When Should I See A Doctor Because Of The Side Effects I Experience From Shingrix
Shingrix causes a strong response in your immune system, so it may produce short-term side effects. These side effects can be uncomfortable, but they are expected and usually go away on their own in 2 or 3 days. You may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Contact your healthcare provider if the symptoms are not improving or if they are getting worse.
In clinical trials, Shingrix was not associated with serious adverse events. In fact, serious side effects from vaccines are extremely rare. For example, for every 1 million doses of a vaccine given, only one or two people might have a severe allergic reaction. Signs of an allergic reaction happen within minutes or hours after vaccination and include hives, swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, or weakness. If you experience these or any other life-threatening symptoms, see a doctor right away.
Is It Possible To Get Shingles Twice
Most people who get shingles only experience it one time in their lives. However, it is possible to get shingles more than once . This is known as recurrent shingles. Getting vaccinated can help minimize the chance that this will happen.
These are only a few of the many questions people may have about Shingrix. To learn more about the vaccine and shingles, individuals can consult a medical professional.
Vaccination Of Immunocompromised Adults 19 Years And Older
CDC recommends two doses of RZV for the prevention of shingles and related complications in adults aged 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy. The second dose of RZV should typically be given 26 months after the first. However, for persons who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed and who would benefit from completing the series in a shorter period, the second dose can be administered 12 months after the first. For more detailed clinical guidance see .
You May Like: Where Can You Get The Shingles Vaccine
Common Questions About The Shingles Vaccine Answered Here
National Library of Medicine
Heres an interesting email from my friend and ID-colleague Dr. Carlos Del Rio :
Went Tuesday to see my PCP for a routine visit and had my second dose of Shingrix that day. I had gotten my first dose about 3 months ago and had severe chills and even a fever of 38.5 after the first dose. With the second dose the response was not as severe but did have chills and rigors for about 18 hrs. Stupid of me, but the next day I went to get my labs checked, and everything was fine except my HS-CRP which was 14.72 .
Anyway..Shingrix is a good vaccine but it is a tough one to take and really gives you a nice TNF storm!
For the few of you out there in ID-World who dont know him, you must understand it takes quite the force to slow down the high-energy machine that is Carlos. He is the very definition of indefatigable. So its not surprising he told me he went to work after both shots, rigors and all.
But Carlos post-shingles vaccine experience reminds me that were now two years into the recombinant zoster vaccine era, and that immunization for this common adult infection shingles, or zoster has brought with it all sorts of new questions.
So here are a bunch of common ones we ID doctors field on a regular basis:
But lets go back to Carlos for a moment, and how these side effects he experienced compare to herpes zoster:
And to be clear, Shingrix side effects way milder than having shingles!
And look, my colleagues agree:
For Patients Who Do Not Report A Prior Episode Of Varicella
When vaccinating immunocompetent adults aged 50 years and older, there is no need to screen for a history of varicella or to conduct laboratory testing for serologic evidence of prior varicella. More than 99% of adults aged 50 years and older worldwide have been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices considers people born in the United States prior to 1980 immune to varicella. Therefore, even if a person does not recall having chickenpox, serologic testing for varicella immunity is not recommended. It is often a barrier to herpes zoster vaccination, and false negatives are common. However, if serologic evidence of varicella susceptibility becomes available to the healthcare provider, providers should follow ACIP guidelines for varicella vaccination. Shingrix has not been evaluated in persons who are seronegative to varicella, and it is not indicated for the prevention of varicella.
For adults 19 years of age and older who are or will be immunocompromised, see .
You May Like: How To Administer Shingles Vaccine
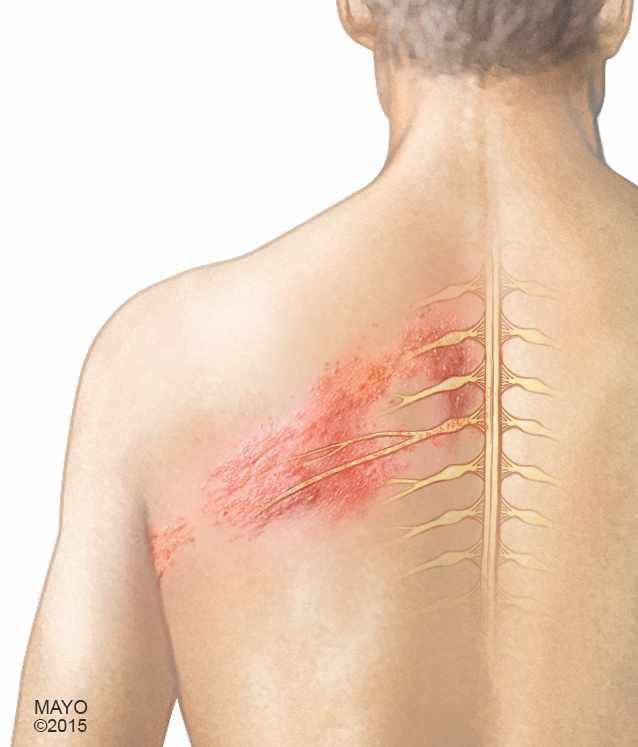
Shingles Can Strike Twice Will The Shingles Vaccine Help
No one who has experienced the burning, stabbing, painful misery of shingles wants to think about it again. But they should. Why? Because shingles can strike twice, or rarely, even a third time. A shingles vaccine can reduce the chances of a recurrence.
