Who Should Not Be Vaccinated With Shingrix
You shouldnt receive the Shingrix vaccine if you:
- Have ever had a severe allergy to this vaccine or any ingredient in this vaccine.
- Are breastfeeding or pregnant.
- Currently have shingles.
- Are ill and have a high fever.
- Have tested negative for immunity to varicella-zoster virus .
Ask your healthcare provider if the benefits of getting the vaccine outweigh any potential risks.
What Can Be Done To Prevent The Spread Of Shingles
A vaccine for chickenpox is available and it is hoped that individuals immunized against chickenpox will be less likely to develop shingles in later life.
The risk of spreading the virus that causes shingles is low if the rash is covered. People with shingles should keep the rash covered, not touch or scratch the rash, and wash their hands often to prevent the spread of shingles. Once the rash has developed crusts, the person is no longer contagious.
What Are The Symptoms
The first sign of shingles is often burning, sharp pain, tingling, or numbness in your skin on one side of your body or face. The most common site is the back or upper abdomen. You may have severe itching or aching. You also may feel tired and ill with fever, chills, headache, and upset stomach or belly pain.
One to 14 days after you start feeling pain, you will notice a rash of small blisters on reddened skin. Within a few days after they appear, the blisters will turn yellow, then dry and crust over. Over the next 2 weeks the crusts drop off, and the skin continues to heal over the next several days to weeks.
Because shingles usually follows nerve paths, the blisters are usually found in a line, often extending from the back or side around to the belly. The blisters are almost always on just one side of the body. Shingles usually doesn’t cross the midline of the body. The rash also may appear on one side of your face or scalp. The painful rash may be in the area of your ear or eye. When shingles occurs on the head or scalp, symptoms can include headaches and weakness of one side of the face, which causes that side of the face to look droopy. The symptoms usually go away eventually, but it may take many months.
In some cases the pain can last for weeks, months, or years, long after the rash heals. This is called postherpetic neuralgia.
Read Also: How Long Does Pain Last After Shingles
Why Doesnt Having Chickenpox Earlier In Life Provide Immunity Against Having Shingles Later
After having chickenpox, your body doesnt rid your system of the virus. Instead, the virus stays in a portion of the spinal nerve root called the dorsal root ganglion. In most people, the virus simply stays there quietly and doesnt cause problems. Scientists arent always sure why the virus gets active again, but they know stress can be a cause.
How Long Does A Shingles Outbreak Last
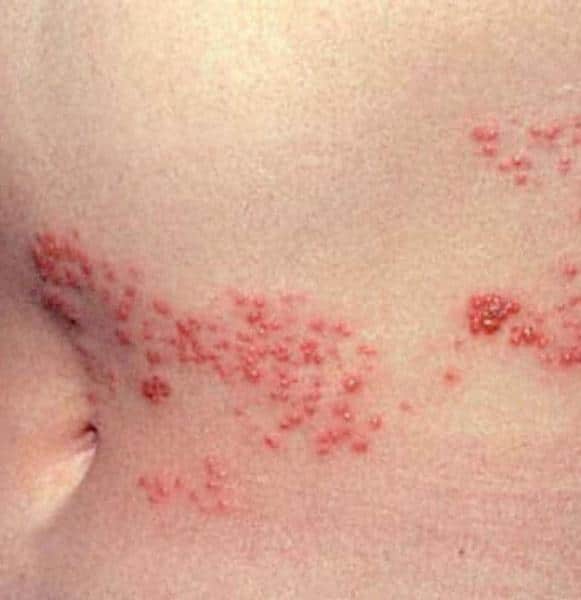
It can take three to five weeks from the time you begin to feel symptoms until the rash totally disappears.
You May Like: Is It Possible To Have Shingles Without Pain
Key Difference Shingles Vs Herpes
Shingles and herpes are two infectious disease conditions caused by viruses. The key difference between shingles and herpes is that shingles is caused the varicella zoster virus but herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus. After the initial infection, varicella zoster virus can remain dormant in the dorsal root ganglia of sensory nerves and get reactivated whenever the persons immunity weakens. The reactivation of the varicella zoster virus in this manner is called shingles. Herpes is the infection that is caused by Herpes Simplex Virus .
