How Is Shingrix Given
Shingrix is given as an injection into a muscle. A healthcare provider will give you this injection.
Shingrix is usually given in a series of 2 shots:
-
the second shot may be given any time within 2 to 6 months after the first shot.
-
for people who have a weak immune system, the second shot may be given any time within 1 to 2 months after the first shot.
You may receive this vaccine at the same time that you get a flu shot.
Read all patient information, medication guides, and instruction sheets provided to you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Fever And Feelings Of Malaise
Fever is one of the most common side effects of many vaccines, including Shingrix. This symptom often accompanies other feelings of malaise, such as muscle pains, chills, and headaches. A fever indicates that the bodys immune system is doing its job of responding to the vaccine.
Ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and other OTC fever reducers can help keep a fever and many accompanying symptoms at bay. However, if you develop a high-grade fever of 103°F or higher, reach out to your doctor immediately.
Why Is The Shingles Vaccine Important
Shingles causes a painful rash and blisters and it can lead to serious complications. The most common complication is post-herpetic neuralgia , a condition that causes burning pain that can last long after the shingles rash and blisters go away. The older you are when you get shingles, the more likely you are to develop PHN.
Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles and PHN.
Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you have chickenpox, the chickenpox virus stays dormant in your body. The virus can activate years later and cause shingles.
Symptoms of shingles include:
Shingles cant spread from person to person like chickenpox. But if you have shingles, you can spread the virus to someone who isnt immune to chickenpox meaning someone who hasnt had chickenpox and isnt vaccinated against it. If that happened, the person might get chickenpox but not shingles. Learn more about shingles.
- Adults age 50 and older
- Adults 19 years and older who have a weakened immune system because of disease or treatments
You need to get 2 doses of Shingrix. Youll need the second dose 2 to 6 months after the first dose. You need to get Shingrix even if you:
- Have already had shingles
- Have been vaccinated against shingles with Zostavax
- Are not sure if youve had chickenpox
Recommended Reading: Is The Shingles Shot Just One Dose
Allergic Reaction To Shingles Vaccination
There is a very small chance of a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine, as there is with other vaccines.
Anaphylaxis is very serious and potentially life-threatening, but it can be treated. All healthcare staff that deliver vaccinations are trained in this. With prompt treatment, people fully recover from anaphylaxis.
A Closer Look At The Safety Data

Both Shingrix and Zostavax shingles vaccines have been shown to be safe and well tolerated. Common side effects, such as soreness and redness at the injection site, are usually mild to moderate in intensity and resolve quickly on their own.
Shingrix
In 8 clinical trials of more than 10,000 participants:
- Grade 3 reactions were common after patients received Shingrix.
- About 1 out of 10 adults who received Shingrix reported grade 3 injection-site symptoms such as pain, redness, and swelling.
- About 1 out of 10 reported grade 3 systemic reactions such as myalgia , fatigue , headache, shivering, fever, and gastrointestinal illness.
- Most people who got Shingrix reported at least some pain at the injection site.
Zostavax
- A 2013 study showed that patients with a history of a previous shingles rash had the same side effects after Zostavax as those with no history of shingles. See Safety of zoster vaccine in elderly adults following documented herpes zoster.
Read Also: What Is A Home Remedy For Shingles
Who Shouldnt Get The Shingles Vaccine
There are a few situations in which shingles vaccination may not be right for you. You should not get Shingrix if youâve ever had a severe reaction to a vaccine. This means you had trouble breathing or swelling in your mouth or airway, a life-threatening condition called anaphylaxis.
You should also skip Shingrix if:
- You have allergies to any parts of the vaccine. These include gelatin and the antibiotic neomycin. If you have other allergies, tell your doctor or pharmacist about them before you get Shingrix.
- You currently have shingles or another illness. You can get the vaccine when youâre well.
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding. You should wait until youâve stopped breastfeeding to get vaccinated.
- You happened to test negative for VZV, the virus that causes chickenpox. If youâre older than 50, you probably had chickenpox even if you donât remember it. The CDC does not recommend testing for this. However, if a blood test shows youâve never had the childhood illness, you should get the chickenpox vaccine instead.
If you have a disease or take medications that affect your immune system, talk to your doctor about the pros and cons of Shingrix.
