Who Should Get Shingrix
Give Shingrix to immunocompetent adults 50 years and older, including those who
- had shingles in the past
- received Zostavax® at least 8 weeks prior
- have health conditions, such as chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, or chronic pulmonary disease
- are receiving other vaccines, such as influenza and pneumococcal vaccines, at the same visit
- are taking low-dose immunosuppressive therapy
While Shingrix is not contraindicated in immunocompromised people, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices at this time does not recommend it for this population. ACIP will review evidence for Shingrix in immunocompromised people as it becomes available.
How Long Does It Take To Work
It takes time for your body to make enough antibodies to fight off germs and protect you from certain diseases.
Results from clinical studies of Shingrix showed that the recommended dosing schedule for Shingrix does cause an immune response.
How long Shingrix takes to work may not be the same for everyone. The timing for you will depend on your body chemistry. In general, you should be protected from shingles soon after the second dose.
Studies in animals showed that there was no risk with Shingrix during pregnancy. However, animal studies dont always predict the way humans would respond.
If youre pregnant or planning to become pregnant, wait until after youve had your baby to get the Shingrix vaccine. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
There havent been enough studies to show whether Shingrix appears in breast milk.
Until more is known, its best to wait until youve finished breastfeeding before getting Shingrix.
Simultaneous Administration With Other Vaccines
RZV and LZV may be administered concomitantly with other live vaccines given by the parenteral, oral, or intranasal routes. For concomitant parenteral injections, different injection sites and separate needles and syringes should be used.
In general, inactivated vaccines including RZV may be administered concomitantly with, or at any time before or after, other inactivated vaccines or live vaccines protecting against a different disease.
LZV may be given at any time before or after live oral or intranasal vaccines. If two live parenteral vaccines are not administered concomitantly, there should be a period of at least 4 weeks before the second live parenteral vaccine is given.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine and LZV has not resulted in decreased efficacy and so the two vaccines can be given concomitantly.
For more information, refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1.
Don’t Miss: When Is Shingles Most Painful
Warnings Of Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix and Zostavax can cause hypersensitivity, or allergic, reactions in those with allergies to vaccine ingredients. Zostavax may cause severe allergic reactions in those with a known allergy to gelatin or neomycin. Severe allergic reactions can lead to severe rash and trouble breathing .
Zostavax should be avoided in those who take immunosuppressive agents and those who are affected by medical conditions that weaken the immune system.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about other precautions before getting a shingles vaccine.
Guidance On Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization
Vaccine providers are asked to report AEFIs through local public health officials and to follow AEFI reporting requirements that are specific to their province or territory. In general, any serious or unexpected adverse event felt to be temporally related to vaccination should be reported.
For LZV the following AEFIs are also of particular interest and should be reported:
- Suspected transmission of vaccine-strain virus to a close household or occupational contact. This phenomenon has been documented following varicella vaccine but it is rare, and transmission has not been documented with LZV.
- Recurrent HZ following immunization of individuals with a history of HZ prior to immunization, noting the area of recurrence.
- Recurrent HZO following immunization of a person who has had a previous episode of HZO. If available, a vitreous fluid specimen should be sent to a laboratory with a request to determine whether the virus is the vaccine strain or wild type virus.
For definitions of serious and unexpected adverse events, refer to Adverse Events Following Immunization in Part 2.
For more information refer to Reporting Adverse Events Following Immunization in Canada.
Recommended Reading: Does Priority Health Cover Shingles Vaccine
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
What Are The Advantages Of Getting The Shingles Vaccine
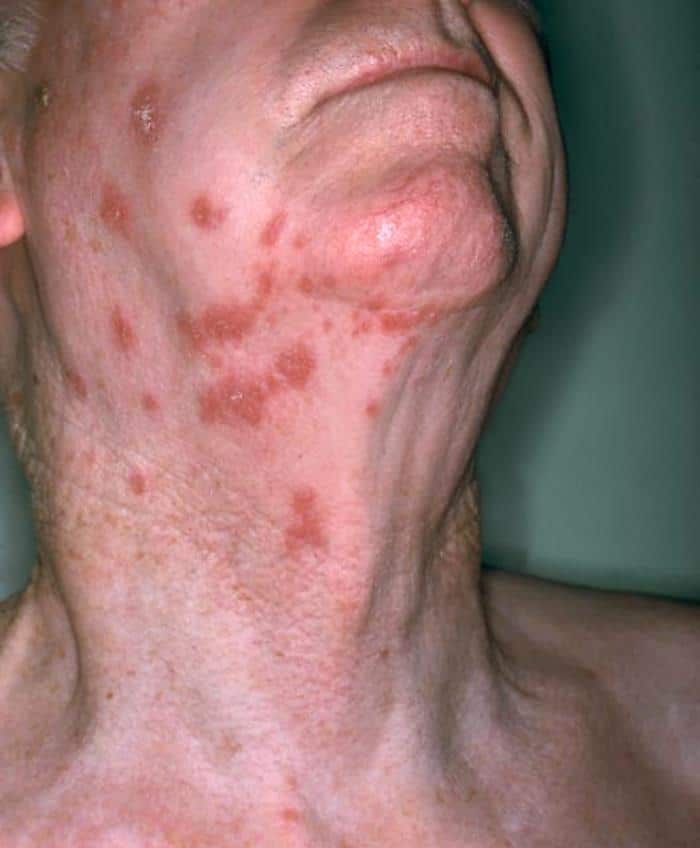
The shingles vaccine reduces your risk of getting shingles. Shingles causes a painful rash that usually develops on one side of your body or face. Some people describe the pain as an intense burning or shooting sensation. The rash is often a single strip that wraps around one side of your body or is on one side of your face. It consists of blisters that normally crust over in seven to 10 days. The rash generally clears up within a month.
