Shingles New Vaccine: Fda Approval
The FDA approved a new shingles vaccine for seniors, age 60 and up, last week. The new vaccine, Shingrix, is recommended even for those already inoculated with the older vaccine. In addition, the FDA recommended that adults 50 and up also get re-vaccinated.
Shingrix, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, is more than 90 percent effective.
Is The Shingles Vaccine Safe And Effective
The shingles vaccine is safe and effective for the prevention of shingles and its complications. Studies have shown that the vaccine reduced the risk of shingles by 51.3 percent and the risk of post-herpetic neuralgia by 66.5 percent. The vaccines effectiveness decreases considerably after 70 years of age.
A vaccine, like any medicine, can cause side effects. Common side effects from the shingles vaccine are mild and can include pain, swelling or redness at the injection site. Other side effects may include a hard lump, itching, warmth, and bruising at the injection site, as well as headache and pain in an arm or leg. Severe reactions are rare.
Outcome Definitions And Follow
Our primary outcome was community HZ, defined by a claim in the OP or PB setting with an International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification diagnosis code for HZ in any position with a claim for HZ-specific antiviral , identified using NDCs, within 7 days of diagnosis. As a sensitivity analysis, we used this same clinical definition without requiring a prescription for antivirals. As secondary outcomes, we evaluated community ophthalmic zoster and PHN. We defined community OZ by a claim in the institutional OP or PB setting with an ICD-10 diagnosis code for OZ in any position , combined with a claim for a prescription for HZ-specific antivirals within 7 days of diagnosis. We defined PHN in the 90180 days after HZ onset using a modified version of the PHN algorithms from Klompas et al and Klein .
Follow-up continued until occurrence of any of the following: a subsequent claim for a third dose of RZV death termination of Medicare Parts A/B or D coverage or enrollment into Part C admission to a nursing home, skilled nursing facility or hospice occurrence of either HZ, OZ, or PHN or end of the study period.
Recommended Reading: Are Shingles Shots Covered By Medicare
Shingles Vaccination Rate Soars But Leaves Many Behind
By Phil GalewitzJuly 9, 2020
We encourage organizations to republish our content, free of charge. Heres what we ask:
You must credit us as the original publisher, with a hyperlink to our khn.org site. If possible, please include the original author and Kaiser Health News in the byline. Please preserve the hyperlinks in the story.
Its important to note, not everything on khn.org is available for republishing. If a story is labeled All Rights Reserved, we cannot grant permission to republish that item.
Have questions? Let us know at
Zostavax And The Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
The Summary of Product Characteristics for Zostavax, the shingles vaccine used in the UK, states that the vaccine should not be given at the same time as the Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine . This is because a clinical trial by the manufacturer had suggested this might make Zostavax less effective. However, the Department of Health advice is that the two vaccines can be given at the same time. This is based on expert advice from the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation , and on research that showed no evidence that people receiving both vaccines together had any increased risk of developing shingles. Read the abstract of the 2011 study by Tseng et al .
Read Also: How To Determine How Many Squares Of Shingles You Need
Risk Of Bias Assessment
Pairs of reviewers independently appraised risk of bias in each study using the Cochrane risk of bias tool33 for randomised controlled trials and quasi-randomised controlled trials, the Newcastle Ottawa Scale34 for observational studies, and the Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care Risk-of-Bias Tool35 for non-randomised trials and quasi-experimental studies. Only reviewers experienced in using the tools were involved at this step. A third reviewer consistently resolved discrepancies.
