Counseling Patients About Shingrix
Know the benefits and side effects of Shingrix so youre prepared to talk with your patients before administering the vaccine.
What to tell patients about Shingrix benefits:
- You can protect yourself against shingles. Shingles is a very painful disease, and your risk of getting it increases as you age. Also, you are more likely to have severe, long-term pain if you get shingles when you are older. About 1 out of every 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime.
- Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and long-term pain from the disease. Two doses of Shingrix are more than 90% effective at preventing shingles. So its very important that you get this vaccine.
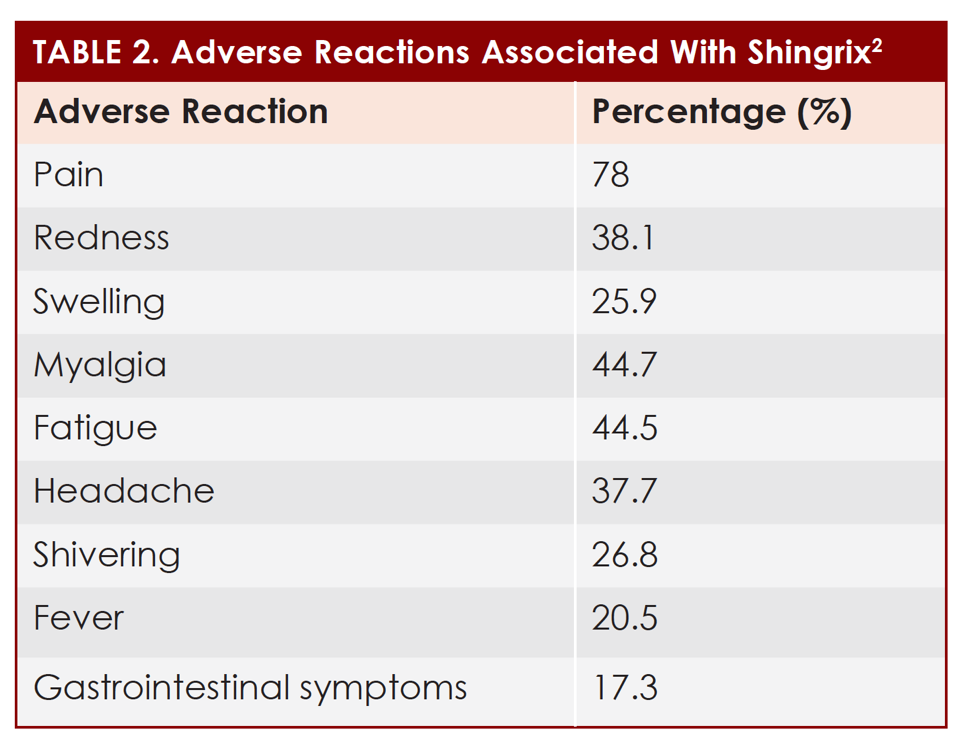
What to tell patients about Shingrix side effects:
What to tell patients about dose two:
- You need to come back in 2 to 6 months for your second dose. We can make that appointment now.
- Even if you have side effects from the first dose, it is important to get the second dose to build strong protection against shingles. Your reaction to each dose may be different just because you have a reaction to the first dose does not mean that you will have a reaction to the second.
What Is The Efficacy Of This Vaccine
The pivotal efficacy trial for the HZ vaccine included more than 38 500 adults 60 years of age and older. In that study, the vaccine reduced the incidence of shingles by 51% and the incidence of persistent, severe pain after shingles by 66%.9,13 For the average 69-year-old, the risk of shingles in the 5-year period after vaccination is expected to be reduced from 5.5% to 2.5% and the risk of PHN from 0.7% to about 0.25% .14
Does The Vaccine Work
In December 2017 Public Health England published an evaluation of the first three years of the shingles vaccination programme in England . This showed that the shingles vaccine was 62% effective against shingles and 70 to 88% effective against post-herpetic neuralgia in this period. Public Health England estimates that there were 17000 fewer GP consultations for shingles than expected in this 3-year period.
