When Is The Best Time To Get The Second Shingrix Shot
In our latest question and answer, the pharmacist discusses the best time to get your second shot of Shingrix.
Question
After your first Shingrix shot I understand that the second dose should be 2-6 later. My question is, in order to be the most effective what month after the first shot was given is the most effective? In other words, is exactly 2 months after too soon? Would waiting for month 3 or 4 be better?
Medical Content Reviewed By HelloPharmacist Staff
Are There Any Restrictions After A Shingles Shot
You should not receive the shingles vaccine if you are pregnant, if you have an active shingles infection, or if you previously had an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine. If youre eligible for the vaccine and receive the vaccination, there are no restrictions afterward and you can leave the doctors office or pharmacy as soon as the shot is complete.
Is Shingrix Or Zostavax More Effective
Shingrix and Zostavax have both been proven to prevent shingles. However, Shingrix is a newer vaccine that is considered more effective than Zostavax. Shingrix is even recommended for those who have already received the Zostavax vaccine in the past.
Clinical trials have shown that Shingrix is 97% effective at preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old. Shingrix is also effective in preventing shingles in older adultsadults over the age of 70, Shingrix is 91% effective.
Zostavax has a 70% efficacy rate in preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old, according to the Zoster Efficacy and Safety Trial . Results from the Shingles Prevention Study showed that Zostavax is 51% effective against shingles. Compared to Shingrix, the effectiveness of Zostavax decreases in older age groups. Based on the SPS results, Zostavax is 64% effective in adults aged 60 to 69 years old 41% effective in adults aged 70 to 79 years old and 18% effective in adults aged 80 years and older.
Your healthcare provider will most likely recommend Shingrix over Zostavax. Shingrix is especially recommended for immunocompromised patients since it is a non-live vaccine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about which shingles vaccine is right for you.
Read Also: How Soon After Shingles Can I Get Vaccine
What Does The Shingles Vaccine Do
The shingles vaccine can prevent shingles. Every year, about 1 million people in the United States get shingles. Anyone whos had chickenpox can get shingles. Thats because the varicella-zoster virus lives silently in your nervous system after youve had chickenpox. The virus can reactivate later in your life if your immune system is weakened. Your risk of getting shingles goes up as you get older. In the United States, 1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
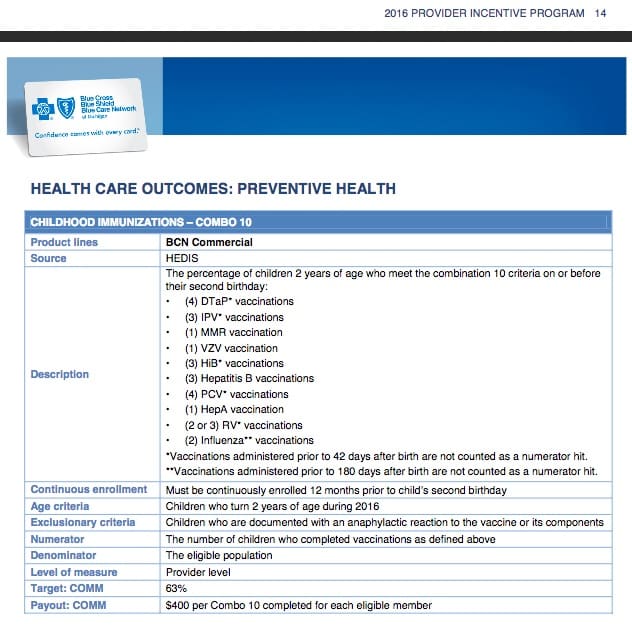
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Don’t Miss: Does Plan F Cover Shingles Vaccine
What Are The Main Differences Between Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix is a recombinant, adjuvanted zoster vaccine that was first FDA-approved in 2017. It uses the varicella-zoster glycoprotein E antigen to produce an immune response in the body. An adjuvant, or added ingredient, helps boost the bodys immune response to the virus. Because Shingrix is an inactivated vaccine, it can be used in immunocompromised patients or those with a weakened immune system.
Shingrix is administered as an injection into the muscle . It is given in two separate doses with a period of two to six months in between. The second dose is necessary to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Zostavax, approved in 2006, is a live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine. In other words, Zostavax contains a weakened version of the actual virus to produce an immune response. For this reason, it is not recommended for those who are immunocompromised. Or else, the vaccine itself could cause an infection.
Zostavax is administered as a single injection underneath the skin . It comes in a frozen version and a refrigerator-stable version. The frozen version must be kept frozen during transport and storage to ensure its effectiveness while the refrigerator-stable Zostavax can be kept in a refrigerator until it needs to be used.
Read Also: Picture Of Shingles On The Back
Itchy Skin Near The Injection Site
Itchy skin, also called pruritus, can potentially occur near the injection site after receiving Shingrix. Itching, swelling, and redness arent usually a huge cause for concern, as they often occur together as a localized reaction.