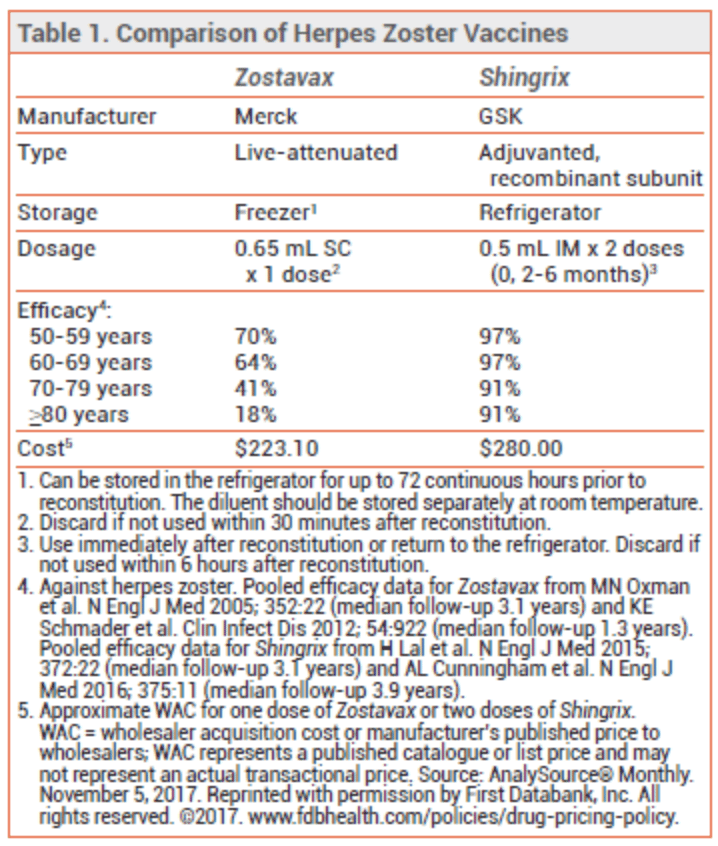
How Well Does Shingrix Work
Two doses of Shingrix provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most common complication of shingles.
- In adults 50 to 69 years old with healthy immune systems, Shingrix was 97% effective in preventing shingles in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective.
- In adults 50 years and older, Shingrix was 91% effective in preventing PHN in adults 70 years and older, Shingrix was 89% effective.
- In adults with weakened immune systems, Shingrix was between 68% and 91% effective in preventing shingles, depending on their underlying immunocompromising condition.
In people 70 years and older who had healthy immune systems, Shingrix immunity remained high throughout 7 years following vaccination.
Recommended Reading: What Antiviral Drugs Are Used To Treat Shingles
A New More Effective Option
This isnt one of those new medicines that only offers small benefits over a previous version. Instead, it offers major benefits over the older vaccine.
First, its safer.
While the previous vaccine uses a live virus to prompt the immune system to create antibodies that defend against the virus, the new Shingrix vaccine contains no living organisms, so cannot cause viral infection even in a severely immune-compromised host.
Secondly, Shingrix is manufactured in yeast cells, by recombinant DNA technology. No aborted human fetal cell lines are used to make this vaccine. This removes a religious objection to the prior Zostavax vaccine.
Finally, Shingrix is much more effective at producing an immune response than the older vaccine. Even among adults older than 80, the vaccine is more than 90 percent effective.
For all these considerations, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, has recommended that this vaccine replace the older vaccine product.
Who Should Not Receive The Shingles Vaccine
Some people should not get the shingles vaccine:
- Individuals with weakened immune systems due to: acute and chronic leukemias lymphoma other conditions affecting the bone marrow or lymphatic system or immunosuppression due to HIV/AIDS
- Individuals on immunosuppressive therapy
- Individuals with a history of severe reaction after previous administration of the vaccine
- Individuals with proven hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine or its container, including gelatin or neomycin
- Individuals with active untreated tuberculosis
- Individuals who are pregnant
You should not get the vaccine if you currently have shingles. If you recently had shingles, you should wait at least one year before receiving the vaccine.
You May Like: 30 Year Vs 50 Year Shingles
Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine: Is It Safe
Shingles is a painful rash caused by varicella zoster, the same virus responsible for chickenpox.
If you had chickenpox as a child, the virus hasnt completely gone away. It hides dormant in your body and can reemerge many years later as shingles.
About 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime. This is why vaccination is important. But you should also be prepared for possible side effects. In this article, well discuss the side effects, and talk about who should get the vaccine.
Older adults are most likely to develop shingles. This is why the shingles vaccine is recommended for people ages 50 and older.
Shingrix is the only shingles vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration .
The Shingrix vaccine is a recombinant vaccine. This means vaccine manufacturers created it by altering and purifying DNA that creates an immune response to fight the virus.
The CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. The Shingrix vaccine is also recommended for anyone who has already gotten another type of shingles vaccine.
Currently, the CDC recommends healthy people ages 50 and older get the Shingrix vaccine. Doctors administer the vaccine in two doses, which are given 2 to 6 months apart.