Theres some disagreement about how often recurrence occurs. In one study, researchers examined medical records of nearly 1,700 patients who had a documented case of shingles between 1996 and 2001. They found that more than 5% of these patients were treated for a second episode within an average of eight years. Thats about as likely as getting shingles in the first place if youre age 60 or older. Other studies have shown the recurrence rate to be much lower.
But the bottom line is the same: having shingles once doesnt protect you from ever having it again.
What Are The Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
Most side effects of the shingles vaccine are mild and typically last only 2 to 3 days.
One of the most common side effects of the shingles vaccine is an injection site reaction. This can include redness, swelling, or soreness where you got your shot.
Other side effects can include:
- muscle aches and pains
Side effects felt throughout your body are typically more common after receiving the second and booster doses of the COVID-19 vaccine. Like the shingles vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine side effects typically last only a couple of days.
When COVID-19 and flu circulate at the same time, it has the potential to cause many people to become ill and overburden the healthcare system. As such, its essential to receive both COVID-19 and flu vaccines.
Its safe to receive your COVID-19 and flu vaccine at the same time.
Though were still learning more about giving the COVID-19 vaccine with other vaccines, a found no safety concerns when the COVID-19 and flu vaccine were given at the same time. Also, participants produced expected antibody responses to both vaccines.
The CDC that all people ages 6 months and older get a flu vaccine. The flu vaccine can help prevent illness and reduce the risk of serious flu-related complications in vulnerable individuals, such as:
Also Check: How Long Before Shingles Rash Appears
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Who Should Not Get The Vaccine
It is safe for most people to get two doses of Shingrix. However, you should talk to your healthcare provider before getting the shingles vaccine if:
- You are pregnant
- You have severe allergies to any of the Shingrix ingredients
- You have ever experienced a severe allergic reaction to Shingrix
If you have a mild sickness, such as a cold, its usually safe to get the shingles vaccine. If you are moderately or severely ill, you should wait until you feel better to get your next dose of Shingrix.
You should still get the shingles vaccine if you dont remember having the chickenpox virus in the past and if youve had shingles previously. Shingrix can protect you against developing shingles again in the future.
You May Like: What Do You Do When You Have Shingles
Contraindications And Precautions For Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Shingrix should not be administered to:
- A person with a history of severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, to any component of this vaccine.
- A person experiencing an acute episode of herpes zoster. Shingrix is not a treatment for herpes zoster or postherpetic neuralgia . The general guidance for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
There is currently no CDC recommendation for Shingrix use in pregnancy therefore, providers should consider delaying vaccination until after pregnancy. There is no recommendation for pregnancy testing before vaccination with Shingrix. Recombinant vaccines such as Shingrix pose no known risk to people who are breastfeeding or to their infants. Providers may consider vaccination without regard to breastfeeding status if Shingrix is otherwise indicated.
Adults with a minor acute illness, such as a cold, can receive Shingrix. Adults with a moderate or severe acute illness should usually wait until they recover before getting the vaccine.
To learn more, see Contraindications and Precautions, General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices .
What You Should Know About The New Shingles Vaccine
Shingles vaccination is the only way to protect against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication from shingles.
CDC recommends that healthy adults 50 years and older get two doses of the shingles vaccine called Shingrix , separated by 2 to 6 months, to prevent shingles and the complications from the disease. Your doctor or pharmacist can give you Shingrix as a shot in your upper arm.
Shingrix provides strong protection against shingles and PHN. Two doses of Shingrix is more than 90% effective at preventing shingles and PHN. Protection stays above 85% for at least the first four years after you get vaccinated. Shingrix is the preferred vaccine, over Zostavax® , a shingles vaccine in use since 2006. Zostavax may still be used to prevent shingles in healthy adults 60 years and older. For example, you could use Zostavax if a person is allergic to Shingrix, prefers Zostavax, or requests immediate vaccination and Shingrix is unavailable.
You May Like: What Is The Best Doctor To See For Shingles
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Why Do I Need Two Doses Of Shingrix
In addition to a painful rash, shingles can lead to serious health complications like PHN, pneumonia, vision loss, hearing problems, and encephalitis . Research indicates that about 1% to 4% of people with shingles will be hospitalized.
Two doses of Shingrix offer effective protection against shingles and related complications for at least seven years. Among healthy adults ages 50-69, Shingrix is more than 90% effective in preventing PHN when two doses are administered. Among adults ages 70 and older, it is 89% effective.