What Are The Symptoms Of Shingles
Early symptoms of shingles may include:
Other signs and symptoms that appear a few days after the early symptoms include:
- An itching, tingling or burning feeling in an area of your skin.
- Redness on your skin in the affected area.
- Raised rash in a small area of your skin.
- Fluid-filled blisters that break open then scab over.
- Mild to severe pain in the area of skin affected.
Also Check: What To Avoid When You Have Shingles
Risk Factors For Shingles
Anyone who has had chickenpox is at risk for shingles later in life. Certain factors increase the risk for such outbreaks.
The Aging Process
The risk for herpes zoster increases as people age. Postherpetic neuralgia is persistent nerve pain and is the most common severe complication of shingles. The risk for PHN also increases after age 50.
Immunosuppression
Chronic medical conditions that weaken the immune system increase the risk for shingles and for getting shingles at a younger age. These conditions may include:
- Cancer, especially Hodgkin disease and lymphomas, and treatments such as bone marrow transplant.
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and inflammatory bowel disorders.
- Type 1 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma.
Sometimes, the drugs used to treat these conditions suppress the immune system and increase the risk for shingles. Drug treatments that may increase risk include:
- Immune suppressing drugs used for treating autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Crohn disease, and ulcerative colitis. These medications include disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs , steroids, and biologic drugs such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
- Immune-suppressing drugs given after organ or bone marrow transplantation.
- Prednisone and other corticosteroids if they are used for extended periods of time.
- Protease inhibitors used for treatment of AIDS.
Signs And Symptoms Of Chickenpox
The symptoms of chickenpox usually last approximately four to seven days the most common symptom is an itchy, painful rash with fluid-filled vesicles, or blisters, that turn into scabs. The rash often breaks out on the chest first, then it may spread to other areas of the body .
It typically takes about seven days for all the blisters to turn into scabs. Eventually, much of the skin may be entirely covered with blisters and scabs.
Symptoms that often occur a day or two before the rash starts to develop include:
Note: In children, the rash is usually the initial sign of the disease, and symptoms such as fatigue and loss of appetite often do not occur before the rash breaks out.
Verywell
Also Check: Can Shingles Break Out On Both Sides Of The Body
Who Is At Risk For Getting Shingles
People who have had chickenpox who are more likely to develop shingles include those:
- With a weakened immune system .
- Over the age of 50.
- Who have been ill.
- Who have experienced trauma.
- Who are under stress.
The chickenpox virus doesnt leave your body after you have chickenpox. Instead, the virus stays in a portion of your spinal nerve root called the dorsal root ganglion. For the majority of people, the virus stays there quietly and doesn’t cause problems. Researchers aren’t always sure why the virus gets reactivated, but this typically occurs at times of stress.
Can You Get Chickenpox If You’ve Been Vaccinated
Yes. About 15% 20% of people who have received one dose of varicella vaccine do still get chickenpox if they are exposed, but their disease is usually mild. Vaccinated persons who get chickenpox generally have fewer than 50 spots or bumps, which may resemble bug bites more than typical, fluid-filled chickenpox blisters. In 2006, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend routine two-dose varicella vaccination for children. In one study, children who received two doses of varicella vaccine were three times less likely to get chickenpox than individuals who have had only one dose.
Also Check: Should I Get A Shingles Shot Every Year
What Laboratory Studies Should You Order And What Should You Expect To Find
Results consistent with the diagnosis
-
Serologic tests can show primary seroconversion for HSV-1 or HSV-2 infection however, it does not definitively diagnose active disease.
Results that confirm the diagnosis
-
Tzank smear: Scraping of the base of an early unroofed blister can demonstrate virally infected multinucleated epithelial giant cells.
-
Tissue biopsy: Biopsy can show virally infected multinucleated epithelial giant cells.
-
Viral tissue culture: This may be positive within 48 hours and can allow for resistance testing if needed.
