Who Shouldnt Get A Shingles Vaccine
The CDC says some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. That includes those who:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix
- Tested negative for VZV immunity
- Currently have shingles
- Have a severe or moderate acute illness, such as a respiratory infection
Your healthcare provider can answer any questions you have about whether the vaccine is safe for you.
Know Your Risk Of Getting Shingles And Complications
About 1 out of every 3 people in the United States will develop shingles during their lifetime.
If youve had chickenpox, you are at risk for shingles. More than 99% of Americans born before 1980 have had chickenpox, even if they dont remember it.
Your risk of getting shingles and having serious complications increases as you get older.
About 1 in 10 people who get shingles develop nerve pain that lasts for months or years after the rash goes away. This is called postherpetic neuralgia and is the most common complication of shingles.
Shingles may lead to other serious complications involving the eye, including blindness. Very rarely, it can also lead to pneumonia, hearing problems, brain inflammation or death.
How Long After Ive Received The Shingles Vaccine Am I Contagious
With the currently authorized shingles vaccine, Shingrix, you wont be contagious. The old vaccine, Zostavax, used a weakened form of the live varicella-zoster virus. Therefore, people worried about spreading the disease to the people around them.
Shingrix doesnt use a live version of the varicella-zoster virus. It is inactivated, which means it uses a dead version of the virus. Therefore, you have no risk of transmitting the disease to anyone.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
No one likes to get shots, especially for something youve already been vaccinated for. But the newer version of the shingles vaccine is one youll want to offer up your arm for. The Shingrix vaccine is more than 90% effective at helping you prevent shingles. Since most of us have had chickenpox in the past, the shingles vaccine is an easy way to prevent the dormant chickenpox virus from creeping up and hitting you again with shingles.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do You Have Shingles
A Closer Look At The Safety Data
Both Shingrix and Zostavax shingles vaccines have been shown to be safe and well tolerated. Common side effects, such as soreness and redness at the injection site, are usually mild to moderate in intensity and resolve quickly on their own.
Shingrix
In 8 clinical trials of more than 10,000 participants:
- Grade 3 reactions were common after patients received Shingrix.
- About 1 out of 10 adults who received Shingrix reported grade 3 injection-site symptoms such as pain, redness, and swelling.
- About 1 out of 10 reported grade 3 systemic reactions such as myalgia , fatigue , headache, shivering, fever, and gastrointestinal illness.
- Most people who got Shingrix reported at least some pain at the injection site.
Zostavax
- A 2013 study showed that patients with a history of a previous shingles rash had the same side effects after Zostavax as those with no history of shingles. See Safety of zoster vaccine in elderly adults following documented herpes zoster.
Side Effects Of Shingles Vaccine
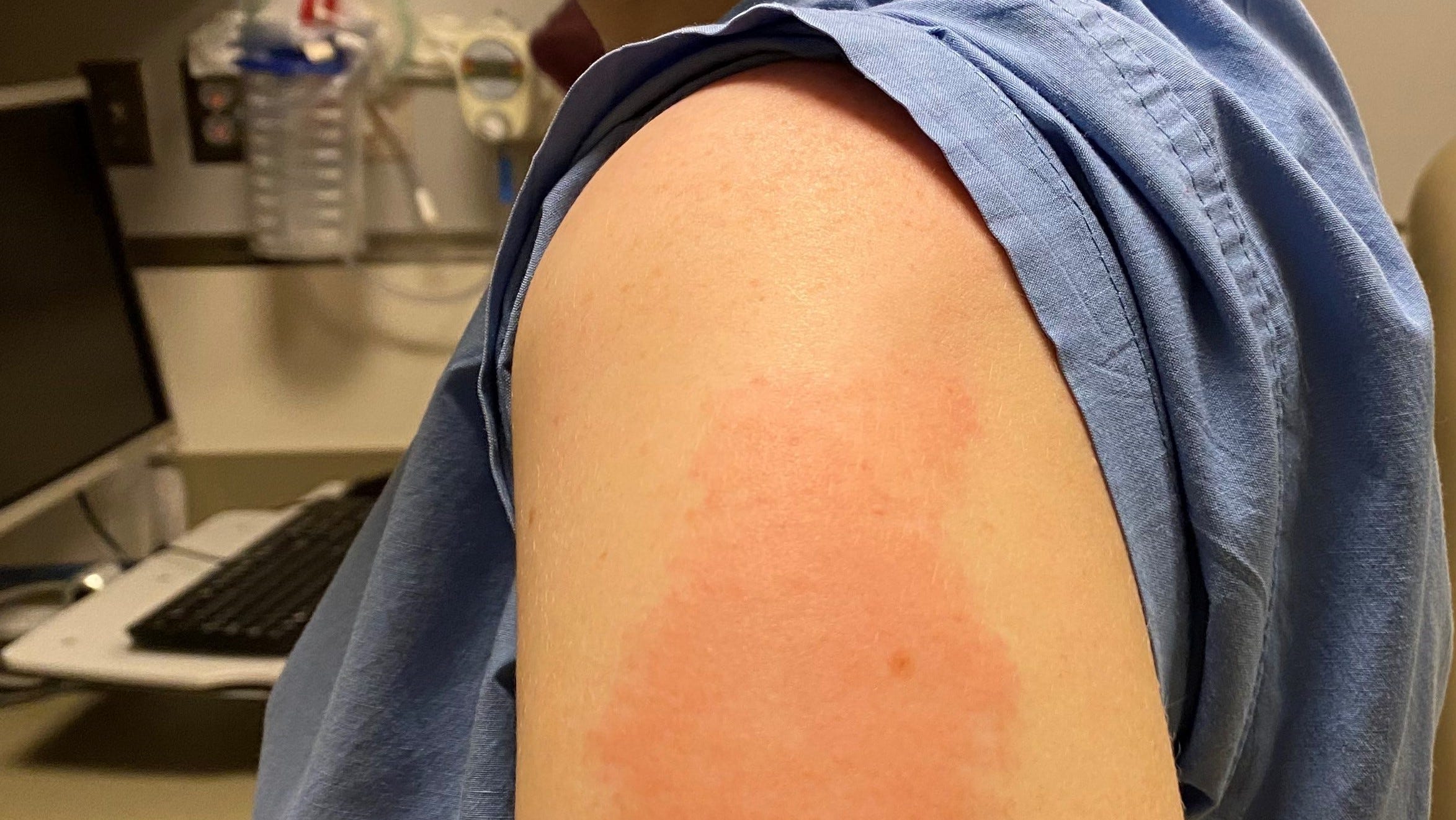