Applying Benadryl gel or hydrocortisone cream around the injection area can help reduce itchy, swollen, or red skin. If the itching worsens or spreads away from the injection site, get in touch with your doctor.
Also Check: When Is Shingles Not Contagious
Risks Of A Vaccine Reaction
- A sore arm with mild or moderate pain is very common after recombinant shingles vaccine. Redness and swelling can also happen at the site of the injection.
- Tiredness, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, and nausea are common after recombinant shingles vaccine.
These side effects may temporarily prevent a vaccinated person from doing regular activities. Symptoms usually go away on their own in 2 to 3 days. You should still get the second dose of recombinant shingles vaccine even if you had one of these reactions after the first dose.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after recombinant zoster vaccine.
People sometimes faint after medical procedures, including vaccination. Tell your provider if you feel dizzy or have vision changes or ringing in the ears.
As with any medicine, there is a very remote chance of a vaccine causing a severe allergic reaction, other serious injury, or death.
Who Can Have The Shingles Vaccination
Shingles vaccination is available to everyone aged 70 to 79.
When you’re eligible, you can have the shingles vaccination at any time of year.
The shingles vaccine is not available on the NHS to anyone aged 80 or over because it seems to be less effective in this age group.
Read more about who can have the shingles vaccine.
Also Check: Mobile Homes For Sale In Shingle Springs
Who Should Get Shingrix
Adults 50 years and older should get two doses of Shingrix, separated by 2 to 6 months. Adults 19 years and older who have or will have weakened immune systems because of disease or therapy should also get two doses of Shingrix. If needed, people with weakened immune systems can get the second dose 1 to 2 months after the first.
You should get Shingrix even if in the past you:
- Received varicella vaccine
There is no maximum age for getting Shingrix.
If you had shingles in the past, Shingrix can help prevent future occurrences of the disease. There is no specific length of time that you need to wait after having shingles before you can receive Shingrix, but generally you should make sure the shingles rash has gone away before getting vaccinated.
Chickenpox and shingles are related because they are caused by the same virus . After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus stays dormant in the body. It can reactivate years later and cause shingles.
Shingrix is available in doctors offices and pharmacies.
If you have questions about Shingrix, talk with your healthcare provider.
* A shingles vaccine called zoster vaccine live is no longer available for use in the United States, as of November 18, 2020. If you had Zostavax in the past, you should still get Shingrix. Talk to your healthcare provider to determine the best time to get Shingrix.
Swelling Around The Injection Site
Swelling around the injection site is another common side effect of Shingrix. Like pain and redness, minor swelling can usually result from a localized immune system response, which isnt necessarily dangerous.
You can apply hydrocortisone cream on or around the injection site to reduce redness and swelling. However, if you experience severe swelling that doesnt go away, or the swelling accompanies other symptoms of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention right away.
You May Like: Pictures Of Shingles In Eye
Why You Shouldn’t Get The Shingles Vaccine
- Medical Reviewer: Dany Paul Baby, MD
Medically Reviewed on 5/24/2022
Shingles is a disease that usually presents with a painful rash that affects one in three people in their lifetime. It is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox the herpes virus varicella-zoster. More than 99% of people born before 1980 have had chickenpox and have this virus dormant in the brain or spinal cord.
Shingles activates when your immunity is low, usually with advancing age. The currently used recombinant zoster vaccine is safe and effective. But not everyone who is a candidate for the shingles vaccine should take it. Like all vaccines, the shingles vaccine has benefits and harms. You should know about both and make an informed decision about taking it.
Who Should Not Get The Vaccine
It is safe for most people to get two doses of Shingrix. However, you should talk to your healthcare provider before getting the shingles vaccine if:
- You are pregnant
- You have severe allergies to any of the Shingrix ingredients
- You have ever experienced a severe allergic reaction to Shingrix
If you have a mild sickness, such as a cold, its usually safe to get the shingles vaccine. If you are moderately or severely ill, you should wait until you feel better to get your next dose of Shingrix.
You should still get the shingles vaccine if you dont remember having the chickenpox virus in the past and if youve had shingles previously. Shingrix can protect you against developing shingles again in the future.
Don’t Miss: What Cream Is Good For Shingles
You Can Get A Shingles Vaccine Two Ways:
At the pharmacy. Youll still need a doctors prescription, but once thats been transmitted, you can get the shot at a retail pharmacy.
Most major chains and some independent pharmacies can administer the vaccine. Just make sure to use a store in your drug plans network so that it can bill your plan directly and youll owe just the copayment.
At the doctors office. If youre vaccinated in a doctors office, check whether it can bill your drug plan directly or works with a pharmacy that can do so. If so, it will work as mentioned above, with you owing a copayment. If not, you may need to pay the full cost up front and then file a claim for reimbursement from your plan.
Remember that the doctors fee for administering the vaccine may exceed your plans allowable charge, in which you case youre on the hook for the difference. It pays to check beforehand.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published on Jan. 1, 2014. It has been updated with the latest information regarding Medicare coverage in 2020.
