How Much Does The Shingles Vaccine Cost With Medicare
Shingles vaccines can be expensive, costing up to $300 per dose without insurance. Having Medicare Part D may help you avoid paying full price, but your out-of-pocket cost will depend on the plan and its deductibles, copays, or coinsurance.
The cost of the shingles vaccine with Medicare depends on the coverage you have and the stage of coverage youre in, but the majority of patients pay less than $50 per dose,according to GSK. If your deductible has already been met, your shingles shot may be free.
Another cost factor is where you get vaccinated. People who choose an in-network pharmacy or a doctors office that coordinates with or can bill their Part D plan directly will pay less. If your doctors office does not coordinate with or bill Part D plans directly, you may be billed for the entire cost of the shingles shot and have to seek reimbursement from your plan later. Reimbursements may not equal the total amount you paid in advance.
Other insurance plans, including private insurance and Medicaid, may cover the shingles vaccine with no out-of-pocket costs. Contact your insurance company for more information and coverage details.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Shingles Disease
Shingrix Dosage And Schedule
Shingrix should be administered to immunocompetent adults aged 50 years and older and adults aged 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy as a two-dose series , 2 to 6 months apart . However, for persons who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed and who would benefit from completing the series in a shorter period, the second dose can be administered 12 months after the first. See more detailed clinical guidance.
If more than 6 months have elapsed since the first dose of Shingrix, you should administer the second dose as soon as possible. However, you do not need to restart the vaccine series.
If the second dose is given less than 4 weeks after the first dose, the second dose should be considered invalid. A valid second dose should be administered 2 months after the invalid dose .
Donât Miss: Why Is The Shingles Vaccine Not Covered By Medicare
Contraindications And Precautions For Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Shingrix should not be administered to:
- A person with a history of severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, to any component of this vaccine.
- A person experiencing an acute episode of herpes zoster. Shingrix is not a treatment for herpes zoster or postherpetic neuralgia . The general guidance for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
There is currently no CDC recommendation for Shingrix use in pregnancy therefore, providers should consider delaying vaccination until after pregnancy. There is no recommendation for pregnancy testing before vaccination with Shingrix. Recombinant vaccines such as Shingrix pose no known risk to people who are breastfeeding or to their infants. Providers may consider vaccination without regard to breastfeeding status if Shingrix is otherwise indicated.
Adults with a minor acute illness, such as a cold, can receive Shingrix. Adults with a moderate or severe acute illness should usually wait until they recover before getting the vaccine.
To learn more, see Contraindications and Precautions, General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices .
Read Also: Can You Lay Shingles On Wet Tar Paper
Approach To Herpes Simplex Virus Therapy
Nucleoside analogs, including acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, remain standard therapies for mucocutaneous and visceral HSV infection. Idoxuridine, trifluorothymidine, vidarabine, and cidofovir are used topically for ocular HSV infections .
Development of HSV resistance to acyclovir and valacyclovir is rare despite extensive use for treatment of infection . Increased prevalence is seen in patients with herpetic keratitis . Antiviral resistance is increased in immunocompromised patients, specifically patients with HIV infections and bone marrow transplants . IV Foscarnet and cidofovir are usually effective for acyclovir resistant viral strains . Continued exposure to cidofovir does not easily induce resistance. However, there have been case reports of cidofovir-resistant HSV and CMV .
Approaches To Vaccine Development
Although there are no currently available vaccines for herpes simplex 1 and 2, there are various candidates in both the pre-clinical and the clinical phases currently in development. Vaccines are being developed with two broad focuses: preventative and therapeutic, some with a dual use. Preventative vaccines are focused on the prevention of primary infection in a seronegative subject. Therapeutic vaccines aim to prevent HSV reactivation, decrease the number of recurrences, or to reduce the severity or duration of clinical symptoms . With regard to vaccine development, given our knowledge of the immunology surrounding HSV, it seems that an effective vaccine would likely stimulate not only humoral responses, but also cell-mediated responses. Different vaccine subtypes have their unique advantages and disadvantages, discussed further in the next section.