One in six people feels ill after being vaccinated with Shingrix, per the Centers for Disease Control . This feeling may last a few days. Of those who react, some may be after the first dose, while others may experience side effects after dose two.
Common side effects of a shingles vaccination include headache and fatigue, muscle pain, fever and chills, stomach discomfort and nausea, as well as redness, swelling, or mild to moderate pain at the injection site.
Side effects from receiving the Zostavax shingles vaccine are allegedly much more severe.
Also Check: Where To Get The Shingles Vaccine For Free
Patient Reports Of Side Effects
During the first eight months of Shingrixs post-marketing use, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS, received 4,381 total reports of adverse events of these 130 were serious.
For every 100,000 doses distributed, the CDC found 136 complaints filed in the system. Approximately 3.2 million doses were distributed by GlaxoSmithKline during the eight-month period of reporting analyzed by the CDC.
Fever, chills and body aches and pain, swelling and redness in the arm receiving the shot were common side effects.
Yet seven patients died within six hours to six weeks of receiving Shingrix, the CDC said. The cause of four of these deaths was cardiovascular disease . Two were immunosuppressed patients who died of sepsis. And one 86-year-old woman died after a fall. v An eighth death after the use of Shingrix was also reported to VAERS, though this was not confirmed by the CDC.
Dr. Elisabeth M. Hesse, lead author of the report and a medical officer in the CDCs Office of Immunization Safety, wrote in an email that no information in medical documentation indicated the reported deaths were related to vaccination.
She noted that the Rotashield vaccine for infants was withdrawn from the market after reports to VAERS of bowel obstruction and an investigation that verified these claims.
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
You May Like: How To Treat Shingles In The Eye
What Could I Collect In A Zostavax Lawsuit
If you are eligible to join a Zostavax lawsuit, your medical bills, suffering, lost wages, and more could be recoverable. Right now, a small group of six bellwether cases, known as Group A Bellwether Pool, is readying for trial. This case pool helps determine each sides weaknesses and strengths. It also helps with future settlement negotiations. Bellwether trial results are not binding.
Reasons To Get The Shingles Vaccine
Once a person develops chickenpox after contracting the varicella-zoster virus, the virus never leaves the body. It remains dormant in the nerve roots and can reappear as shingles later in life.
The primary symptom of shingles is a painful rash on one side of the body, most often on the torso or face. People initially have pain or a burning sensation on the skin without a rash, and then painful blisters develop. The rash lasts approximately seven to 10 days and fully clears within two to four weeks.
The likelihood of developing shingles increases dramatically after age 50. Therefore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all adults age 50 and over receive two doses of Shingrix to prevent shingles. The vaccine is recommended even if a person is unsure if they have ever had chickenpox.
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk for shingles. Therefore, the Food and Drug Administration also recently approved Shingrix vaccination for adults age 18 and older who are at risk for shingles due to immunodeficiency or immunosuppression caused by an underlying disease or medication.
Read Also: Can You Shingle Over Existing Shingles
Know The Benefits And The Side Effects
Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and long-term nerve pain. You may experience some short-term side effects because Shingrix causes a strong response in your immune system.
After getting Shingrix:
- Most people had a sore arm.
- Many people had redness and swelling where they got the shot .
- Many felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea.
About 1 out of 6 people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities like yardwork or swimming. Side effects usually go away after 2 to 3 days. Remember that the pain from shingles can last a lifetime, and these side effects should only last a few days.
Read Also: What Type Of Shingles Are There
When Should I Get The Second Dose
The CDC recommends that adults ages 50 and older get a second dose of Shingrix two to six months after their first dose. If youve waited longer than six months since your first dose of Shingrix, its safe to get a second dose right away. Most people dont need to repeat the first dose.
Some immunocompromised adults may need a second dose within one to two months. If you have a disease or are taking medication that affects your immune system, talk to your healthcare provider about the best timeline for your two doses of the shingles vaccine.
Recommended Reading: What Can You Put On Shingles Rash
You May Like: Where To Buy Certainteed Presidential Shingles
Can My Grandfather With Shingles Give My Baby Daughter Chickenpox
Yes, although people with shingles cannot pass shingles to someone else, they can pass chickenpox virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If your baby has not yet had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine, she could become infected with the virus and develop chickenpox.
Unlike chickenpox that can be passed to others through coughs or sneezes, people with shingles can only pass the virus to others through direct contact with the rash. If the rash has yet to develop or has crusted, the patient cannot transmit the virus. Similarly, people who still have pain without the rash are no longer able to transmit the virus.
Is The Shingles Vaccine Safe
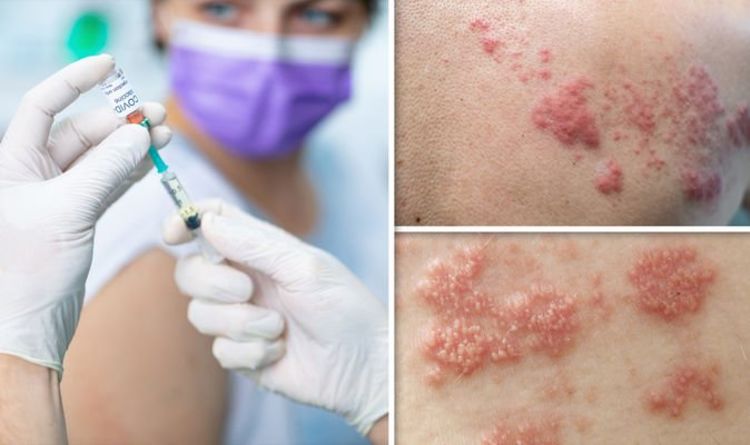
The FDA have approved the use of both shingles vaccines in healthy adults over the age of 50.
However, there are some instances in which a person should not get either vaccine â if they are pregnant or breastfeeding, allergic to any ingredient in the vaccine, or have a weakened immune system, for example.
Read Also: How Many Shingles Vaccines Do I Need
Another Jab At Shingles
In October 2018, the FDA approved Shingrix, a two-shot shingles vaccine for patients 50 and older. To be the most effective, patients must get the second shot between two to six months after the first. Clinical trials demonstrated that it was 91% to 97% effective in preventing shingles, and that protection seems to stay strong, at least for the first four years in the patients who were tracked.
There has slowly been uptick, but still very large group of those aged 50 and older who have not received it, saysNatalie Baker, DNP, president of the gerontological advanced practice nursing association .
Given its improved efficacy and the fact that the efficacy of Zostavaxwanes over the course of a few years, regulators recommended getting the Shingrix shots even if you already received Zostavax, which was discontinued in 2020. A lot of our older adults have received Zostavax, but, unfortunately, it just does not continue to be effective, she says, explaining that even those patients should get the Shingrix vaccine.
Make A Plan To Get 2 Doses
- You can get Shingrix at your doctors office or pharmacy. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about getting Shingrix.
- Plan to get your second dose of Shingrix 2 to 6 months after your first dose.
Five years later, I still take prescription medication for pain. My shingles rash quickly developed into open, oozing sores that in only a few days required me to be hospitalized. I could not eat, sleep, or perform even the most minor tasks. It was totally debilitating. The pain still limits my activity levels to this day.
A 63-year-old harpist who was unable to continue playing due to shingles
Recommended Reading: What Do Shingles Bumps Look Like
Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, zoster vaccine, inactivated may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking zoster vaccine, inactivated:
Rare
- Ankle, knee, or great toe joint pain
- fever greater than 39 degree Celsius
- joint stiffness or swelling
- lower back or side pain
- swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin
Incidence not known
- Hives, welts, or itching
- inability to move the arms and legs
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- redness of the skin
- sudden numbness and weakness in the arms and legs
Shingles Disease And How To Protect Against It
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash that develops on one side of the face or body. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus , the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who has had chickenpox in the past can get shingles because VZV remains in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. VZV can reactivate many years later, causing shingles.
Shingles is more common in older adults, people who have medical conditions that weaken the immune system, and people who take medications that suppress their immune systems. Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles.
Also Check: How Do They Test For Shingles
What Are Side Effects Of Inactivated Viral Vaccines
Side effects of inactivated viral vaccines may include the following:
- Injection site reactions include:
Information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible side effects, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. Check with your doctor or pharmacist to make sure these drugs do not cause any harm when you take them along with other medicines. Never stop taking your medication and never change your dose or frequency without consulting your doctor.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Its normal to have questions before you get a vaccine. Some common questions you may want to discuss with your healthcare provider include:
- When should I get the shingles vaccine?
- What side effects should I expect?
- How does the shingles vaccine work?
- When should I schedule each dose of the shingles vaccine?
- How effective is the shingles vaccine?
- Is there any reason I shouldnt get the shingles vaccine?
- What could happen if I dont get the shingles vaccine?
Also Check: When Is Shingles Not Contagious
Can The Shingles Shot Cause Guillain
Though rare, but Guillain-Barré syndrome can occur with both the shingles vaccine and the shingles virus itself.
Symptoms of this serious autoimmune disorder include a loss of sensation and muscle paralysis that tends to come on quickly, typically spreading up from your lower extremities.
It can be life-threatening, so contact a healthcare provider immediately if you think you may have symptoms.
How Is The Shingles Vaccine Made
The shingles vaccine available in the U.S., Shingrix®, contains a single protein from the surface of herpes zoster virus as well as two adjuvants: QS21 and monophosphoryl lipid A. QS21 is a soap-based molecule isolated from the bark of the Quillaja saponaria tree. Monophosphoryl lipid A is a detoxified form of lipopolysaccharide, a potent adjuvant taken from the surface of common bacteria.
The first shingles vaccine, called Zostavax®, is no longer available in the U.S. However, this version contained a more concentrated version of the same live, weakened virus as the current chickenpox vaccine. It contained about 14 times the amount of weakened chickenpox virus than the vaccine for children. This amount of virus was necessary to obtain a protective response in the aging immune systems of older adults. The introduction of Shingrix vaccine was important because adjuvants in the vaccine improved immune responses in older adults and decreased the need to use large quantities of the live, weakened virus also necessary to make chickenpox vaccine. For these two reasons Zostavax is no longer available in the U.S.
Don’t Miss: Where On The Body Can You Get Shingles
Why Do I Need Two Doses Of Shingrix
In addition to a painful rash, shingles can lead to serious health complications like PHN, pneumonia, vision loss, hearing problems, and encephalitis . Research indicates that about 1% to 4% of people with shingles will be hospitalized.
Two doses of Shingrix offer effective protection against shingles and related complications for at least seven years. Among healthy adults ages 50-69, Shingrix is more than 90% effective in preventing PHN when two doses are administered. Among adults ages 70 and older, it is 89% effective.
How Cdc Monitors Vaccine Safety
CDC and FDA monitor the safety of vaccines after they are approved or authorized. If a problem is found with a vaccine, CDC and FDA will inform health officials, health care providers, and the public.
CDC uses 3 systems to monitor vaccine safety:
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System : an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and FDA, to monitor for potential vaccine safety problems. Anyone can report possible vaccine side effects to VAERS.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink : a collaboration between CDC and 9 health care organizations that conducts vaccine safety monitoring and research.
- The Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project: a partnership between CDC and several medical research centers that provides expert consultation and conducts clinical research on vaccine-associated health risks.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Shingle Roofs Last In Florida
How Is Shingrix Given
Shingrix is given as an injection into a muscle. A healthcare provider will give you this injection.
Shingrix is usually given in a series of 2 shots:
-
the second shot may be given any time within 2 to 6 months after the first shot.
-
for people who have a weak immune system, the second shot may be given any time within 1 to 2 months after the first shot.
You may receive this vaccine at the same time that you get a flu shot.
Read all patient information, medication guides, and instruction sheets provided to you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.