-
HSV deoxyribonucleic acid detection: Gene amplification by PCR, ligase chain reaction, or other methods can be done on skin lesions or cerebral spinal fluid .
-
Direct fluorescent antibody: Cells scraped from the base of an early unroofed blister are stained with a direct fluorescent antibody.
Which Individuals Are Of Greater Risk Of Developing Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
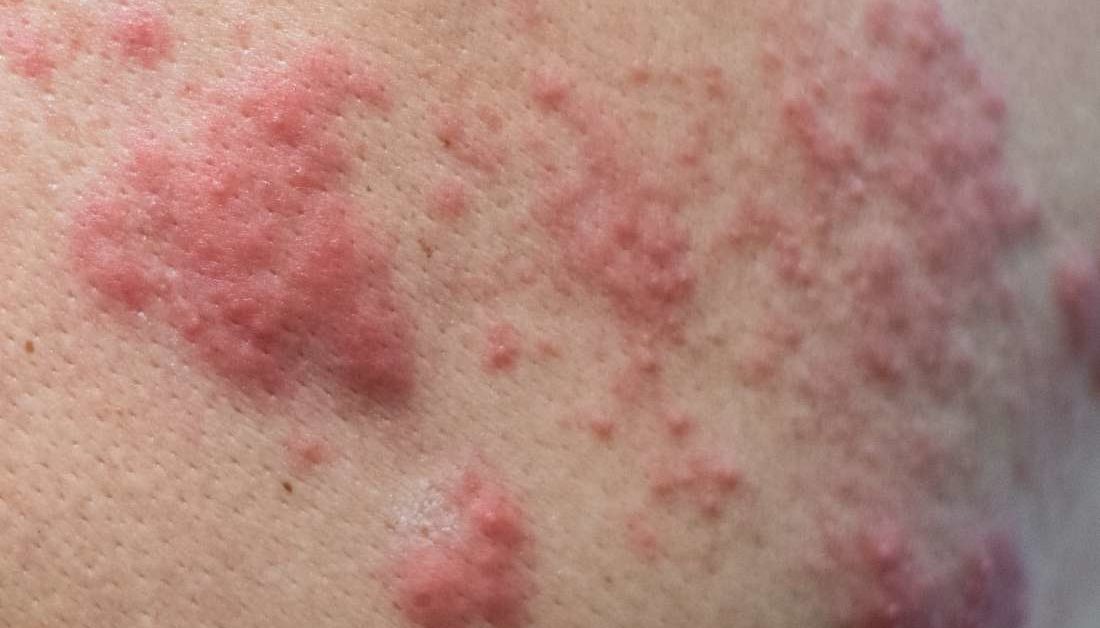
-
Oral disease is commonly acquired in childhood and 90% of young adults are HSV-1 antibody positive.
-
Risk factors for acquiring genital disease are age 15 to 30 years, increased number of sexual partners, black or Hispanic race, and HIV positivity.
-
As the cluster of differentiation 4 count decreases in patients with HIV , prevalence of active herpes simplex virus infection increases.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Shingles On The Scalp
Specific Complications Of Shingles
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is pain that persists for longer than a month after the onset of herpes zoster. It is the most common severe complication of shingles. Risk factors for PHN include:
- Age. PHN usually affects people with herpes zoster who are over 60 years old. The older a person is the longer PHN is likely to last. It rarely occurs in people under age 40.
- Gender. Some studies suggest that women may be at slightly higher risk for PHN than men.
- Severe or complicated shingles. People who had prodromal symptoms or a severe attack during the initial shingles episode are also at high risk for PHN. People whose eyes have been affected also have increased risk for PHN.
Skin Infections
If the blistered area is not kept clean and free from irritation, it may become infected with group A Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria. If the infection is severe, scarring can occur.
In very rare cases, herpes zoster is associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome, an extensive and serious condition in which widespread blisters cover mucous membranes and large areas of the body.
Eye Infections
If shingles occurs in the face, the eyes are at risk, particularly if the path of the infection follows the side of the nose. If the eyes become involved , a severe infection can occur that is difficult to treat and can threaten vision. People with HIV/AIDS may be at particular risk for a chronic infection in the cornea of the eye.