The Shingrix vaccine has high success rates in protecting people against shingles.
The Shingrix vaccine is as much as effective in preventing shingles. The same is true for Shingrix and postherpetic neuralgia.
Uncommon Rare And Very Rare Adverse Events
Uncommon adverse events occur in 0.1% to less than 1% of vaccinees. Rare and very rare adverse events occur, respectively, in 0.01% to less than 0.1% and less than 0.01% of vaccinees.
Both HZ vaccines are safe with serious adverse events reported very rarely in immunocompetent individuals.
Recurrence or exacerbation of herpes zoster ophthalmicus following LZV vaccination has been reported very rarely, involving several cases world-wide following LZV immunization. Following a causality assessment of seven cases of HZO which were temporally associated with the administration of LZV, NACI concluded that there was insufficient evidence to recommend for or against the administration of LZV in individuals with a history of HZO. More evidence is required for further assessment of risk related to HZO recurrence in LZV recipients. At this time, there is insufficient evidence to assess the risk related to HZO recurrence following RZV recipients.
See Contraindications and Precautions if considering vaccinating a person with previous HZO.
For more information, refer to Adverse Events Following Immunization in Part 2 and the product monograph in Health Canada’s Drug Product Database.
Don’t Miss: How To Clear Up Shingles Scars
If Youre 50 Or Older Get Shingrix
- Shingrix provides strong protection from shingles and long-term nerve pain.
- Get Shingrix even if you already had shingles, because you can get the disease more than once.
- Your risk of shingles and complications increases as you age.
- You need 2 doses of Shingrix. Get the second dose 2 to 6 months after you get the first dose.
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingrix
Studies show that Shingrix is safe. The vaccine helps your body create a strong defense against shingles. As a result, you are likely to have temporary side effects from getting the shots. The side effects might affect your ability to do normal daily activities for 2 to 3 days.
Most people got a sore arm with mild or moderate pain after getting Shingrix, and some also had redness and swelling where they got the shot. Some people felt tired, had muscle pain, a headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, or nausea. Some people who got Shingrix experienced side effects that prevented them from doing regular activities. Symptoms went away on their own in about 2 to 3 days. Side effects were more common in younger people.
You might have a reaction to the first or second dose of Shingrix, or both doses. If you experience side effects, you may choose to take over-the-counter pain medicine such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after Shingrix. There is also a very small increased risk of GBS after having shingles.
If you experience side effects from Shingrix, you should report them to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System . Your doctor might file this report, or you can do it yourself through the VAERS websiteexternal icon, or by calling 1-800-822-7967.
If you have any questions about side effects from Shingrix, talk with your doctor.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Shingles In Eye
Does The Shingles Vaccine Contain Thimerosal
You may be concerned about additives to the shingles vaccine, like thimerosal.
Thimerosal is a preservative that contains mercury. Its added to some vaccines to prevent bacteria and other germs from growing in them. The shingles vaccine contains thimerosal.
The worry about thimerosal arose when early research linked it to autism. This connection has since been found to be untrue.
Efficacy Effectiveness And Safety Of Herpes Zoster Vaccines In Adults Aged 50 And Older: Systematic Review And Network Meta
- Accepted 3 September 2018
Read Also: Is There A Booster For Shingles Vaccine
New Shingles Vaccine 90 Percent Effective In Preventing The Virus
From the time a person contracts chickenpox, a more sinister virus lies sleeping in the human body.
Shingles rises to the surface when a person?s immune system becomes stressed or weak, whether from getting older or other factors. While there is a vaccine to fight against shingles, there still is a 30 percent chance of developing the virus. However, with a new vaccine on the market at the end of this year, all that could change.
Shingrix, the new shingles vaccine, was licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on Oct. 20. It is the new recommendation in preventing shingles, with research showing it provides better protection several years down the road than the formerly recommended vaccine, Zostavax.
?The science was just there, especially when you are looking at protection,? said Bethany Kintigh, Iowa Department of Public Health Immunization program manager. ?It?s just a better vaccine. It gives better protection to our adult population.?
The Shingrix vaccine has a 90 percent protection against shingles even four years after vaccination. Unlike Zostavax, Shingrix is a two-dose series, which is unusual for an adult vaccine. The second dose is supposed to be given two to six months after the first.
