Shingles Vaccine Side Effects: What To Expect
Shingles is a commonand preventableviral illness that can cause significant discomfort and serious health complications, including vision loss and long-term pain.
Caused by a reactivation of varicella zoster, the virus that causes chickenpox, shingles most often affects adults older than 50 years.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that healthy adults ages 50 years and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Shingrix is also approved for people 18 years and older whose immune system is weakened or compromised by a medical condition or immune-suppressing medications . Two doses of the vaccine, administered 2 to 6 months apart, are required for full vaccination.
You can get the Shingrix vaccine even if you:
- Dont know if you have had chickenpox
- Have had shingles
- Previously had the Zostavax vaccine
Side Effects Of Shingles Vaccine
The most common shingles shot side effects include pain and soreness at the injection site. Some people also notice a bit of redness, swelling or itching at the site of the shot. Other side effects of the shingles vaccine may include fatigue, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. According to the CDC, side effects are more common in younger people than older people.
Most people can resume their regular activities immediately after vaccination. However, about 1 out of 6 people develop flu-like symptoms that last anywhere from 1 to 3 days.
Side effects can occur after the first, second, or both doses of Shingrix vaccine. If possible, it is a good idea to schedule vaccination the day before some downtime, so you can rest if you develop side effects.
If you develop flu-like symptoms after shingles vaccination, you can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to control your fever and improve comfort. Those who develop flu-like symptoms after their first dose of vaccine may want to pre-medicate with ibuprofen or acetaminophen an hour or so before their second dose. Your healthcare provider can answer your questions about shingles vaccine side effects and pre-medication for vaccination.
Serious side effects are rare, but not impossible, after shingles vaccination. If you develop hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, a rapid heartbeat, or sudden dizziness or weakness, and seek medical care immediately.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Its normal to have questions before you get a vaccine. Some common questions you may want to discuss with your healthcare provider include:
- When should I get the shingles vaccine?
- What side effects should I expect?
- How does the shingles vaccine work?
- When should I schedule each dose of the shingles vaccine?
- How effective is the shingles vaccine?
- Is there any reason I shouldnt get the shingles vaccine?
- What could happen if I dont get the shingles vaccine?
Also Check: What Is The Best Doctor To See For Shingles
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of zoster vaccine, inactivated may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- itching at the injection site
When To See A Healthcare Provider
For most people, the effects of Shingrix are mild and short-term. In very rare cases, Shingrix can cause more serious side effects.
Seek urgent medical care if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction a few minutes or hours after your second dose of Shingrix, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Facial swelling
- Swelling in the throat or mouth
You should also let your healthcare provider know if your Shingrix side effects are severe or arent going away on their own.
Don’t Miss: What Brings On The Shingles Virus
Risks Of A Vaccine Reaction
- A sore arm with mild or moderate pain is very common after recombinant shingles vaccine. Redness and swelling can also happen at the site of the injection.
- Tiredness, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, and nausea are common after recombinant shingles vaccine.
These side effects may temporarily prevent a vaccinated person from doing regular activities. Symptoms usually go away on their own in 2 to 3 days. You should still get the second dose of recombinant shingles vaccine even if you had one of these reactions after the first dose.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after recombinant zoster vaccine.
People sometimes faint after medical procedures, including vaccination. Tell your provider if you feel dizzy or have vision changes or ringing in the ears.
As with any medicine, there is a very remote chance of a vaccine causing a severe allergic reaction, other serious injury, or death.
How Can I Learn More
- Ask your health care provider.
- Visit the website of the Food and Drug Administration for vaccine package inserts and additional information at www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines.
- Contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention :
- Call 1-800-232-4636 or
- Visit CDCâs website at www.cdc.gov/vaccines.
Vaccine Information Statement
Don’t Miss: How Often Is Shingles Vaccine Given
What Everyone Should Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Shingles vaccination is the only way to protect against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication from shingles.
CDC recommends that adults 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine called Shingrix to prevent shingles and the complications from the disease. Adults 19 years and older who have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and related complications.
Your doctor or pharmacist can give you Shingrix as a shot in your upper arm.
Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and PHN. In adults 50 years and older who have healthy immune systems, Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and PHN. Immunity stays strong for at least the first 7 years after vaccination. In adults with weakened immune systems, studies show that Shingrix is 68%-91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on the condition that affects the immune system.
What Other Drugs Interact With Zoster Vaccine Recombinant
If your medical doctor is using this medicine to treat your pain, your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any possible drug interactions and may be monitoring you for them. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine before checking with your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist first.
- Zoster Vaccine Recombinant has severe interactions with no other drugs.
- Zoster Vaccine Recombinant has serious interactions with the following drugs:
This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects. Visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker for any drug interactions. Therefore, before using this product, tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the products you use. Keep a list of all your medications with you and share this information with your doctor and pharmacist. Check with your health care professional or doctor for additional medical advice, or if you have health questions or concerns.