Neurological Complications
How Is Postherpetic Neuralgia Treated
Treatments include lotions or creams and/or other medications not specifically used for pain, such as antidepressants or drugs for epilepsy. Regular pain relievers are not usually effective for this type of pain.
If your pain doesnt lessen, you might try therapies like nerve blocks or steroid injections near the area where the nerves exit the spine. Your provider might suggest an implantable nerve stimulator device for severe, ongoing pain that hasnt responded to other treatments.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Shingles On Your Body
Why Does Shingles Appear Mostly On One Side Or In One Area Of Your Body
The virus travels in specific nerves, so you will often see shingles occur in a band on one side of your body. This band corresponds to the area where the nerve transmits signals. The shingles rash stays somewhat localized to an area. It doesnt spread over your whole body. Your torso is a common area, as is your face.
Shingles Disease And How To Protect Against It
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash that develops on one side of the face or body. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus , the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who has had chickenpox in the past can get shingles because VZV remains in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. VZV can reactivate many years later, causing shingles.
Shingles is more common in older adults, people who have medical conditions that weaken the immune system, and people who take medications that suppress their immune systems. Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles.
Don’t Miss: Who Pays For Shingles Vaccine
How Is Chickenpox Spread
Chickenpox is spread through direct contact with an infected individual as well as airborne droplets. Varicella-zoster is the virus that causes chickenpox. It takes about 14 to 16 days before someone starts showing symptoms of chickenpox after coming into contact with varicella-zoster.
Unvaccinated individuals living in crowded areas are especially at risk for spreading and contracting chickenpox. Individuals with a weakened immune system and those who live in poorly sanitized areas without access to clean and nutritious food are also at risk of contracting chickenpox as well as other communicable diseases.
Summary And Quick Facts For Herpes And Shingles
- Herpes and shingles are both caused by members of the Herpesviridae family of viruses, which can establish latent infections that remain dormant before reactivating at a later time under certain conditions. Herpes simplex virus-1 and herpes simplex virus-2 cause oral and genital herpes, and varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children and shingles later in life.
- In this protocol, you will learn about the viruses that cause herpes and shingles, and how these infections are conventionally treated. Several natural ingredients that may help ease the symptoms of herpes and shingles will also be discussed, and important lifestyle and dietary considerations that can help prevent outbreaks will be examined as well.
- Antiviral medication is the standard treatment for both shingles and herpes. Although there is no effective cure for herpes virus infections, several natural interventions may help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Herpes and shingles are both caused by members of the Herpesviridae family of viruses, which can establish latent infections that remain dormant and then reactivate under certain conditions. Herpes simplex virus-1 and herpes simplex virus-2 cause oral and genital herpes, and varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox in children and shingles later in life.
You May Like: Why Does One Get Shingles
Are There Complications
The most common complication of chicken pox is cellulitis , an infection of the skin caused by bacteria, such as streptococci and staphylococci . Skin irritation from repeatedly scratching pox sores allows the bacteria to invade the skin. In some cases, varicella infection can spread to the lungs causing pneumonia. Newborn babies, teens, and adults are more likely to develop this complication. Even in healthy people, chicken pox pneumonia can be dangerous and may be fatal. Adults are also more at risk of other serious but rare complications, including liver and kidney disease and encephalitis . If a woman becomes infected with chicken pox early in her pregnancy, the virus can cause in the baby. In the final stages of pregnancy, a mothers chicken pox can cause a life-threatening infection in her baby. Left untreated, a shingles rash anywhere near the eye can spread to the eye. If the becomes involved, temporary or permanent blindness can result. More serious widespread infection from chicken pox or shingles can occur in anyone with a weakened immune system .
