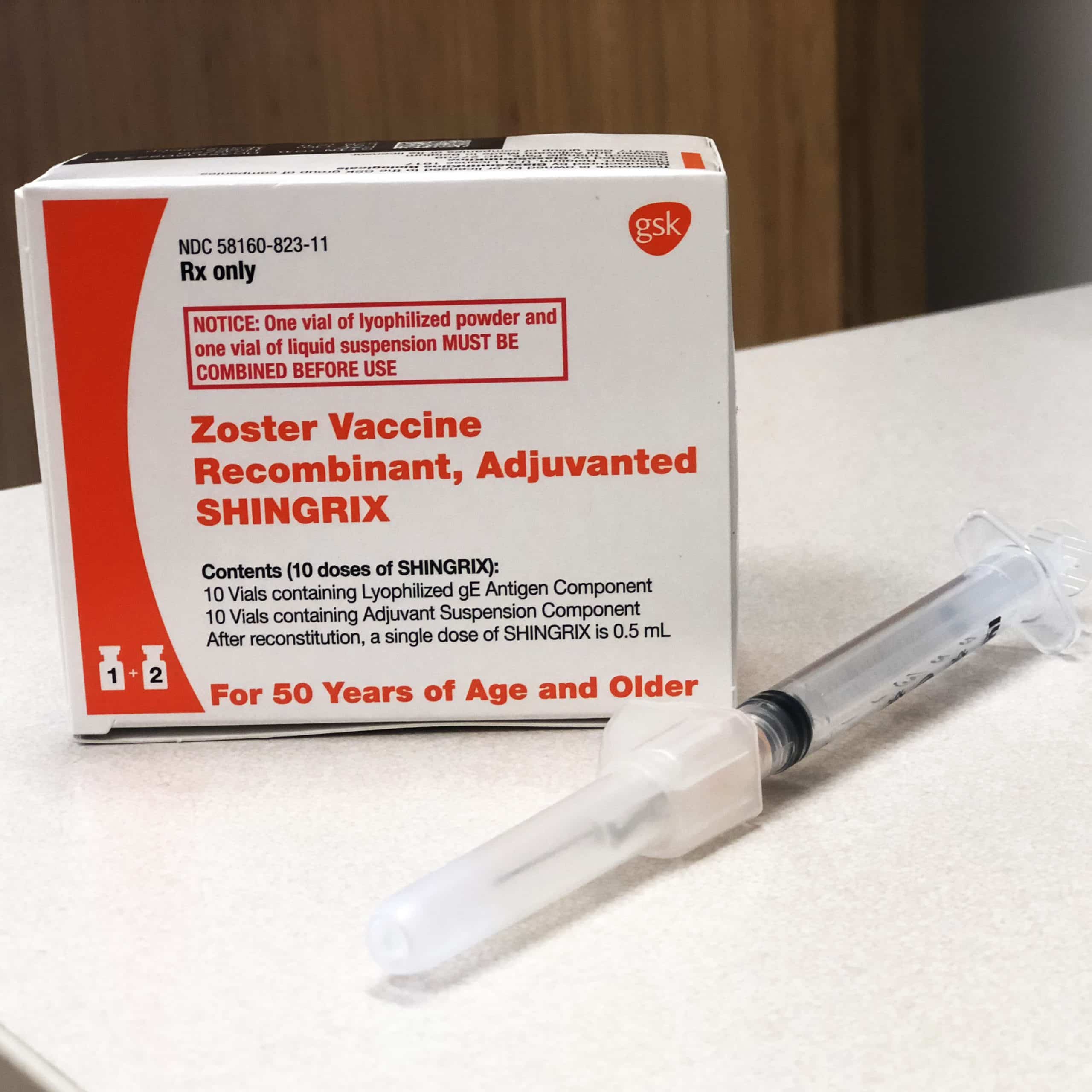
Shingles Vaccine Lawsuit Update
Our law firm is handling Zostavax and Shingrix vaccine lawsuits. These vaccines were intended for the prevention of herpes zoster which is more commonly known as the shingles virus.