Recombinant vaccines are usually composed of proteins that are not strong immunoactivators. Therefore, they require adjuvants to stimulate the innate immune system. This leads to the humoral response and proper inoculation. They are not needed for live-attenuated viruses. Different constituents can enhance and target different facets of the immune response. It is important to focus on the adjuvants in each vaccine trial and evaluate their role in eliciting a lasting humoral and cell-mediated response .
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Buy Wood Shingles
Replication Defective Virus Vaccine
Dl5-29 is a strain of HSV-2 with mutations in essential viral genes UL5 and UL29 making it replication defective. It was tested as both a prophylactic and therapeutic vaccine. It was shown to be safe, producing neutralizing antibodies and CD4+ T-cell responses in seronegative subjects who were vaccinated . Recent studies have demonstrated the production of antibodies mediating NK cell activation. Additionally, HSV-2 gD antibodies were detected in cervicovaginal fluid at around one-third of the serum level .
Simultaneous Administration With Other Vaccines
RZV and LZV may be administered concomitantly with other live vaccines given by the parenteral, oral, or intranasal routes. For concomitant parenteral injections, different injection sites and separate needles and syringes should be used.
In general, inactivated vaccines including RZV may be administered concomitantly with, or at any time before or after, other inactivated vaccines or live vaccines protecting against a different disease.
LZV may be given at any time before or after live oral or intranasal vaccines. If two live parenteral vaccines are not administered concomitantly, there should be a period of at least 4 weeks before the second live parenteral vaccine is given.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine and LZV has not resulted in decreased efficacy and so the two vaccines can be given concomitantly.
For more information, refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1.
Read Also: Can You Get Shingles Vaccine If You Had Shingles
What The Research Says
What we do know is that when your immune system is compromised or distracted fighting off another virus, it tends to give the herpes zoster virus a chance to reactivate.
Past research has established that immune-suppressing medications like chemotherapy and corticosteroids as well as health conditions that attack your immune system like Crohns disease, HIV, and lupus increase your risk for a shingles outbreak.
Researchers are currently trying to understand whether COVID-19 may do the same thing.
Preliminary data suggests that this could be the case, but we do not know yet.
A small 2021 study involving 491 vaccinated people in Israel showed that six participants experienced shingles for the first time after getting their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine. All six individuals had pre-existing conditions that lowered their natural immune response, and all six fully recovered after developing shingles.
This study prompted researchers to advocate for more studies on COVID-19 vaccines as possible triggers for the shingles virus.
Data gathered in Brazil also showed an increase of 10.7 cases of shingles per million inhabitants during the time of the pandemic.
Its impossible to know exactly how and to what extent the effect of increased stress of the pandemic and other factors played into these numbers increasing during that span of time. Stress has long been suspected to be a possible factor in developing shingles.
Can You Get Shingles After Youve Been Vaccinated
While the shingles vaccine is highly effective, some people can still get shingles. However, people who do get shingles after getting the shingles vaccine usually have milder symptoms and a shorter illness. Youll also be less likely to have complications from shingles, including postherpetic neuralgia.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Light Case Of Shingles Look Like
What Illnesses Does Varicella
Chickenpox first occurs as a blister-like skin rash and fever. It takes from 10-21 days after exposure for someone to develop chickenpox. The sores commonly occur in batches with different stages present at the same time. The blisters usually scab over in 5 days. A person with chickenpox is contagious 1-2 days before the rash appears and until all blisters have formed scabs. Children with weakened immune systems may have blisters occurring for a prolonged time period. Adults can develop severe pneumonia and other serious complications.
