Jab At Shingles
In October 2018, the FDA approved Shingrix, a two-shot shingles vaccine for patients 50 and older. To be the most effective, patients must get the second shot between two to six months after the first. Clinical trials demonstrated that it was 91% to 97% effective in preventing shingles, and that protection seems to stay strong, at least for the first four years in the patients who were tracked.
There has slowly been uptick, but still very large group of those aged 50 and older who have not received it, saysNatalie Baker, DNP, president of the gerontological advanced practice nursing association .
Given its improved efficacy and the fact that the efficacy of Zostavaxwanes over the course of a few years, regulators recommended getting the Shingrix shots even if you already received Zostavax, which was discontinued in 2020. A lot of our older adults have received Zostavax, but, unfortunately, it just does not continue to be effective, she says, explaining that even those patients should get the Shingrix vaccine.
You May Like: What Does Shingles Look Like And Feel Like
Shingrix Dosage And Schedule
Shingrix should be administered to immunocompetent adults aged 50 years and older and adults aged 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy as a two-dose series , 2 to 6 months apart . However, for persons who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed and who would benefit from completing the series in a shorter period, the second dose can be administered 12 months after the first. See more detailed clinical guidance.
If more than 6 months have elapsed since the first dose of Shingrix, you should administer the second dose as soon as possible. However, you do not need to restart the vaccine series.
If the second dose is given less than 4 weeks after the first dose, the second dose should be considered invalid. A valid second dose should be administered 2 months after the invalid dose .
Swelling Around The Injection Site
Swelling around the injection site is another common side effect of Shingrix. Like pain and redness, minor swelling can usually result from a localized immune system response, which isnt necessarily dangerous.
You can apply hydrocortisone cream on or around the injection site to reduce redness and swelling. However, if you experience severe swelling that doesnt go away, or the swelling accompanies other symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention right away.
You May Like: What Medicine Is Used For Shingles
Is The Vaccine Safe
The vaccine can be given to people with a previous history of shingles infection. It should not be given to anyone who currently has shingles. As stated above, the vaccine should not be given to people who are clinically immunosuppressed because the vaccine strain could replicate too much and cause a serious infection. For more information see the MHRA’s Drug Safety Update .
In clinical trials of the vaccine, there have been no reports of someone who was vaccinated passing the virus on to anyone else. However, because the shingles vaccine is a live vaccine, it is thought that this may be possible in rare cases.
There is thought to be a very small risk that someone who has been vaccinated could pass on the virus to someone who is not immune to chickenpox. This is only thought to be a risk if the person who has been vaccinated develops a shingles type rash at the injection site or elsewhere on the body.
The shingles vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women as a matter of caution. However, studies have been carried out on pregnant women who have accidentally received chickenpox or shingles vaccines. These have not shown any link between the weakened virus in the vaccine and any specific problems in babies born to these women. See this Public Health England statement for more information.
Patient Reports Of Side Effects

During the first eight months of Shingrixs post-marketing use, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS, received 4,381 total reports of adverse events of these 130 were serious.
For every 100,000 doses distributed, the CDC found 136 complaints filed in the system. Approximately 3.2 million doses were distributed by GlaxoSmithKline during the eight-month period of reporting analyzed by the CDC.
Fever, chills and body aches and pain, swelling and redness in the arm receiving the shot were common side effects.
Yet seven patients died within six hours to six weeks of receiving Shingrix, the CDC said. The cause of four of these deaths was cardiovascular disease . Two were immunosuppressed patients who died of sepsis. And one 86-year-old woman died after a fall. v An eighth death after the use of Shingrix was also reported to VAERS, though this was not confirmed by the CDC.
Dr. Elisabeth M. Hesse, lead author of the report and a medical officer in the CDCs Office of Immunization Safety, wrote in an email that no information in medical documentation indicated the reported deaths were related to vaccination.
She noted that the Rotashield vaccine for infants was withdrawn from the market after reports to VAERS of bowel obstruction and an investigation that verified these claims.
Don’t Miss: How Far Apart Shingles Vaccines
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of zoster vaccine, inactivated may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- itching at the injection site
When Should I See A Doctor Because Of The Side Effects I Experience From Shingrix
Shingrix causes a strong response in your immune system, so it may produce short-term side effects. These side effects can be uncomfortable, but they are expected and usually go away on their own in 2 or 3 days. You may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Contact your healthcare provider if the symptoms are not improving or if they are getting worse.
In clinical trials, Shingrix was not associated with serious adverse events. In fact, serious side effects from vaccines are extremely rare. For example, for every 1 million doses of a vaccine given, only one or two people might have a severe allergic reaction. Signs of an allergic reaction happen within minutes or hours after vaccination and include hives, swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, or weakness. If you experience these or any other life-threatening symptoms, see a doctor right away.
Also Check: What Kind Of Doctor To See For Shingles
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Read Also: How To Figure How Many Shingles You Need