These herpes lawsuits allege that the shingles vaccine was unsafe for patients. The key injury, incredibly, is that the Zostavax shingles vaccine causes shingles and zoster-related injuries. So the very thing meant to protect them against shingles actually caused shingles.
The Zostavax shingles suits make a lot of allegations against Merck. Many of the extraneous claims have already been dismissed. Lawyers make a lot of claims when they file lawsuits like this, sometimes too many. But the core of it is plaintiffs attorneys allege that Merck knew or should have known of the risks and reactions associated with their product.
Because Merck knew of the risks, it had a legal obligation to provide warnings. These should have fairly and accurately depicted the severity of the risks associated with the Zostavax. This is particularly true because there were better options available than Zostavax on the market.
- Speculation about Zostavax claims settlement value based on the value of similar types of cases and injuries
- Shingrix recall
The Shingles Virus The New Jersey Lawsuit
This lawsuit filed in New Jersey alleges that nearly 1,000 victims took Zostavax vaccine to avoid shingles, but instead developed a recurring strain of herpes zoster, which is more difficult to treat than usual.
Zostavax MDL Update
How Well Does Zostavax Work
Zostavax®, the shingles vaccine, reduced the risk of shingles by 51% and the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia by 67% based on a large study of more than 38,000 adults aged 60 years or older. Protection from shingles vaccine lasts about 5 years.
While the vaccine was most effective in people 60 through 69 years old, it also provides some protection for people 70 years old and older.
Adults vaccinated before age 60 years might not be protected later in life when the risk for shingles and its complications are greatest.
Does The Vaccine Work
In December 2017 Public Health England published an evaluation of the first three years of the shingles vaccination programme in England . This showed that the shingles vaccine was 62% effective against shingles and 70 to 88% effective against post-herpetic neuralgia in this period. Public Health England estimates that there were 17000 fewer GP consultations for shingles than expected in this 3-year period.
In the early 2000s researchers carried out a very large study of Zostavax, the shingles vaccine used in the UK, involving over 38,000 adults aged 60 or older. The results showed that:
- In adults aged between 60 and 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 51.3%
- In adults aged over 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 38%
- The vaccine reduced the incidence of post-herpetic neuralgia by over 66% in all age groups
- For those who did get shingles, the vaccine reduced the severity of the disease.
Read the abstract of this study , published in 2005 by Oxman et al.
Adults aged 80 or over are not offered the shingles vaccine. This is because the effectiveness of the vaccine declines with age in older age groups.
Recommended Reading: What To Do If You Think You Have Shingles Rash
Simultaneous Administration With Other Vaccines
RZV and LZV may be administered concomitantly with other live vaccines given by the parenteral, oral, or intranasal routes. For concomitant parenteral injections, different injection sites and separate needles and syringes should be used.
In general, inactivated vaccines including RZV may be administered concomitantly with, or at any time before or after, other inactivated vaccines or live vaccines protecting against a different disease.
LZV may be given at any time before or after live oral or intranasal vaccines. If two live parenteral vaccines are not administered concomitantly, there should be a period of at least 4 weeks before the second live parenteral vaccine is given.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine and LZV has not resulted in decreased efficacy and so the two vaccines can be given concomitantly.
For more information, refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1.
When Should You Get Immunised Against Shingles
Anyone aged 60 years and over who wants to protect themselves against shingles can talk to their doctor about getting immunised.
Shingles immunisation is recommended for:
- adults aged 60 years and over who have not previously received zoster vaccine
- adults aged 70 years to 79 years, for free under the National Immunisation Program
- adults aged 50 or over who live in the same household as someone who has a weakened immune system.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Shingles Without Having Chicken Pox
Research Into Mrna Vaccines For Shingles
Several companies are researching the potential use of mRNA vaccines for shingles. Pfizer and BioNTech are partnering on an mRNA shingles vaccine just as they did with vaccines for the flu and COVID-19.
A major advantage to the technology is the ability to develop new vaccines quickly. The fact that mRNA vaccines are synthetic and dont rely on actual virus particles also means they can be quickly produced in large numbers.