âItâs an individualized decision based on factors such as the specific medications and conditions of the person sitting in front of you,â Kistler says. She often consults with her patientsâ specialist doctors to make decisions about Shingrix.
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
Recommended Reading: What Happens If Shingles Go Untreated
What Vaccines Can Help Prevent Shingles
There is currently one vaccine available in the U.S. to prevent shingles. Shingrix was approved in 2017 and it is more than 90% effective in preventing shingles. With Shingrix, you get two shots between 2 and 6 months apart and protection lasts an estimated 4-5 years. Doctors recommend it for healthy people over 50 as well as those 19 years of age and older who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to disease or therapy..
An earlier vaccine called Zostavax was removed from the market in 2020. That vaccine used a weak form of the chickenpox virus to send your bodys immune system into action to fight the disease. Shingrix does not. If you received the Zostavax vaccine, it is recommended that you also receive Shingrix.
Who Should Not Get Shingrix
You should not get Shingrix if you:
- Have ever had a severe allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine or after a dose of Shingrix.
- Currently have shingles.
- Currently are pregnant. Women who are pregnant should wait to get Shingrix.
If you have a minor illness, such as a cold, you may get Shingrix. But if you have a moderate or severe illness, with or without fever, you should usually wait until you recover before getting the vaccine.
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Shingles
Other Side Effects Of Shingrix
Some side effects of zoster vaccine, inactivated may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
What Else To Know About The Shingles Vaccine
Ready to get vaccinated? This is the essential info on how the shots are given, what to expect with side effects, and more.
You need two doses of Shingrix to get full protection from shingles. You should get your second dose 2 to 6 months after the first. Your doctor or pharmacist will inject the vaccine into the muscle of your upper arm, so wear clothes that give easy access to that area.
If it has been more than 6 months since you got your first dose, go ahead and get your second dose. You donât need to start over, Dooling says.
Because Shingrix is so new, experts arenât sure whether youâll eventually need another shot, or a booster, years down the road.
âThe CDC is actively following how protected people remain after the two-dose series,â she says. We know that after 4 years, protection remains above 85%. Only time will tell how durable that protection is.â
You do not have to wait between Shingrix and COVID-19 vaccination. The CDC has determined its safe to get the COVID-19 vaccine at the same time as Shingrex, but recommends they be given in different arms. You should not get eithe vaccine if you have COVID.
Side effects are fairly common. You may have heard that people sometimes have unpleasant side effects soon after they get the shingles vaccine.
âShingrix tends to have has more side effects than some vaccines, like those for the seasonal flu,â says Kistler. The shingles vaccine may cause:
Also Check: Shingles Vaccine If Never Had Chickenpox
Who Is At Risk Of Getting Shingles
The risk of shingles increases as individuals get older. In fact, about one in three Canadians will develop shingles in their lifetime and two out of three cases occur in individuals over 50 years of age. The severity of shingles and its complications increase with age. Individuals with weakened immune system are also at greater risk of getting shingles. People who develop shingles usually only have one episode in their lifetime, but it is possible to have recurring episodes.
The shingles vaccine can reduce your risk of getting shingles and the long-term pain it can cause.
Does The Shingles Vaccine Contain Thimerosal
You may be concerned about additives to the shingles vaccine, like thimerosal.
Thimerosal is a preservative that contains mercury. Its added to some vaccines to prevent bacteria and other germs from growing in them. The shingles vaccine contains thimerosal.
The worry about thimerosal arose when early research linked it to autism. This connection has since been found to be untrue.
Also Check: Is Lysine Good For Shingles
Pain At Injection Site
Pain at the injection site is a common side effect of many vaccines, including Shingrix. This pain is generally mild but can feel like anything from slight discomfort to deep bruising. In some cases, injection site pain can be severe enough to limit arm movement.
To ease this discomfort, you can apply cold packs to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time.
If these arent effective, over-the-counter pain remedies may help. However, if you have injection site pain that is severe or lasts longer than 2 to 3 days, follow up with your doctor.
Is The Shingles Vaccine Safe
According to the CDC, research has shown that Shingrix is safe.
Some people experience short-term adverse effects, such as a fever, muscle aches, and headaches. However, these usually last only 2â3 days .