Also Check: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Chest
Who Shouldnt Get The Shingles Vaccine
You shouldnt receive the shingles vaccine if:
- Youve had a previous severe allergic reaction to Shingrix or any of its ingredients.
- Youre pregnant or breastfeeding.
- You have no immunity to chickenpox, which means you should get the chickenpox vaccine instead.
Having a mild illness like a cold isnt a reason to not get your shingles vaccine.
However, if you have a moderate to severe illness or a fever of 101.3 or higher, you should recover before getting your shingles vaccine.
state that the COVID-19 vaccine may be given without regard to the timing of other vaccines.
This means you dont have to wait to receive your COVID-19 and shingles vaccinations.
In fact, you can get your COVID-19 vaccine and shingles vaccine at the same time. If you choose to do this, make sure to receive your injections at two different sites.
Who Should Get Zostavax
People 60 years of age or older should get shingles vaccine . They should get the vaccine whether or not they recall having had chickenpox, which is caused by the same virus as shingles. Studies show that more than 99% of Americans aged 40 and older have had chickenpox, even if they dont remember getting the disease. There is no maximum age for getting shingles vaccine.
Two vaccines are licensed and recommended to prevent shingles in the U.S.. Zoster vaccine live has been in use since 2006. Recombinant zoster vaccine , has been in use since 2017 and is recommended by ACIP as the preferred shingles vaccine.
Even if you have had shingles, you can still receive shingles vaccine to help prevent future occurrences of the disease. There is no specific length of time you must wait after having shingles before receiving shingles vaccine, but generally you should make sure the shingles rash has disappeared before getting vaccinated. The decision on when to get vaccinated should be made with your healthcare provider.
Talk with your healthcare provider if you have questions about shingles vaccine. Shingles vaccine is available in doctors offices and pharmacies. To find doctors offices or pharmacies near you that offer the vaccine, visit Zostavax or HealthMap Vaccine Finder.
You May Like: When To Get Shingles Vaccine
How To Pay For Shingrix
Commercial insurance covers about 96% of insured people for the Shingrix vaccine. Most people with private insurance will pay under $5 for each dose.
Programs like Medicaid cover Shingrix in certain states. Medicare Parts A and B do not cover the shingles vaccine. But individuals covered under Medicare prescription drug plans, or Part D, will have their vaccines covered.
For people who do not have access to insurance, there are a number of vaccine assistance programs and affordable health coverage options available. Many of these programs provide vaccines at little or no cost.
What Is The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine can protect you against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , which is the most common complication of shingles. Shingles is a painful rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. The rash usually develops on one side of your body or face. It starts with red bumps and then the bumps turn into fluid-filled blisters.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Shingles Show Up On The Body
Will There Be Any Side Effects From The Shingles Vaccination
There are 2 shingles vaccines: Zostavax and Shingrix .
With both vaccines it’s quite common to get redness and discomfort at the vaccination site, headaches and fatigue, but these side effects should not last more than a few days. See a GP if you have side effects that last longer than a few days, or if you develop a rash after having the shingles vaccination.
Read more about the shingles vaccine side effects.
How Well Does Zostavax Work
Zostavax®, the shingles vaccine, reduced the risk of shingles by 51% and the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia by 67% based on a large study of more than 38,000 adults aged 60 years or older. Protection from shingles vaccine lasts about 5 years.
While the vaccine was most effective in people 60 through 69 years old, it also provides some protection for people 70 years old and older.
Adults vaccinated before age 60 years might not be protected later in life when the risk for shingles and its complications are greatest.
You May Like: How Often Can You Have Shingles
How Do You Catch Shingles
You do not “catch” shingles it comes on when there’s a reactivation of chickenpox virus that’s already in your body.
After you’ve recovered from chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus lies dormant in your nerve cells and can reactivate at a later stage when your immune system is weakened.
Anyone who has had chickenpox can get shingles.
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
You May Like: Are Shingles Itchy At First
Nosocomial Transmission Of Vzv
Nosocomial transmission of VZV is well-recognized and can be life threatening to certain groups of patients. Reports of nosocomial transmission are uncommon in the United States since introduction of varicella vaccine.
Patients, healthcare providers, and visitors with varicella or herpes zoster can spread VZV to susceptible patients and healthcare providers in hospitals, long-term-care facilities, and other healthcare settings. In healthcare settings, transmissions have been attributed to delays in the diagnosis or reporting of varicella and herpes zoster and failures to implement control measures promptly.
Although all susceptible patients in healthcare settings are at risk for severe varicella and complications, certain patients without evidence of immunity are at increased risk:
- Premature infants born to susceptible mothers
- Infants born at less than 28 weeks gestation or who weigh 1000 grams, regardless of maternal immune status
- Immunocompromised people, including those who are undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, have malignant disease, or are immunodeficient