How Is Shingles Spread
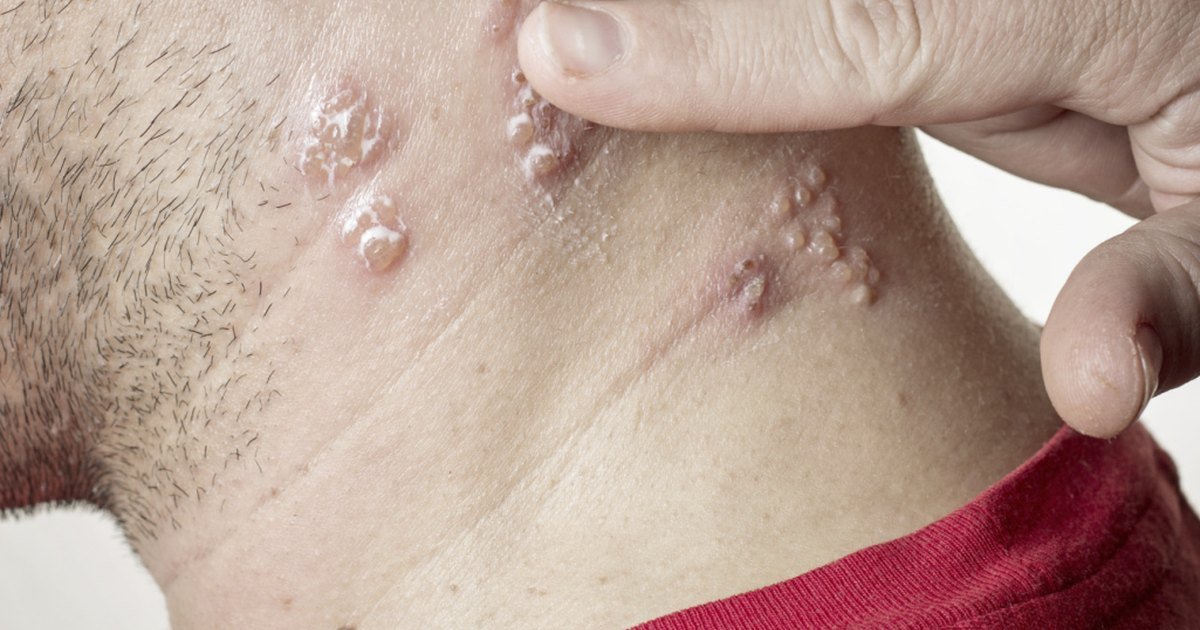
A person must have already had chickenpox in the past to develop shingles. A person cannot get shingles from a person that has shingles. However, the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles can be spread from a person with active shingles to a person who has never had chickenpox or had the chickenpox vaccine. The person exposed to the virus would develop chickenpox, not shingles. A person with shingles can spread the virus when the rash is in the blister-phase. The blister fluid is filled with virus particles. The virus is spread through direct contact with the rash or through breathing in virus particles that get mixed in the air. Once the rash has developed crusts, the person is no longer contagious. A person is not infectious before blisters appear or if pain persists after the rash is gone .
You May Like: What Is The Best Doctor To See For Shingles
What Are The Complications Of Shingles
After the shingles rash has disappeared, you might continue to have nerve pain in that same area. Postherpetic neuralgia can last for months or years and become quite severe.
More than 10% of people who get shingles develop postherpetic neuralgia. Researchers dont know why some people get postherpetic neuralgia and others dont. It may be that nerves become more sensitive or that the virus may be invading and damaging the central nervous system.
Other complications include:
- Other types of nerve issues like numbness or itching.
- A bacterial infection of the shingles rash.
- Eye and ear inflammation if the rash is near these organs.
How Can I Take Care Of Myself
- Take a pain-relief medicine such as acetaminophen. Take other medicine as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Put cool, moist washcloths on the rash.
- Rest in bed during the early stages if you have fever and other symptoms.
- Try not to let clothing or bed linens rub against the rash and irritate it.
- You develop worsening pain or fever.
- You develop a severe headache, stiff neck, hearing loss, or changes in your ability to think.
- The blisters show signs of bacterial infection, such as increasing pain or redness, or milky yellow drainage from the blister sites.
- The blisters are close to the eyes or you have pain in your eyes or trouble seeing.
- You have trouble walking.
You May Like: How Contagious Is Shingles Virus