In the early 2000s researchers carried out a very large study of Zostavax, the shingles vaccine used in the UK, involving over 38,000 adults aged 60 or older. The results showed that:
- In adults aged between 60 and 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 51.3%
- In adults aged over 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 38%
- The vaccine reduced the incidence of post-herpetic neuralgia by over 66% in all age groups
- For those who did get shingles, the vaccine reduced the severity of the disease.
Read the abstract of this study , published in 2005 by Oxman et al.
Adults aged 80 or over are not offered the shingles vaccine. This is because the effectiveness of the vaccine declines with age in older age groups.
You May Like: Shingle Over Ridge Vent Installation
Vaccinating Patients With A Negative History Of Varicella Disease
Most adults are unlikely to have negative varicella serology even if they cannot recall having clinical varicella disease. Performing serology prior to vaccination is not routinely recommended.
If serology is known, and a patient is seronegative, injection site reactions may occur at a slightly higher rate, however immunisation is still safe and effective.
If patients are known to be seronegative, then they could receive a 2 dose course of varicella vaccine at least 4 weeks apart rather than Zostavax®.
If Youre 50 Or Older Get Shingrix
- Shingrix provides strong protection from shingles and long-term nerve pain.
- Get Shingrix even if you already had shingles, because you can get the disease more than once.
- Your risk of shingles and complications increases as you age.
- You need 2 doses of Shingrix. Get the second dose 2 to 6 months after you get the first dose.
You May Like: Pictures Of What Shingles Look Like
Know Your Risk Of Getting Shingles And Complications
About 1 out of every 3 people in the United States will develop shingles during their lifetime.
If youve had chickenpox, you are at risk for shingles. More than 99% of Americans born before 1980 have had chickenpox, even if they dont remember it.
Your risk of getting shingles and having serious complications increases as you get older.
About 1 in 10 people who get shingles develop nerve pain that lasts for months or years after the rash goes away. This is called postherpetic neuralgia and is the most common complication of shingles.
Shingles may lead to other serious complications involving the eye, including blindness. Very rarely, it can also lead to pneumonia, hearing problems, brain inflammation or death.
Read Also: When Do You Get The Second Shingles Shot
Rate Of Complications From Herpes Zoster
Overall, 1326% of patients with herpes zoster develop complications. Complications occur more often in older people and people who are immunocompromised.51,52
Post-herpetic neuralgia is the most common complication of herpes zoster, but it occurs very infrequently in children and young adults. PHN occurs in approximately 1 in 5 herpes zoster cases in people aged > 80 years, compared with approximately 1 in 10 cases in people aged 5059 years.4,5,9 The population-based incidence of PHN is 3 times higher in people 7079 years of age than in people 5059 years of age .4
You May Like: Where Does Shingles Show Up On The Body
What Do I Do If My Immunocompromised Patient Is Inadvertently Administered Zostavax
If an immunocompromised patient is inadvertently administered a dose of Zostavax®, prompt action is required. Medical review by an infectious diseases specialist or immunisation expert must be facilitated and the appropriate anti-viral therapy and monitoring commenced.
The error must also be reported to the relevant authority to ensure appropriate follow up and support can be provided. In Victoria, this service is SAEFVIC.
If the error occurs out of hours, seek specialist advice from the patients treating specialist or an infectious diseases specialist at your local tertiary hospital.
Contraindications To Zoster Vaccine Administration
The live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine is contraindicated in all significantly immunosuppressed patients regardless of the cause. Specific contraindications include the following: pregnancy or intent to become pregnant in 4 weeks after administration previous severe allergic reaction to the vaccine or any of its components active, untreated tuberculosis and severe immunosuppression . The only contraindications for RZV are known allergy to any component of the vaccine. For patients who are ineligible for live varicella or zoster vaccines, it is also important to note that acyclovir and valacyclovir prophylaxis are highly effective and safe in severely immunocompromised patients for prevention of varicella zoster.