Some people with shingles also experience additional symptoms including fever, headache, chills or upset stomach.
For some people, the pain from the rash can last for months or even years after the rash goes away. This long-term pain is called postherpetic neuralgia , and it is the most common complication of shingles.
Read Also: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Hands
Is Shingrix Or Zostavax More Effective
Shingrix and Zostavax have both been proven to prevent shingles. However, Shingrix is a newer vaccine that is considered more effective than Zostavax. Shingrix is even recommended for those who have already received the Zostavax vaccine in the past.
Clinical trials have shown that Shingrix is 97% effective at preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old. Shingrix is also effective in preventing shingles in older adultsadults over the age of 70, Shingrix is 91% effective.
Zostavax has a 70% efficacy rate in preventing shingles in adults aged 50 to 69 years old, according to the Zoster Efficacy and Safety Trial . Results from the Shingles Prevention Study showed that Zostavax is 51% effective against shingles. Compared to Shingrix, the effectiveness of Zostavax decreases in older age groups. Based on the SPS results, Zostavax is 64% effective in adults aged 60 to 69 years old 41% effective in adults aged 70 to 79 years old and 18% effective in adults aged 80 years and older.
Your healthcare provider will most likely recommend Shingrix over Zostavax. Shingrix is especially recommended for immunocompromised patients since it is a non-live vaccine. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about which shingles vaccine is right for you.
Does Shingrix Require 2 Shots
Shingrix is an intramuscular injection requiring 2 injections, with the second dose given 2 to 6 months after the first. In those who are immunodeficient or immunosuppressed and require a shorter vaccination schedule, the second dose can be administered 1 to 2 months after the first dose.
Temporary injection site pain was reported in 78% of those receiving Shingrix, as expected with an intramuscular injection.
Related: FDA Requires a Warning about Guillain-Barré Syndrome for Shingrix
This is not all the information you need to know about Shingrix or Zostavax for safe and effective use and does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your treatment. Review the full product information, and discuss this information and any questions you have with your doctor or other health care provider.
Don’t Miss: Does Champva Cover Shingles Vaccine
New Shingles Vaccine: What You Need To Know
Nov. 13, 2019 — Unlike some vaccines, thereâs been so much demand for the new shingles vaccineShingrix that itâs not always easy to find. It was approved in 2017, and the CDC recommends the vaccine for adults 50 and older to prevent this painful, blistering illness. It is being used in place of the previous vaccine, Zostavax.
More than a year later, doctors say they are learning more about how it works, its safety risks, and how it compares to Zostavax.
How effective is Shingrix?
âIt’s just remarkable,” says Wilbur Chen, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “It has performed better than I expected.”
In studies, Shingrix was more than 97% effective at preventing shingles in people 50 and older. It works just as well in older adults, who are at greater risk for a painful shingles complication called postherpetic neuralgia . “When 70- and 80-year-olds get shingles, it can be extremely debilitating,” Chen says.
By contrast, Zostavax cuts the risk of shingles by only 51% and PHN by 67%. It’s only about 38% effective in people over age 70.
How safe is Shingrix?
“So far so good,” Schaffner says. The main side effect is soreness in the arm where you get the shot.
Other side effects are mild and usually last for 2 to 3 days, including:
Who shouldn’t get Shingrix?
Can I get the Shingrix vaccine now?
What do doctors still need to learn about Shingrix?
Shingles Disease And How To Protect Against It
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a painful skin rash that develops on one side of the face or body. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus , the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who has had chickenpox in the past can get shingles because VZV remains in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. VZV can reactivate many years later, causing shingles.
Shingles is more common in older adults, people who have medical conditions that weaken the immune system, and people who take medications that suppress their immune systems. Getting vaccinated is the best way to prevent shingles.
Also Check: Is It Possible To Have Shingles Without Pain
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.
Shingrix Use For Immunocompromised Adults
The CDC stated on Feb. 17, 2022: that the Shingrix vaccine is recommended for persons 19 years old and older who have altered immunocompetence. And vaccination of Contacts of Persons with Altered Immunocompetence Household contacts and other close contacts of persons with altered immunocompetence should receive all age- and exposure-appropriate vaccines, except for the smallpox vaccine.