While the Shingrix vaccination is considered safe, the FDA has confirmed a link between Shingrix and Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Phasing out the old vaccine with the introduction of a new one, as the FDA did when Shingrix replaced Zostavax, might eliminate this potential issue.
Pfizer and BioNTech hope to begin clinical trials later this year.
Dont Miss: How To Install Timberline Shingles
What Should You Do If You Have Shingles
These simple steps can help you reduce the severity and spread of shingles:
- Cover the rash at all times
- Do not touch or scratch the rash
- Wash hands often to prevent the spread of the virus
- Before the rash develops crusts, avoid contact with:
- pregnant women who have never had chickenpox or been vaccinated against it
- premature or low birth-weight infants
- people with weakened immune systems including those receiving immunosuppressive medications or undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients, and people with HIV.
Don’t Miss: Does Medicare Cover Shingles Shots At Walgreens
Who Should Get The Shingles Vaccine
The CDC recommends all healthy adults ages 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine to prevent shingles and problems that can develop after youve had the disease. The two doses should be separated by two to six months. You should get the shingles vaccine even if you:
- Have had shingles: If youve had shingles in the past, you should get the shingles vaccine to help prevent getting the disease again. You should wait until the shingles rash is gone before getting the vaccine.
- Arent sure if youve had chickenpox: Studies show more than 99% of Americans ages 40 and older have had chickenpox at some point in their lives. You should get the shingles vaccine whether or not you remember having chickenpox because theyre caused by the same virus.
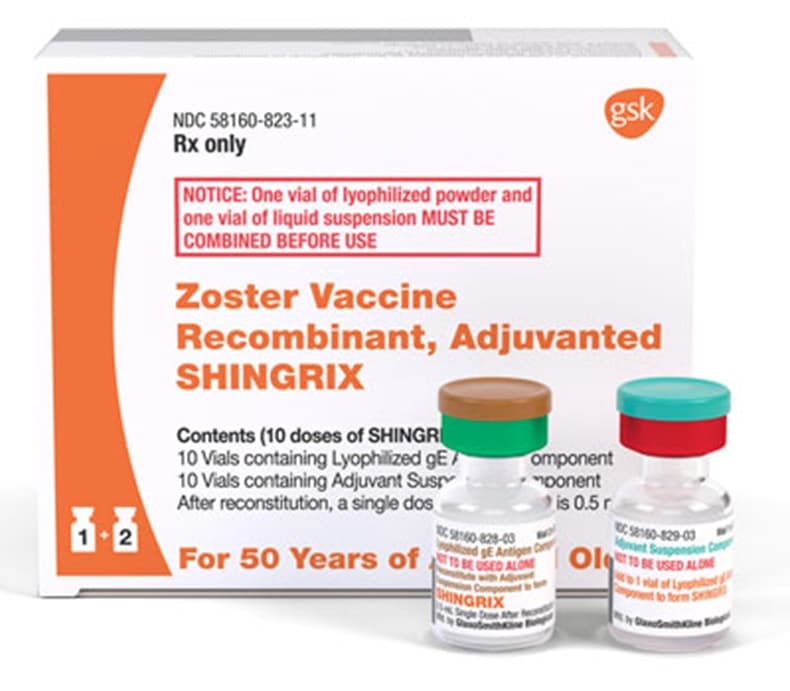
- Received the old shingles vaccine : Before November 18, 2020, people were vaccinated with a shingles vaccine called Zostavax. You cant get Zostavax in the United States anymore. If you were vaccinated with Zostavax, you should get vaccinated with the new shingles vaccine, Shingrix.
Which Type Should People With Diabetes Get
There used to be two shingles vaccines available in the United States: Zostavax and Shingrix. As of November 2020, Zostavax is no longer available in the United States. Shingrix, however, is safe and effective. The Shingrix vaccine is given in two doses two to six months apart.