James G. MarksJr MD, Jeffrey J. Miller MD, in, 2019
Recommended Reading: When Should You Get A Shingles Shot
Know The Benefits And The Side Effects
Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and long-term nerve pain. You may experience some short-term side effects because Shingrix causes a strong response in your immune system.
After getting Shingrix:
- Most people had a sore arm.
- Many people had redness and swelling where they got the shot .
- Many felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea.
About 1 out of 6 people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities like yardwork or swimming. Side effects usually go away after 2 to 3 days. Remember that the pain from shingles can last a lifetime, and these side effects should only last a few days.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Does Insurance Pay For Shingles Vaccine
Contraindications And Precautions For Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Shingrix should not be administered to:
- A person with a history of severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, to any component of this vaccine.
- A person experiencing an acute episode of herpes zoster. Shingrix is not a treatment for herpes zoster or postherpetic neuralgia . The general guidance for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
There is currently no CDC recommendation for Shingrix use in pregnancy therefore, providers should consider delaying vaccination until after pregnancy. There is no recommendation for pregnancy testing before vaccination with Shingrix. Recombinant vaccines such as Shingrix pose no known risk to people who are breastfeeding or to their infants. Providers may consider vaccination without regard to breastfeeding status if Shingrix is otherwise indicated.
Adults with a minor acute illness, such as a cold, can receive Shingrix. Adults with a moderate or severe acute illness should usually wait until they recover before getting the vaccine.
To learn more, see Contraindications and Precautions, General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices .
What Everyone Should Know About The Shingles Vaccine

Shingles vaccination is the only way to protect against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication from shingles.
CDC recommends that adults 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine called Shingrix to prevent shingles and the complications from the disease. Adults 19 years and older who have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix, as they have a higher risk of getting shingles and related complications.
Your doctor or pharmacist can give you Shingrix as a shot in your upper arm.
Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and PHN. In adults 50 years and older who have healthy immune systems, Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and PHN. Immunity stays strong for at least the first 7 years after vaccination. In adults with weakened immune systems, studies show that Shingrix is 68%-91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on the condition that affects the immune system.
Also Check: Why Does One Get Shingles
Itchy Skin Near The Injection Site
Itchy skin, also called pruritus, can potentially occur near the injection site after receiving Shingrix. Itching, swelling, and redness arent usually a huge cause for concern, as they often occur together as a localized reaction.
Applying Benadryl gel or hydrocortisone cream around the injection area can help reduce itchy, swollen, or red skin. If the itching worsens or spreads away from the injection site, get in touch with your doctor.
How Cdc Monitors Vaccine Safety
CDC and FDA monitor the safety of vaccines after they are approved or authorized. If a problem is found with a vaccine, CDC and FDA will inform health officials, health care providers, and the public.
CDC uses 3 systems to monitor vaccine safety:
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System : an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and FDA, to monitor for potential vaccine safety problems. Anyone can report possible vaccine side effects to VAERS.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink : a collaboration between CDC and 9 health care organizations that conducts vaccine safety monitoring and research.
- The Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project: a partnership between CDC and several medical research centers that provides expert consultation and conducts clinical research on vaccine-associated health risks.
Also Check: Is It Possible To Have A Mild Case Of Shingles
How To Pay For Shingrix
Commercial insurance covers about 96% of insured people for the Shingrix vaccine. Most people with private insurance will pay under $5 for each dose.
Programs like Medicaid cover Shingrix in certain states. Medicare Parts A and B do not cover the shingles vaccine. But individuals covered under Medicare prescription drug plans, or Part D, will have their vaccines covered.
For people who do not have access to insurance, there are a number of vaccine assistance programs and affordable health coverage options available. Many of these programs provide vaccines at little or no cost.