During the U.S. CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices meeting on October 20, 2021, Tara Anderson, DVM, MPH, Ph.D., presented: Interpretation of the EtR Regarding Use of RZV in Immunocompromised Adults, Considerations for Use, and Proposed Policy Options. The ACIP’s Recommendation is: Two doses of recombinant zoster vaccine are recommended for adults aged 19 years who are immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to disease or therapy to prevent herpes zoster and its complications.
Previously, Camille Nelson Kotton, M.D., Chair, ACIP Herpes Zoster Work Group, presented the Introduction Zoster Vaccines Session on September 29, 2021 Ismael R. Ortega-Sanchez, Ph.D. presented ‘Economics of vaccinating immunocompromised 1949-years-old adults against herpes zoster in the USA Tara Anderson, DVM, MPH, Ph.D. presented ‘Preliminary Evidence to Recommendations Framework Regarding Use of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in Immunocompromised Adults and Next Steps.’
Read Also: How To Remove Mildew From Shingles
Cdc Recommends New Shingles Vaccine To Replace Older One
Shingrix is recommended over Zostavax, the existing shingles vaccine
Revaccination with Shingrix is recommended for people who have received Zostavax
A new adult vaccine has received a double thumbs-up from the American federal health system.
On the heels of the Food and Drug Administration approval of Shingrix, a new vaccine from GlaxoSmithKline for the prevention of shingles, a federal committee of immunization experts voted Wednesday to recommend Shingrix for all Americans 50 and older.
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a painful, itchy rash that develops on one side of the body and can last for two to four weeks. One in three Americans will develop shingles in their lifetime, with the risk increasing to half of adults over 85, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which advises the CDC on vaccine usage, also recommended that adults who received Zostavax, a shingles vaccine made by Merck, be revaccinated with Shingrix.
Additionally, the committee expressed its preference for Shingrix over Zostavax.
GlaxoSmithKline says Shingrix will be available shortly.
Zostavax was licensed and recommended by the committee in 2006 for people 60 and older, including those who have had an episode of shingles. Until now, it has been the only approved vaccine to protect against the virus.
What Are The Risks And Costs
Virtually no medication is without some risk, though the side effects of this new vaccine are relatively mild. Because it requires an injection into the muscles, most people who receive it will have localized pain and swelling at the injection site for a short time.
Overall, about 1 in 6 people who received this vaccine experienced side effects that kept them from regular activities, though symptoms went away on their own within about 2 to 3 days.
This vaccine also requires two doses be given a few months apart.
The vaccines manufacturer is charging $280 for both doses, though the cost could vary. At that price, a recent study in the Journal of the American Medical Association found the new vaccine is likely to be cost-effective, meaning its health benefits outweighed the financial costs.
The company that makes the new vaccine says most insurance plans cover it, though you should check for yourself to be sure if youre covered.
Don’t Miss: Is The Shingles Shot Free For Seniors
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Very Common And Common Adverse Events
Very common adverse events occur in 10% or more of vaccinees. Common adverse events occur in 1% to less than 10% of vaccinees.
Injection site reactions are very commonly reported for both LZV and RZV. For LZV recipients the frequency is slightly higher in adults aged < 60 years. For all ages, the majority of these events were rated mild or moderate in intensity and lasted less than 2 days.
Due to the adjuvant in RZV, which induces a high cellular immune response and helps address the natural age-related decline in immunity, RZV is more reactogenic than LZV.
Injection site AEs are very commonly reported by recipients of RZV. Approximately 80% report injection-site pain and approximately 30% report redness at the site of injection.
Systemic adverse events, primarily fatigue and myalgia are common in LZV recipients and very common in RZV recipients . For RZV, they include headache .
Local and systemic reactions that were severe enough to interfere with normal activities have been more frequently reported following the receipt of RZV than LZV. However, these reactions have been temporary . Patient education on the short-term reactogenicity of the RZV is recommended prior to vaccine administration to promote adherence to the second dose.
Also Check: What Type Of Doctor Treats Shingles
Administering And Storing Shingrix
- Adults 50 years and older should receive 2 doses of Shingrix. Give the second dose 2 to 6 months after the first.
- Administer Shingrix intramuscularly in the deltoid region of the upper arm with a 1- to 1.5-inch needle.
- Both vials of Shingrix must be refrigerated at a temperature of 36-46° F. Do not use if exposed to temperatures below 36° F.
Shingrix Vs Zostavax: Differences Similarities And Which Is Better For You
Drug overview & main differences | Conditions treated | Efficacy | Insurance coverage and cost comparison | Side effects | Drug interactions | Warnings | FAQ
There are currently two vaccines that can be given to prevent herpes zoster, more commonly known as shingles: Shingrix and Zostavax. A shingles vaccine is recommended for adults once they turn 50.
Most people have been infected with the varicella zoster virus if theyve ever had chickenpox. After chickenpox resolves, the varicella zoster virus lies dormant in the body for years, if not forever. Later in life, the virus can reactivate as shingles and cause a painful rash that usually wraps around the face or torso.
Although Shingrix and Zostavax work in similar ways to prevent shingles, there are some important differences between the two.
Also Check: Will The Shingles Vaccine Help With Genital Herpes