Shingles Virus Can Sleep Reactivate
Shingles is caused by the same virus the varicella zoster virus that causes chickenpox. Once you have had chickenpox, the virus that caused it remains inside your nerves. It is inactive, but it can be reactivated later in life. This causes shingles.
When the virus reactivates, the infected nerves, and the skin the nerves go to, become inflamed, causing a burning or stabbing pain. A few days later, when the virus reaches the skin, a rash of blisters appear along the affected nerve. The skin may be very sensitive, unable to tolerate even the lightest touch.
About 1 in 10 adults who get shingles experience long-term pain, even after the rash has healed completely. This condition is called post-herpetic neuralgia . It may last for months, or even years. And it can be debilitating.
After causing shingles, the virus again goes “back to sleep” inside your nerves. But it can still flare up again.
You May Like: What Can Shingles Do To You
Talk With Your Health Care Provider
Tell your vaccination provider if the person getting the vaccine:
- Has had an allergic reaction after a previous dose of recombinant shingles vaccine, or has any severe, life-threatening allergies
- Is currently experiencing an episode of shingles
In some cases, your health care provider may decide to postpone shingles vaccination until a future visit.
People with minor illnesses, such as a cold, may be vaccinated. People who are moderately or severely ill should usually wait until they recover before getting recombinant shingles vaccine.
Your health care provider can give you more information.
Why Is It Important To Receive A Vaccination Against Shingles
About 33% of adults in the U.S. will develop shingles at some point in their lives. Shingles can cause painful blisters, a rash, chills, and fever, among other symptoms. Many people who have shingles later develop PHN, which can cause long-lasting pain that is difficult to treat.
Getting the Shingrix vaccine can help individuals avoid shingles and PHN and help prevent shingles from spreading to vulnerable people.
Don’t Miss: What Is Shingles And How Do You Get It
Redness At Injection Site
Redness at and around the injection site is common and may appear immediately or some days after receiving Shingrix. This redness commonly develops due to a localized immune system response, which shouldnt cause further concern.
Arm redness should disappear within a few days after receiving the vaccine. However, if you experience redness with a rash or severe pain, let your doctor know as soon as possible.
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Read Also: Can You Get Shingles In The Groin Area
Why Is Shingrix Administered In Two Doses
Shingrix is typically given in two doses, usually as a shot to the upper arm.
A 2021 study found that adults over 65 were significantly less likely to develop either shingles or PHN after getting two doses of Shingrix than they were after one dose. Two doses of Shingrix also offered better protection against shingles complications to adults over 80 and immunocompromised adults.
Previously, Zostavax was offered to older and immunocompromised adults to prevent shingles, PHN, and other shingles-related health problems. Zostavax is a live vaccine, which means it contains a weakened version of the herpes zoster virus. Shingrix is a recombinant vaccine, meaning that it uses only a small piece of the virus.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. Zostavax is no longer available in the U.S. People who have gotten Zostavax in the past should now get Shingrix.
Studies have shown that Zostavaxa one-dose vaccineis generally less effective than two doses of Shingrix in preventing shingles complications among older and immunocompromised adults. Shingrix currently offers the best chance of protection against shingles, PHN, and shingles-related hospitalization.
Is Shingrix Or Zostavax Better

Shingrix is more effective than Zostavax. Shingrix is 97% effective at preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old whereas Zostavax is only 70% effective at preventing shingles in the same age group. Shingrix consistently prevents shingles in older adults while the effectiveness of Zostavax decreases with increasing age. However, Shingrix has more systemic side effects than Zostavax.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take To Recover From Shingles
What Are The Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
Most side effects of the shingles vaccine are mild and typically last only 2 to 3 days.
One of the most common side effects of the shingles vaccine is an injection site reaction. This can include redness, swelling, or soreness where you got your shot.
Other side effects can include:
- muscle aches and pains
Side effects felt throughout your body are typically more common after receiving the second and booster doses of the COVID-19 vaccine. Like the shingles vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine side effects typically last only a couple of days.
When COVID-19 and flu circulate at the same time, it has the potential to cause many people to become ill and overburden the healthcare system. As such, its essential to receive both COVID-19 and flu vaccines.
Its safe to receive your COVID-19 and flu vaccine at the same time.
Though were still learning more about giving the COVID-19 vaccine with other vaccines, a found no safety concerns when the COVID-19 and flu vaccine were given at the same time. Also, participants produced expected antibody responses to both vaccines.
The CDC that all people ages 6 months and older get a flu vaccine. The flu vaccine can help prevent illness and reduce the risk of serious flu-related complications in vulnerable individuals, such as:
Read Also: Does Cvs Give Free Shingles Shots
When To See A Healthcare Provider
For most people, the effects of Shingrix are mild and short-term. In very rare cases, Shingrix can cause more serious side effects.
Seek urgent medical care if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction a few minutes or hours after your second dose of Shingrix, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Facial swelling
- Swelling in the throat or mouth
You should also let your healthcare provider know if your Shingrix side effects are severe or arent going away on their own.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Shingles Vaccine While You Have Shingles