Who Should Get The Shingles Vaccine
The CDC recommends it for healthy adults over the age of 50, but the FDA has approved Shingrix for people 18 and older who are or who will be at increased risk of shingles due to immunodeficiency or immunosuppression caused by known disease or therapy. This includes those who have already had shingles, which you can have more than once. Vaccination lowers the chances of a second round of the painful rash and of a serious outbreak and complications, Kistler says.
Thatâs why Duncan Isley, who had shingles at 45, recently got vaccinated. The outbreak he had was âfairly mildâ compared with the stories heâs heard from others. But itâs something he doesnât want to repeat.
âI had the classic torso rash and back pain. It was a very painful experience to be sure, and I still have some lingering, minor nerve sensations from time to time,â says Isley, who is now 53 and lives in Durham, NC. âI tell my close friends they should get vaccinated.â
You should also get vaccinated with Shingrix if you got an older shingles vaccine called Zostavax, which was withdrawn from the market in 2020. Zostavaxâs protection wears off with time, says Kathleen Dooling, MD, MPH, a medical officer and shingles disease expert at the CDC.
In the first year after vaccination, Zostavax prevented shingles about 60% of the time. âThat decreases in subsequent years, so that after a number of years itâs not clear that the vaccine is providing any protection,â she says.
Also Check: Is There Any Cure For Shingles
How Long After Ive Received The Shingles Vaccine Am I Contagious
With the currently authorized shingles vaccine, Shingrix, you wont be contagious. The old vaccine, Zostavax, used a weakened form of the live varicella-zoster virus. Therefore, people worried about spreading the disease to the people around them.
Shingrix doesnt use a live version of the varicella-zoster virus. It is inactivated, which means it uses a dead version of the virus. Therefore, you have no risk of transmitting the disease to anyone.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
No one likes to get shots, especially for something youve already been vaccinated for. But the newer version of the shingles vaccine is one youll want to offer up your arm for. The Shingrix vaccine is more than 90% effective at helping you prevent shingles. Since most of us have had chickenpox in the past, the shingles vaccine is an easy way to prevent the dormant chickenpox virus from creeping up and hitting you again with shingles.
Who Should Be Immunised
Zostavax® is registered for use in Australia as a single dose from 50 years of age for the prevention of zoster . It is recommended for immunocompetent adults aged over 60 years. Zostavax® is funded on the National Immunisation Program for people aged 70 years, with a catch up program for people aged 71-79-years . It is also available for private purchase for patients wishing to be immunised outside of this funded age group. There is currently no recommendations for booster doses when early vaccination is given.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Risks Of The Shingles Vaccine
New Shingles Vaccine: What You Need To Know
Nov. 13, 2019 — Unlike some vaccines, thereâs been so much demand for the new shingles vaccineShingrix that itâs not always easy to find. It was approved in 2017, and the CDC recommends the vaccine for adults 50 and older to prevent this painful, blistering illness. It is being used in place of the previous vaccine, Zostavax.
More than a year later, doctors say they are learning more about how it works, its safety risks, and how it compares to Zostavax.
How effective is Shingrix?
âIt’s just remarkable,” says Wilbur Chen, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “It has performed better than I expected.”
In studies, Shingrix was more than 97% effective at preventing shingles in people 50 and older. It works just as well in older adults, who are at greater risk for a painful shingles complication called postherpetic neuralgia . “When 70- and 80-year-olds get shingles, it can be extremely debilitating,” Chen says.
By contrast, Zostavax cuts the risk of shingles by only 51% and PHN by 67%. It’s only about 38% effective in people over age 70.
How safe is Shingrix?
“So far so good,” Schaffner says. The main side effect is soreness in the arm where you get the shot.
Other side effects are mild and usually last for 2 to 3 days, including:
Who shouldn’t get Shingrix?
Can I get the Shingrix vaccine now?
What do doctors still need to learn about Shingrix?