Shingles occurs when the virus, which has been inactive for some time, becomes active again. Severe pain and numbness along nerve pathways, commonly on the trunk or on the face, are present. Clusters of blisters appear 1 to 5 days later. The blisters are usually on one side of the body and closer together than in chickenpox. Shingles does not spread as shingles from one person to another. If people who have never had chickenpox come in contact with the fluid from shingles blisters, they can develop chickenpox.
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Autoimmune disease
Although definitive data are lacking, individuals with autoimmune disease not being treated with immunosuppressive drugs are not considered significantly immunocompromised. Individuals 50 years of age without contraindications should receive RZV.
Read Also: How Do You Feel When You Have Shingles
Don’t Miss: What Is Shingles And Is It Contagious
What To Think About
The vaccine is less effective in preventing shingles the older a person gets. A person who receives the vaccine at 60 years of age is less likely to get shingles than someone who receives it at 80 years of age. But pain and other symptoms of shingles infection are often reduced in people who have received the vaccine.
Who’s Most At Risk Of Shingles
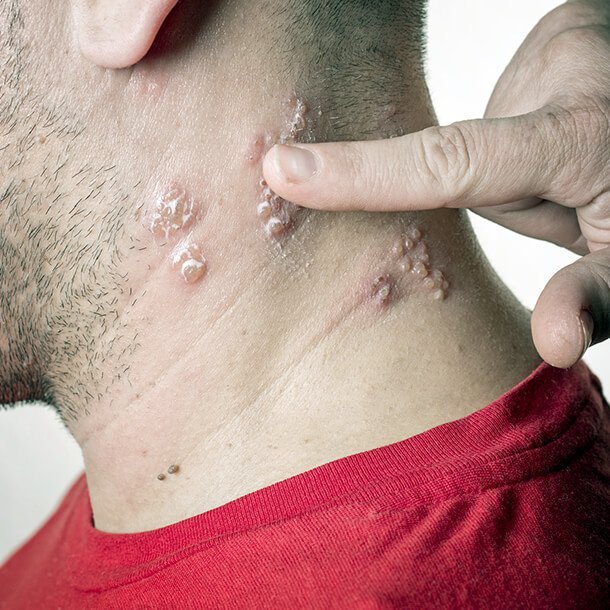
People tend to get shingles more often as they get older, especially over the age of 70. And the older you are, the worse it can be. The shingles rash can be extremely painful, such that sufferers cannot even bear the feeling of their clothes touching the affected skin.
The pain of shingles can also linger long after the rash has disappeared, even for many years. This lingering pain is called post-herpetic neuralgia .
Recommended Reading: How Does Shingles Start On Your Body
Routine Vaccination Of People 60 Years Old And Older
CDC recommends a single dose of Zostavax® for people 60 years old or older, whether or not the person reported a prior episode of herpes zoster . People with chronic medical conditions may be vaccinated unless a contraindication or precaution exists for their condition. Zostavax is a live virus vaccine. It can be administered concurrently with all other live and inactivated vaccines, including those routinely recommended for people 60 years old and older, such as influenza and pneumococcal vaccines.
When vaccinating people 60 years old or older, there is no need to screen for a history of varicella infection or to conduct laboratory testing for serologic evidence of prior varicella infection. Even if a person reports that they have not had varicella, they can still receive the herpes zoster vaccine. The Zostavax®zoster vaccine package insert makes no reference to varicella history, and almost all people 60 years old or older are immune to varicella. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices states that people born in the United States prior to 1980 are considered immune to varicella. If serologic evidence of varicella susceptibility becomes available to the healthcare provider, the patient should be offered varicella vaccine not herpes zoster vaccine.
The general guideline for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
Is Chickenpox And Shingles A Form Of Herpes
Though shingles and herpes are two distinct conditions caused by two distinct viruses, the viruses are both members of a family formally known as herpesviridae. The herpes simplex virus takes its formal name from this umbrella term, while the varicella-zoster virus does not.
Although it is a condition unrelated to herpes, shingles is sometimes referred to as herpes zoster, a nickname that references the shared family of the viruses that cause them. Within this viral family, only the herpes simplex virus causes the condition we know today as herpes.