This is a small, yet valid, concern for health professionals administering Shingrix. Kintigh said this is the first vaccine for adults where a two-dose vaccine is recommended.
?We have really good health care providers in Iowa,? Kintigh added.
Will We Always Need Shingles Shots
People over the age of 50 usually had chickenpox as kids because the virus that causes it, varicella-zoster, is highly contagious. That said, theres now a generation of people who managed to avoid the once-common childhood illness because a chickenpox vaccine has been available in the United States since 1995.
Poland pointed out that only people who had chickenpox can get shingles, and since chickenpox can be prevented, there may come a time when shingles will be rare.
Once we reach a point where most people were vaccinated against chickenpox as children, Poland said its still an open question as to whether shingles vaccines will continue to be necessary.
Read Also: What Do Shingles Look Like When They First Start Out
Data Sources And Study Design
The primary data sources were Medicare claims and enrollment databases. We derived demographic and death information from the enrollment databases and information on vaccinations, health covariates, preventive services, and outcomes from Medicare Part A , Part B , and Part D claims. Supplemental data on health-seeking attitudes and frailty conditions were captured from the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey . We used a prospective cohort design with a study period from 1 November 2017 to 20 October 2019 .
Patient And Public Involvement
No patients or the public were involved in setting the research question or outcome measures, nor were they involved in the design and implementation of the study. This is because the commissioning agency and the primary knowledge user, NACI, did not allow for patient engagement, as they had an expedited timeline to make policy decisions on herpes zoster vaccines.
Don’t Miss: Why Does A Person Get Shingles
What Does The Shingles Vaccine Do
The shingles vaccine can prevent shingles. Every year, about 1 million people in the United States get shingles. Anyone whos had chickenpox can get shingles. Thats because the varicella-zoster virus lives silently in your nervous system after you’ve had chickenpox. The virus can reactivate later in your life if your immune system is weakened. Your risk of getting shingles goes up as you get older. In the United States, 1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.
Does The Vaccine Work
In December 2017 Public Health England published an evaluation of the first three years of the shingles vaccination programme in England . This showed that the shingles vaccine was 62% effective against shingles and 70 to 88% effective against post-herpetic neuralgia in this period. Public Health England estimates that there were 17000 fewer GP consultations for shingles than expected in this 3-year period.
In the early 2000s researchers carried out a very large study of Zostavax, the shingles vaccine used in the UK, involving over 38,000 adults aged 60 or older. The results showed that:
- In adults aged between 60 and 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 51.3%
- In adults aged over 70, the vaccine reduced the number of cases of shingles by 38%
- The vaccine reduced the incidence of post-herpetic neuralgia by over 66% in all age groups
- For those who did get shingles, the vaccine reduced the severity of the disease.
Read the abstract of this study , published in 2005 by Oxman et al.
Adults aged 80 or over are not offered the shingles vaccine. This is because the effectiveness of the vaccine declines with age in older age groups.
Recommended Reading: Does Shingles Make You Sick
New Shingles Vaccine: What You Need To Know
Nov. 13, 2019 — Unlike some vaccines, thereâs been so much demand for the new shingles vaccineShingrix that itâs not always easy to find. It was approved in 2017, and the CDC recommends the vaccine for adults 50 and older to prevent this painful, blistering illness. It is being used in place of the previous vaccine, Zostavax.
More than a year later, doctors say they are learning more about how it works, its safety risks, and how it compares to Zostavax.
How effective is Shingrix?
âIt’s just remarkable,” says Wilbur Chen, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “It has performed better than I expected.”
In studies, Shingrix was more than 97% effective at preventing shingles in people 50 and older. It works just as well in older adults, who are at greater risk for a painful shingles complication called postherpetic neuralgia . “When 70- and 80-year-olds get shingles, it can be extremely debilitating,” Chen says.
By contrast, Zostavax cuts the risk of shingles by only 51% and PHN by 67%. It’s only about 38% effective in people over age 70.
How safe is Shingrix?
“So far so good,” Schaffner says. The main side effect is soreness in the arm where you get the shot.
Other side effects are mild and usually last for 2 to 3 days, including:
Who shouldn’t get Shingrix?
Can I get the Shingrix vaccine now?
What do doctors still need to learn about Shingrix?