People who previously got the Zostavax vaccine should now get the Shingrix vaccine. Zostavax was much less effective at preventing shingles than Shingrix, and what protection Zostavax gave waned within five years. Talk to a healthcare provider about getting Shingrix if you had Zostavax.
Don’t Miss: Can Shingles Appear Anywhere On The Body
Shingles Vaccine And Insurance
Private health insurance plans often cover vaccination costs. Still, a patient might have a charge depending on the specific insurance plan.
Medicaid may or may not cover the vaccine cost.Medicare Part D plans cover the shingles vaccine, but there may be a cost to the patient depending on the plan. Usually, the fees are less than $50 per dose.
Medicare Part B does not cover the shingles vaccine.
Persons With No Documented History Of Varicella Varicella Vaccination Or Herpes Zoster
Shingles is caused by VZV . After a person recovers from varicella, the virus stays dormant in their body. The virus can reactivate years or decades later, causing shingles.
- Persons who have neither experienced varicella nor received varicella vaccine are not at risk for shingles.
- More than 99% of Americans born before 1980 have had varicella, even if they dont remember it .
- Children and adolescents who have received live-attenuated varicella vaccines are at lower risk for shingles than are those who experienced varicella .
RZV is not indicated and has not been studied for the prevention of varicella.
- Receipt of RZV is not considered proof of prior varicella disease or varicella immunity.
- RZV cannot be considered as either of the two doses of the varicella vaccine series.
For immunocompromised persons, evidence of immunity to varicella includes:
- Documentation of two doses of varicella vaccine, or
- Laboratory evidence of immunity or laboratory confirmation of disease, or
- Diagnosis or verification of a history of varicella or herpes zoster by a healthcare provider.
It is important to note that:
For immunocompromised adults with no documented history of varicella, varicella vaccination, or shingles:
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Shingles
Are There Any Restrictions After A Shingles Shot
You should not receive the shingles vaccine if you are pregnant, if you have an active shingles infection, or if you previously had an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine. If youre eligible for the vaccine and receive the vaccination, there are no restrictions afterward and you can leave the doctors office or pharmacy as soon as the shot is complete.
When Should I See A Doctor Because Of The Side Effects I Experience From Shingrix
Shingrix causes a strong response in your immune system, so it may produce short-term side effects. These side effects can be uncomfortable, but they are expected and usually go away on their own in 2 or 3 days. You may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Contact your healthcare provider if the symptoms are not improving or if they are getting worse.
In clinical trials, Shingrix was not associated with serious adverse events. In fact, serious side effects from vaccines are extremely rare. For example, for every 1 million doses of a vaccine given, only one or two people might have a severe allergic reaction. Signs of an allergic reaction happen within minutes or hours after vaccination and include hives, swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, or weakness. If you experience these or any other life-threatening symptoms, see a doctor right away.
Also Check: What Do You Put On Shingles
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Autoimmune disease
Although definitive data are lacking, individuals with autoimmune disease not being treated with immunosuppressive drugs are not considered significantly immunocompromised. Individuals 50 years of age without contraindications should receive RZV.
For more information, refer to Immunization of Immunocompromised Persons, and Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3.
Can My Grandfather With Shingles Give My Baby Daughter Chickenpox
Yes, although people with shingles cannot pass shingles to someone else, they can pass chickenpox virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If your baby has not yet had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine, she could become infected with the virus and develop chickenpox.
Unlike chickenpox that can be passed to others through coughs or sneezes, people with shingles can only pass the virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If the rash has yet to develop or has crusted, the patient cannot transmit the virus. Similarly, people who still have pain without the rash are no longer able to transmit the virus.
Also Check: How To Repair Nerve Damage From Shingles
Vaccine Safety And Side Effects
Vaccines are very safe, and they can help keep you from getting serious or life-threatening diseases. The most common side effects for all these vaccines are mild and may include pain, swelling, or redness where the vaccine was given.
Before getting any vaccine, talk with a doctor or pharmacist about your health history, including past illnesses and treatments, as well as any allergies. A health care provider can address any concerns you have.