Also Check: Where Can Shingles Appear On The Body
Administration With Other Vaccines
CDC general recommendations advise that recombinant and adjuvanted vaccines, such as Shingrix, can be administered concomitantly, at different anatomic sites, with other adult vaccines, including COVID-19 vaccines. Concomitant administration of Shingrix with Fluarix Quadrivalent , 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine and Tetanus Toxoid, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine, Adsorbed , and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine has been studied, and there was no evidence for interference in the immune response to either vaccine or safety concerns. Coadministration of Shingrix with adjuvanted influenza vaccine and COVID-19 vaccines is being studied.
Shingrix and pneumococcal vaccine can be administered at the same visit if the person is eligible for both. When both pneumococcal conjugate vaccine PCV13 and PPSV23 are recommended for an adult, PCV13 should always be administered first and can be administered concomitantly with Shingrix.
When Should I Get The Second Dose
The CDC recommends that adults ages 50 and older get a second dose of Shingrix two to six months after their first dose. If youve waited longer than six months since your first dose of Shingrix, its safe to get a second dose right away. Most people dont need to repeat the first dose.
Some immunocompromised adults may need a second dose within one to two months. If you have a disease or are taking medication that affects your immune system, talk to your healthcare provider about the best timeline for your two doses of the shingles vaccine.
You May Like: What Do You Put On Shingles
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingles Immunisation

All medicines and vaccines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time theyre not.
For most people, the chance of having a serious side effect from a vaccine is much lower than the chance of serious harm if you caught the disease.
Talk to your doctor about possible side effects of shingles vaccines, or if you have possible side effects that worry you.
Common side effects of shingles vaccines include:
- pain, redness, swelling or itching where the needle went in
Serious reactions to immunisation are rare. With Zostavax® vaccination, very rarely a generalised chickenpox-like rash may occur around 24 weeks after vaccination. This may be associated with fever and feeling unwell. This rash may be a sign of a serious reaction to the virus in the vaccine. Seek medical attention and inform of recent Zostavax vaccination if you experience this reaction.
The Consumer Medicine Information links in How do you get immunised against shingles? list the side effects of each vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Shingles Vaccination
Does The Shingles Vaccine Contain Thimerosal
You may be concerned about additives to the shingles vaccine, like thimerosal.
Thimerosal is a preservative that contains mercury. Its added to some vaccines to prevent bacteria and other germs from growing in them. The shingles vaccine contains thimerosal.
The worry about thimerosal arose when early research linked it to autism. This connection has since been found to be untrue.
What Are The Advantages Of Getting The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine reduces your risk of getting shingles. Shingles causes a painful rash that usually develops on one side of your body or face. Some people describe the pain as an intense burning or shooting sensation. The rash is often a single strip that wraps around one side of your body or is on one side of your face. It consists of blisters that normally crust over in seven to 10 days. The rash generally clears up within a month.
Some people with shingles also experience additional symptoms including fever, headache, chills or upset stomach.
For some people, the pain from the rash can last for months or even years after the rash goes away. This long-term pain is called postherpetic neuralgia , and it is the most common complication of shingles.
You May Like: Is The Shingles Vaccine A Live Vaccine
Can You Get Shingles After Youve Been Vaccinated
While the shingles vaccine is highly effective, some people can still get shingles. However, people who do get shingles after getting the shingles vaccine usually have milder symptoms and a shorter illness. Youll also be less likely to have complications from shingles, including postherpetic neuralgia.
Allergic Reaction To Shingles Vaccination
There is a very small chance of a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine, as there is with other vaccines.
Anaphylaxis is very serious and potentially life-threatening, but it can be treated. All healthcare staff that deliver vaccinations are trained in this. With prompt treatment, people fully recover from anaphylaxis.
Read Also: What To Put On Shingles Blisters
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Who Can Get Shingles
Anyone who has had and has recovered from chickenpox can develop shingles, even children. However, the risk increases as people age and is most common in people 50 and older.
Additionally, there are those who are at a higher risk of developing shingles, such as:
- Those with certain medical conditions that affect the immune system, like cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma, and human immunodeficiency virus .
- People currently receiving immunosuppressive drugs, such as steroids and drugs administered after an organ transplant.
Most people who end up developing shingles usually only have one episode during their lifetime. However, having a second or even a third episode is not uncommon.
Read Also: Pacific Coast Red Cedar Sidewall Shingles
Another Jab At Shingles
In October 2018, the FDA approved Shingrix, a two-shot shingles vaccine for patients 50 and older. To be the most effective, patients must get the second shot between two to six months after the first. Clinical trials demonstrated that it was 91% to 97% effective in preventing shingles, and that protection seems to stay strong, at least for the first four years in the patients who were tracked.
There has slowly been uptick, but still very large group of those aged 50 and older who have not received it, saysNatalie Baker, DNP, president of the gerontological advanced practice nursing association .