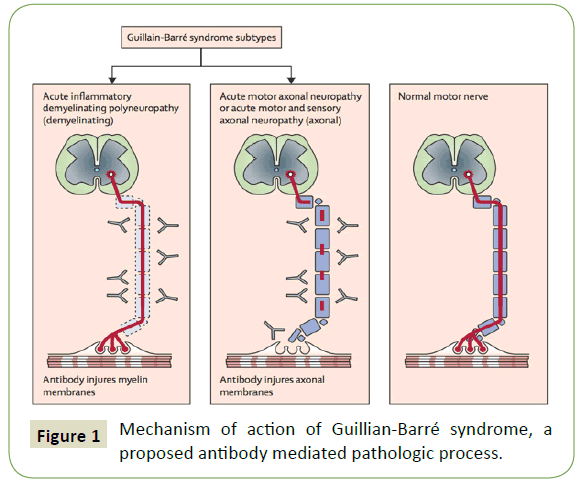
In rare cases, people have developed Guillain-Barré syndrome after having the shingles vaccine. However, this can also happen after shingles. GBS is a severe nervous system disorder.
The recommends Shingrix for people who have or are likely to have a weakened immune system due to a health condition or treatment. Having a weakened immune system increases a personâs risk of developing shingles.
It can happen with the following:
- a medical condition that compromises the immune system, such as AIDS
- cancer that affects the lymphatic system or bone marrow
- cancer treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy
- medications that affect the immune system, such as steroids
However, a person with a weakened immune system should speak with their doctor about whether to have the vaccine and when.
Don’t Miss: What Is Shingles In Adults
Itchy Skin Near The Injection Site
Itchy skin, also called pruritus, can potentially occur near the injection site after receiving Shingrix. Itching, swelling, and redness arent usually a huge cause for concern, as they often occur together as a localized reaction.
Applying Benadryl gel or hydrocortisone cream around the injection area can help reduce itchy, swollen, or red skin. If the itching worsens or spreads away from the injection site, get in touch with your doctor.
Side Effects Of Shingles Vaccine
The most common shingles shot side effects include pain and soreness at the injection site. Some people also notice a bit of redness, swelling or itching at the site of the shot. Other side effects of the shingles vaccine may include fatigue, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. According to the CDC, side effects are more common in younger people than older people.
Most people can resume their regular activities immediately after vaccination. However, about 1 out of 6 people develop flu-like symptoms that last anywhere from 1 to 3 days.
Side effects can occur after the first, second, or both doses of Shingrix vaccine. If possible, it is a good idea to schedule vaccination the day before some downtime, so you can rest if you develop side effects.
If you develop flu-like symptoms after shingles vaccination, you can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to control your fever and improve comfort. Those who develop flu-like symptoms after their first dose of vaccine may want to pre-medicate with ibuprofen or acetaminophen an hour or so before their second dose. Your healthcare provider can answer your questions about shingles vaccine side effects and pre-medication for vaccination.
Serious side effects are rare, but not impossible, after shingles vaccination. If you develop hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, a rapid heartbeat, or sudden dizziness or weakness, and seek medical care immediately.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Light Case Of Shingles Look Like
Complications Of The Shingles Vaccine
Some research has linked Shingrix with minimal risk for Guillain-Barré syndrome .
GBS is a rare neurological disorder that can cause temporary weakness or, in extreme cases, paralysis. But even in those severe cases, most people recover from GBS .
While the link between Shingrix and GBS is uncertain, some research has found an increased riskabout six additional GBS cases per 1 million peopleamong those age 65 or older who were vaccinated with Shingrix. All of those cases occurred within 42 days of the initial Shingrix shot .
Along with those links to GBS, Shingrix can, in rare cases, cause a severe allergic reaction. According to the CDC, only 1 or 2 people out of 1 million who receive the Shingrix vaccine will have this kind of reaction .
The symptoms of an allergic reaction to Shingrix start within minutes or hours and include:
If you have any of these symptoms, get medical attention immediately .
Shingles Disease And How To Protect Against It
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash that develops on one side of the face or body. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus , the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who has had chickenpox in the past can get shingles because VZV remains in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. VZV can reactivate many years later, causing shingles.
Shingles is more common in older adults, people who have medical conditions that weaken the immune system, and people who take medications that suppress their immune systems. Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles.
Also Check: How Many Shingles In Bundle
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.