Its a good idea to keep your own vaccination record, listing the types and dates of your shots, along with any side effects or problems.
How Does The Shingles Vaccine Work
Shingrix is a recombinant vaccine: It is made in the lab using a protein found in the outer shell of the varicella-zoster virus. The vaccine prompts the body to produce an immune response against the virus protein. This way, the immune system will recognize and fight the virus when it reactivates in the body, preventing shingles. It does not contain a weakened form of the virus, like many vaccines do.
The largest clinical trial of the vaccine, which was done in 18 countries, found that it was 97.2% effective at preventing shingles in adults aged 50 years and older. In a later trial, completed at the same locations, vaccine efficacy was 89.8% in people 70 years of age and older.
In addition to preventing shingles from developing, the vaccine offers other benefits. The small percentage of people who got shingles after receiving the vaccine in clinical trials reported less pain than did those who got the disease and were not vaccinated. Additionally, the vaccine prevented shingles-related complications in all but one person.
You might have heard about a different shingles vaccine called Zostavax that was approved in 2006. But it is no longer available as of November 2020. Fortunately, Shingrix has higher efficacy than Zostavax.
Read Also: When Can You Get A Shingles Shot
Reasons To Get The Shingles Vaccine
Once a person develops chickenpox after contracting the varicella-zoster virus, the virus never leaves the body. It remains dormant in the nerve roots and can reappear as shingles later in life.
The primary symptom of shingles is a painful rash on one side of the body, most often on the torso or face. People initially have pain or a burning sensation on the skin without a rash, and then painful blisters develop. The rash lasts approximately seven to 10 days and fully clears within two to four weeks.
The likelihood of developing shingles increases dramatically after age 50. Therefore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all adults age 50 and over receive two doses of Shingrix to prevent shingles. The vaccine is recommended even if a person is unsure if they have ever had chickenpox.
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for shingles. Therefore, the Food and Drug Administration also recently approved Shingrix vaccination for adults age 18 and older who are at risk for shingles due to immunodeficiency or immunosuppression caused by an underlying disease or medication.
Is The Vaccine Safe
The vaccine can be given to people with a previous history of shingles infection. It should not be given to anyone who currently has shingles. As stated above, the vaccine should not be given to people who are clinically immunosuppressed because the vaccine strain could replicate too much and cause a serious infection. For more information see the MHRA’s Drug Safety Update .
In clinical trials of the vaccine, there have been no reports of someone who was vaccinated passing the virus on to anyone else. However, because the shingles vaccine is a live vaccine, it is thought that this may be possible in rare cases.
There is thought to be a very small risk that someone who has been vaccinated could pass on the virus to someone who is not immune to chickenpox. This is only thought to be a risk if the person who has been vaccinated develops a shingles type rash at the injection site or elsewhere on the body.
The shingles vaccine is not recommended for pregnant women as a matter of caution. However, studies have been carried out on pregnant women who have accidentally received chickenpox or shingles vaccines. These have not shown any link between the weakened virus in the vaccine and any specific problems in babies born to these women. See this Public Health England statement for more information.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Shingles On The Face
What Are The Benefits Of The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccines are the best way to protect you from getting shingles. The vaccines have been shown to reduce the risk of getting shingles by 50% for Zostavax® II, and to more than 90% for Shingrix®.
For those who still get shingles after being immunized, the vaccines can reduce pain, including the type of pain that lasts after shingles.
How Cdc Monitors Vaccine Safety
CDC and FDA monitor the safety of vaccines after they are approved or authorized. If a problem is found with a vaccine, CDC and FDA will inform health officials, health care providers, and the public.
CDC uses 3 systems to monitor vaccine safety:
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System : an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and FDA, to monitor for potential vaccine safety problems. Anyone can report possible vaccine side effects to VAERS.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink : a collaboration between CDC and 9 health care organizations that conducts vaccine safety monitoring and research.
- The Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project: a partnership between CDC and several medical research centers that provides expert consultation and conducts clinical research on vaccine-associated health risks.
Recommended Reading: What Do Pictures Of Shingles Look Like