Given its improved efficacy and the fact that the efficacy of Zostavaxwanes over the course of a few years, regulators recommended getting the Shingrix shots even if you already received Zostavax, which was discontinued in 2020. A lot of our older adults have received Zostavax, but, unfortunately, it just does not continue to be effective, she says, explaining that even those patients should get the Shingrix vaccine.
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
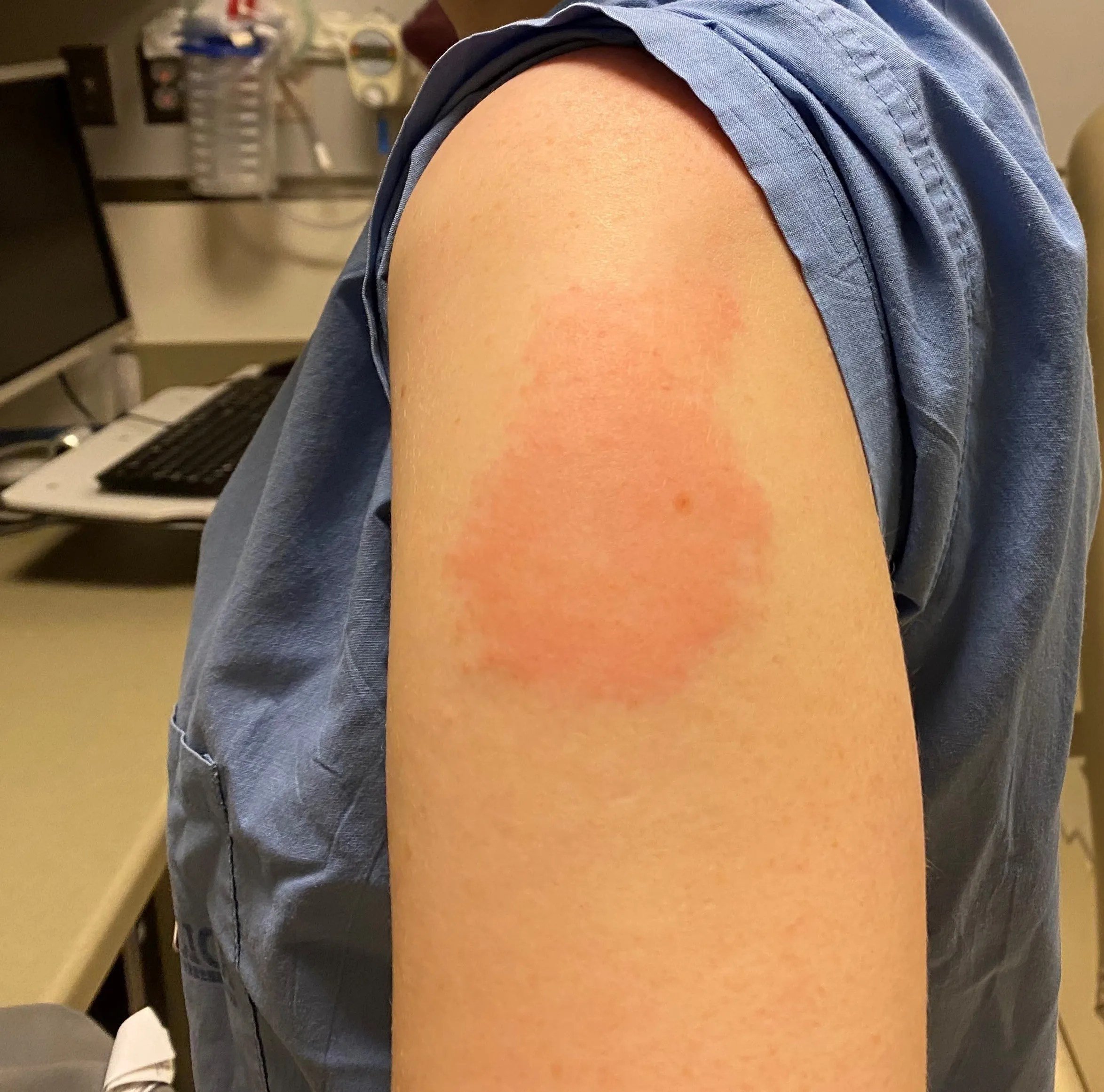
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
You May Like: Can You Get Shingles On Your Buttocks
What Are Dosages Of Zoster Vaccine Recombinant
Adult dosage
- Adults aged above 18 years: 0.5 mL IM x2 doses administered 1-2 months apart
- ACIP recommendation
- Administer 2 doses of recombinant zoster vaccine 2-6 months apart to adults aged above 50 years regardless of past episode of herpes zoster or receipt of zoster vaccine live as of November 2020, Zostavax is no longer marketed in the United States
- Administer 2 doses of RZV 2-6 months apart to adults who previously received ZVL at least 2 months after ZVL
- Current immunization schedules available at http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/index.html
- Limitations of Use
- Shingrix is not indicated for the prevention of primary varicella infection
Dosage Considerations Should be Given as Follows: