What Are The Main Differences Between Shingrix And Zostavax
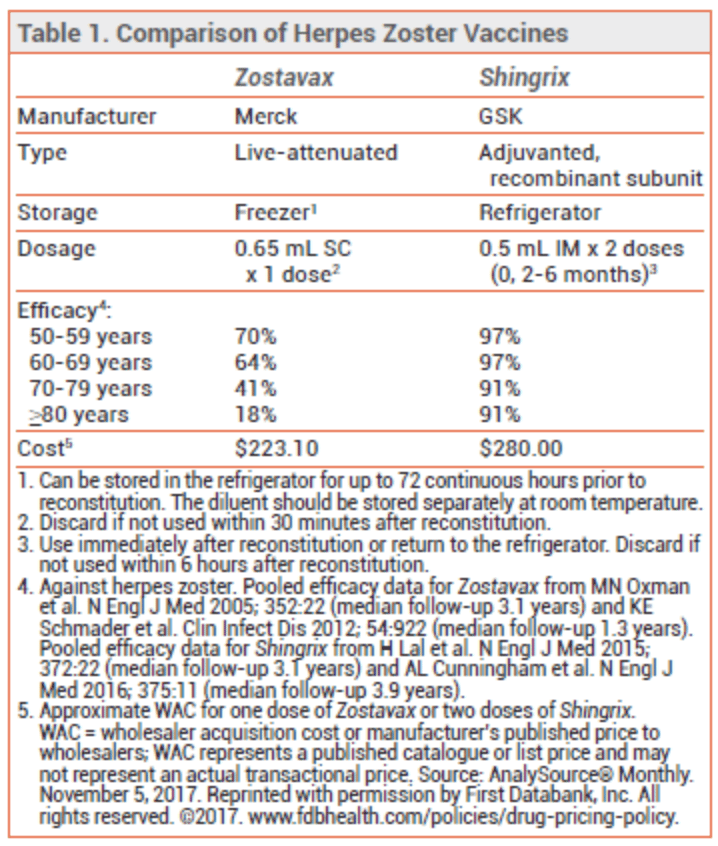
Shingrix is a recombinant, adjuvanted zoster vaccine that was first FDA-approved in 2017. It uses the varicella-zoster glycoprotein E antigen to produce an immune response in the body. An adjuvant, or added ingredient, helps boost the bodys immune response to the virus. Because Shingrix is an inactivated vaccine, it can be used in immunocompromised patients or those with a weakened immune system.
Shingrix is administered as an injection into the muscle . It is given in two separate doses with a period of two to six months in between. The second dose is necessary to ensure long-term effectiveness.
Zostavax, approved in 2006, is a live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine. In other words, Zostavax contains a weakened version of the actual virus to produce an immune response. For this reason, it is not recommended for those who are immunocompromised. Or else, the vaccine itself could cause an infection.
Zostavax is administered as a single injection underneath the skin . It comes in a frozen version and a refrigerator-stable version. The frozen version must be kept frozen during transport and storage to ensure its effectiveness while the refrigerator-stable Zostavax can be kept in a refrigerator until it needs to be used.
So Should I Get The Chickenpox Vaccine Or The Shingles Vaccine
For most healthy people, if youre between 30 and 50 years old, theres no need for either vaccine, Orrange said. There are some exceptions, including health care workers, pregnant women, teachers and those who are HIV-positive. If youre an adult who hasnt received the vaccine or you think youve never been exposed to chickenpox, you can ask your primary care doctor to run a blood test called varicella titers. It shows your level of chickenpox immunity.
But if youre 50 or older, you can and should get the new shingles vaccine, Shingrix, whether or not you remember getting chickenpox in childhood. Its given as a shot in two doses, two to six months apart.
Theres also an older shingles vaccine called Zostavax. Its given to those 50 and over with certain medical conditions, and to people 60 and over. Zostavax is 19 times stronger than the chickenpox vaccine. Its unknown, by the way, whether the shingles vaccines protect against the varicella virus that would lead to chickenpox in adults who were never exposed. The makers of Shingrix or Zostavax would have to run a study on that question, Orrange said, but theres little incentive to do so since a chickenpox vaccine already exists.
Vaccination Of Immunocompromised Adults 19 Years And Older
CDC recommends two doses of RZV for the prevention of shingles and related complications in adults aged 19 years who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed because of disease or therapy. The second dose of RZV should typically be given 26 months after the first. However, for persons who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed and who would benefit from completing the series in a shorter period, the second dose can be administered 12 months after the first. For more detailed clinical guidance see .
You May Like: What Do Pictures Of Shingles Look Like
Shingrix Vs Zostavax: How Do Various Shingles Vaccines Stack Up
Its important to understand what shingles is. Shingles is essentially a reactivation of chickenpox. Chickenpox is a bit of a misnomer. The pox ending refers to its blistering rash. For much of human history it was thought to be similar to smallpox . However, the two infections are entirely unrelated.
Why it was called chicken-pox is not entirely clear since the disease has nothing to do with chickens. A few theories have been put forward. One is that chicken-pox is a linguistic corruption of child-pox since the disease generally affects children. But the real reason is likely lost to history. In any case, we are better off referring to chickenpox by its scientific name of varicella.
Varicella is caused by the aptly named Varicella-zoster virus . Varicella is not a benign illness and it can be fatal, but most people survive the initial infection. However, even though the characteristic rash eventually disappears, the virus is never entirely cleared from the human body. It remains dormant in the dorsal root ganglia, a cluster of nerve cells that run parallel to the spine. Your immune system normally keeps the virus in check. But as we age, immunity can wane. By age 55, 30-40% of people have lost the specific immunity they had to the varicella-zoster virus and the virus can re-awaken.
Can You Get Shingles If Youve Never Had Chickenpox

You can only get shingles if youve previously had chickenpox. After a chickenpox infection, the virus stays in your nervous system. If the virus becomes reactive again, it leads to shingles. The first time youre infected with the virus it leads to chickenpox.
Vaccines are now widely available to protect against chickenpox and shingles. Getting vaccinated is the most effective way to prevent both before they develop.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Should You Avoid If You Have Shingles
How Cdc Monitors Vaccine Safety
CDC and FDA monitor the safety of vaccines after they are approved or authorized. If a problem is found with a vaccine, CDC and FDA will inform health officials, health care providers, and the public.
CDC uses 3 systems to monitor vaccine safety:
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System : an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and FDA, to monitor for potential vaccine safety problems. Anyone can report possible vaccine side effects to VAERS.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink : a collaboration between CDC and 9 health care organizations that conducts vaccine safety monitoring and research.
- The Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project: a partnership between CDC and several medical research centers that provides expert consultation and conducts clinical research on vaccine-associated health risks.
Warnings Of Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix and Zostavax can cause hypersensitivity, or allergic, reactions in those with allergies to vaccine ingredients. Zostavax may cause severe allergic reactions in those with a known allergy to gelatin or neomycin. Severe allergic reactions can lead to severe rash and trouble breathing .
Zostavax should be avoided in those who take immunosuppressive agents and those who are affected by medical conditions that weaken the immune system.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about other precautions before getting a shingles vaccine.
Don’t Miss: What Does A Mild Shingles Rash Look Like
Why Is Shingrix Administered In Two Doses
Shingrix is typically given in two doses, usually as a shot to the upper arm.
A 2021 study found that adults over 65 were significantly less likely to develop either shingles or PHN after getting two doses of Shingrix than they were after one dose. Two doses of Shingrix also offered better protection against shingles complications to adults over 80 and immunocompromised adults.
Previously, Zostavax was offered to older and immunocompromised adults to prevent shingles, PHN, and other shingles-related health problems. Zostavax is a live vaccine, which means it contains a weakened version of the herpes zoster virus. Shingrix is a recombinant vaccine, meaning that it uses only a small piece of the virus.
In 2017, the Food and Drug Administration approved Shingrix for the prevention of shingles and related complications. Zostavax is no longer available in the U.S. People who have gotten Zostavax in the past should now get Shingrix.
Studies have shown that Zostavaxa one-dose vaccineis generally less effective than two doses of Shingrix in preventing shingles complications among older and immunocompromised adults. Shingrix currently offers the best chance of protection against shingles, PHN, and shingles-related hospitalization.
Routine Vaccination Of People 50 Years Old And Older
CDC recommends Shingrix for the prevention of herpes zoster and related complications. CDC recommends two doses of Shingrix separated by 2 to 6 months for immunocompetent adults aged 50 years and older:
- Whether or not they report a prior episode of herpes zoster.
- Whether or not they report a prior dose of Zostavax, a shingles vaccine that is no longer available for use in the United States.
- It is not necessary to screen, either verbally or by laboratory serology, for evidence of prior varicella.
Recombinant and adjuvanted vaccines, such as Shingrix, can be administered concomitantly, at different anatomic sites, with other adult vaccines, including COVID-19 vaccines. Coadministration of RZV with adjuvanted influenza vaccine and COVID-19 vaccines is being studied.
Don’t Miss: Is The Shingles Vaccination A Live Virus
Cdc Recommendation For The Shingles Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend Shingrix as the preferred vaccine to prevent shingles and other complications from the disease.
The CDC found that Shingrix was more effective than Zostavax. It recommends that you receive Shingrix, even if youve had Zostavax in the past.
The following information describes dosages that are commonly used or recommended. However, be sure to take the dosage your doctor prescribes for you. Your doctor will determine the best dosage to suit your needs.
Who Should Not Get The Shingles Vaccine
Some people shouldnt get the shingles vaccine. These people include those:
- Who currently have shingles.
- Who have had a severe allergic reaction to the shingles vaccine in the past.
- Who have tested negative for immunity to the varicella-zoster virus, meaning youve never had chickenpox. If youve never had chickenpox, you should get the chickenpox vaccine.
- Who are ill. You should wait until your illness has passed before receiving the shingles vaccine.
- Who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Read Also: How To Administer Shingles Vaccine
Also Check: When Was Shingles Vaccine Developed
Is The Shingles Vaccine Covered By Insurance
The shingles vaccine may be covered by insurance depending upon the insurance program:
- Medicare: Medicare Part D covers shingles vaccine expenses, but it depends on the plan. You may need to pay either in part or full and then get it reimbursed. Medicare part B does not cover the vaccine.
- Medicaid: Medicaid may or may not cover the vaccine. You can find out by contacting your insurer.
- Private health insurance: Most private health insurance programs cover the shingles vaccine, but you may need to pay some part of the expenses depending on your plan.
- Vaccine assistance program: Check with the Shingrix manufacturer, GlaxoSmithKline, if they have a Shingrix vaccine assistance program. Through vaccine assistance programs, people who cannot afford the vaccine can get help in the form of free vaccination.
Is Chickenpox And Shingles A Form Of Herpes
Though shingles and herpes are two distinct conditions caused by two distinct viruses, the viruses are both members of a family formally known as herpesviridae. The herpes simplex virus takes its formal name from this umbrella term, while the varicella-zoster virus does not.
Although it is a condition unrelated to herpes, shingles is sometimes referred to as herpes zoster, a nickname that references the shared family of the viruses that cause them. Within this viral family, only the herpes simplex virus causes the condition we know today as herpes.
If you are ever unsure whether your doctor is referring to herpes simplex or shingles when you hear the word herpes, ask for clarification.
Also Check: What Does Shingles Look Like Pictures
How You Get Shingles
You dont catch shingles. Chickenpox virus caught earlier in your life reactivates later to cause shingles. You cant catch shingles from someone who has chickenpox.
However, if you have shingles blisters, the virus in the fluid can infect someone who has not had chickenpox and they may develop chickenpox.
How Does The Shingles Vaccine Work
The vaccine recommended for most people is a live vaccine called Zostavax. It contains a weakened chickenpox virus . It’s similar, but not identical, to the chickenpox vaccine.
People with a weakened immune system cannot have live vaccines. They will be offered a non-live vaccine called Shingrix. It activates the immune system but also contains an ingredient called an adjuvant, which helps to boost the response to the vaccine.
Very occasionally, people develop chickenpox following shingles vaccination . Talk to a GP if this happens to you.
You May Like: How Many Shingles Vaccines Are There
What Is Mrna And What Is An Mrna Vaccine
Messenger RNA is a bit of genetic code that teaches the bodys immune system how to make antigens, which are proteins that prompt an immune system response.
Messenger RNA vaccines carry this code inside a fatty covering that is injected into muscle tissue. If you contract the virus later, your body will already know how to fight it.
BioNTech co-founder Özlem Türeci told The Atlantic that mRNA vaccines were like showing our immune system a wanted poster of a foe and instructing the immune system to target that outlaw for destruction.
Contraindications And Precautions For Herpes Zoster Vaccination
Shingrix should not be administered to:
- A person with a history of severe allergic reaction, such as anaphylaxis, to any component of this vaccine.
- A person experiencing an acute episode of herpes zoster. Shingrix is not a treatment for herpes zoster or postherpetic neuralgia . The general guidance for any vaccine is to wait until the acute stage of the illness is over and symptoms abate.
There is currently no CDC recommendation for Shingrix use in pregnancy therefore, providers should consider delaying vaccination until after pregnancy. There is no recommendation for pregnancy testing before vaccination with Shingrix. Recombinant vaccines such as Shingrix pose no known risk to people who are breastfeeding or to their infants. Providers may consider vaccination without regard to breastfeeding status if Shingrix is otherwise indicated.
Adults with a minor acute illness, such as a cold, can receive Shingrix. Adults with a moderate or severe acute illness should usually wait until they recover before getting the vaccine.
To learn more, see Contraindications and Precautions, General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices .
Also Check: Shingle Creek Reserve At The Oaks
Chickenpox Shingles And Vaccines: Expert Shares What You Need To Know
Chickenpox and shingles generally wont kill you, but for some adults, they could result in a trip to the hospital. So with a new shingles vaccine now available, should you consider vaccination to avoid chickenpox and shingles as an adult?
Physician Sharon Orrange, MD, clinical associate professor of medicine at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, said the answer depends on a few factors.
What is chickenpox, exactly?
Its an infection caused by the varicella zoster virus. In children, its usually a mild disease that runs its course in five to 10 days and requires no medical intervention. But in those who develop chickenpox as teens or adults, theres a risk of complications, including pneumonia, skin infections and brain swelling.
Whats the difference between chickenpox and shingles?
Adults can develop shingles if theyve already had chickenpox. Also called herpes zoster, shingles is a reactivation of the virus that causes chickenpox. After you recover from chickenpox, the virus doesnt entirely disappear it lies dormant in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain. When it springs into action again as a painful skin rash, thats shingles.
This time, the pain will likely come before the rash some people only experience the pain without any visible symptoms. Like chickenpox, shingles usually isnt life-threatening, but it can cause complications, including neurological problems, skin infections and eye infections that lead to vision loss.
Connie Sommer
Whats The Difference Between Chickenpox And Shingles
Adults can develop shingles if theyve already had chickenpox. Also called herpes zoster, shingles is a reactivation of the virus that causes chickenpox. After you recover from chickenpox, the virus doesnt entirely disappear it lies dormant in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain. When it springs into action again as a painful skin rash, thats shingles.
This time, the pain will likely come before the rash some people only experience the pain without any visible symptoms. Like chickenpox, shingles usually isnt life-threatening, but it can cause complications, including neurological problems, skin infections and eye infections that lead to vision loss.
You May Like: What Is The Best Thing To Put On Shingles
What Are The Side Effects
The shingles vaccines are very safe.
Common side effects to the vaccines include headache as well as soreness, redness and swelling where the vaccine was given. Itching and a rash may also occur after getting Zostavax® II. Other reactions that may occur after getting Shingrix® include fever, muscle soreness, fatigue, shivering, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
It is important to stay in the clinic for 15 minutes after getting any vaccine because there is an extremely rare possibility of anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening allergic reaction. This may include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the throat, tongue, or lips. The chance of true anaphylaxis is about 1 in 1 million vaccine doses. Should this reaction occur, your health care provider is prepared to treat it. Emergency treatment includes administration of epinephrine and transfer by ambulance to the nearest emergency department. If symptoms develop after you leave the clinic, call 9-1-1 or the local emergency number. Learn more about anaphylaxis on our vaccine side effects page.
It is important to always report serious or unexpected reactions to your health care provider.
Dose Route Of Administration And Schedule

Live attenuated zoster vaccine
Dose
Each dose is 0.65 mL .
Route of administration
Each dose is 0.5 mL .
Route of administration
Intramuscular, into the deltoid region of the upper arm.
Administration of the RZV as a subcutaneous injection is a vaccine administration error and should be avoided. However, if Shingrix is inadvertently administered subcutaneously, that dose will be considered as valid in the vaccine series. The second dose will be given as per vaccine schedule.
For more information, refer to Vaccine Administration Practices in Part 1.
Schedule
2 doses, 2 to 6 months apart. A 0,12 months schedule may be considered for improved adherence to the 2nd dose .
Providers should consider different strategies to promote adherence to the two dose schedule for RZV .
Read Also: Can You Have Internal Shingles