If you are ever unsure whether your doctor is referring to herpes simplex or shingles when you hear the word herpes, ask for clarification.
Don’t Miss: What Can Cause Shingles To Come Back
Can You Get Chickenpox If You’ve Been Vaccinated
Yes. About 15% 20% of people who have received one dose of varicella vaccine do still get chickenpox if they are exposed, but their disease is usually mild. Vaccinated persons who get chickenpox generally have fewer than 50 spots or bumps, which may resemble bug bites more than typical, fluid-filled chickenpox blisters. In 2006, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted to recommend routine two-dose varicella vaccination for children. In one study, children who received two doses of varicella vaccine were three times less likely to get chickenpox than individuals who have had only one dose.
Herpes Zoster In Australia
In Australia, there are about 560 cases of herpes zoster per 100,000 population per year in all age groups.50
In comparison, there are about 1174 cases per 100,000 population in people aged 50 years.50 Herpes zoster incidence increases with age, from an estimated rate of 630 per 100,000 population in people aged 5059 years, to 1531 per 100,000 population in people aged 7079 years.50
Also Check: What Are The Complications Of Shingles
Shingrix Vaccine Efficacy And Duration Of Protection
Among immunocompetent adults 50 years and older, the efficacy of two doses of Shingrix for the prevention of herpes zoster was high among all age groups. In a clinical trial of more than 30,000 participants, vaccine efficacy was 96.6% in adults aged 50 to 59 years, 97.4% in adults aged 60 to 69 years, and 91.3% in adults aged 70 years and older.
The efficacy of two doses of Shingrix for the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia was high: 91.2% in adults aged 50 years and older, and 88.8% in adults aged 70 years and older.
Vaccine efficacy was estimated among several immunocompromised groups:
- 68.2% among adult autologous hematopoietic cell transplant recipients.
- 87.2% in a post hoc efficacy analysis of adult patients with hematologic malignancies.
- 90.5% in a post hoc efficacy analysis of adult patients with immune-mediated diseases who were not taking immunosuppressive medication.
In immunocompetent adults 70 years and older, vaccine efficacy remained high, at or above 84% in all 7 years after vaccination.
For Patients Who Previously Received Zostavax
Zostavax is no longer available for use in the United States, as of November 18, 2020. Consider the patients age and when he or she received Zostavax to determine when to vaccinate with Shingrix. Studies examined the safety of Shingrix vaccination 5 or more years after Zostavax vaccination. Shorter intervals were not studied, but there are no theoretical or data concerns to indicate that Shingrix would be less safe or effective if administered less than 5 years after a patient received Zostavax.
You may consider an interval shorter than 5 years between Zostavax and Shingrix based on the age at which the patient received Zostavax. Differences in efficacy between Shingrix and Zostavax are most pronounced among older patients. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of Zostavax wanes substantially over time, leaving recipients with reduced protection against herpes zoster. For example, the vaccine efficacy among adults aged 70 to 79 years and adults aged 80 years and older is 41% and 18%, respectively, on average during the first 3 years following Zostavax vaccination.
You should wait at least 8 weeks after a patient received Zostavax to administer Shingrix.
You May Like: How To Care For Shingles At Home
Is There A Way I Can Keep From Being Infected With Chickenpox
Yes, make sure all your vaccines are up to date, especially if you are planning a pregnancy. Vaccination is the best way to protect yourself and those you love. If you are not immune, you should be vaccinated. You will receive two doses of varicella vaccine one month apart. You should avoid becoming pregnant for at least one month after the last vaccination. Varicella vaccine should not be given to pregnant women. If you are pregnant, have your healthcare provider give you the varicella vaccine after your baby is delivered.
Open Access License / Drug Dosage / Disclaimer

This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License . Usage and distribution for commercial purposes requires written permission. Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug. Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. The publisher and the editor disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Second Shingles