Research Into Mrna Vaccines For Shingles
Several companies are researching the potential use of mRNA vaccines for shingles. Pfizer and BioNTech are partnering on an mRNA shingles vaccine just as they did with vaccines for the flu and COVID-19.
A major advantage to the technology is the ability to develop new vaccines quickly. The fact that mRNA vaccines are synthetic and dont rely on actual virus particles also means they can be quickly produced in large numbers.
While the Shingrix vaccination is considered safe, the FDA has confirmed a link between Shingrix and Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Phasing out the old vaccine with the introduction of a new one, as the FDA did when Shingrix replaced Zostavax, might eliminate this potential issue.
Pfizer and BioNTech hope to begin clinical trials later this year.
Dont Miss: How To Install Timberline Shingles
What Does The Shingles Vaccine Do
The shingles vaccine can prevent shingles. Every year, about 1 million people in the United States get shingles. Anyone whos had chickenpox can get shingles. Thats because the varicella-zoster virus lives silently in your nervous system after you’ve had chickenpox. The virus can reactivate later in your life if your immune system is weakened. Your risk of getting shingles goes up as you get older. In the United States, 1 in 3 people will get shingles in their lifetime.
Which Vaccine Should Be Used
Shingrix is preferred over Zostavax for people aged 50 years and over, for the prevention of herpes zoster and its complications due to its higher efficacy. Shingrix is now available in Australia under private prescription only. The manufacturer has not submitted it for supply on the NIP at this stage.
Zostavax remains an alternative to Shingrix for people who are immunocompetent. It is available on the NIP for all people at 70 years of age.
People who are immunocompromised
Zostavax is generally contraindicated in people who are immunocompromised. Shingrix is recommended in this population.
Zoster Vaccine Efficacy
Shingrix demonstrated a high efficacy against herpes zoster of about 97% in adults 50 years and older and about 91% in those aged 70 years and older.
In clinical trials, Zostavax efficacy was lower and decreased with increasing age .
10 Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation Clinical Advise Statement of Clinical Use of Zoster Vaccines in Older Adults in Australia Issue date August 2021
11 TGA registered on 16 December 2021:
Don’t Miss: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Hands
Warnings Of Shingrix And Zostavax
Shingrix and Zostavax can cause hypersensitivity, or allergic, reactions in those with allergies to vaccine ingredients. Zostavax may cause severe allergic reactions in those with a known allergy to gelatin or neomycin. Severe allergic reactions can lead to severe rash and trouble breathing .
Zostavax should be avoided in those who take immunosuppressive agents and those who are affected by medical conditions that weaken the immune system.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about other precautions before getting a shingles vaccine.
New Shingles Vaccine Now Available In Australia June 2021
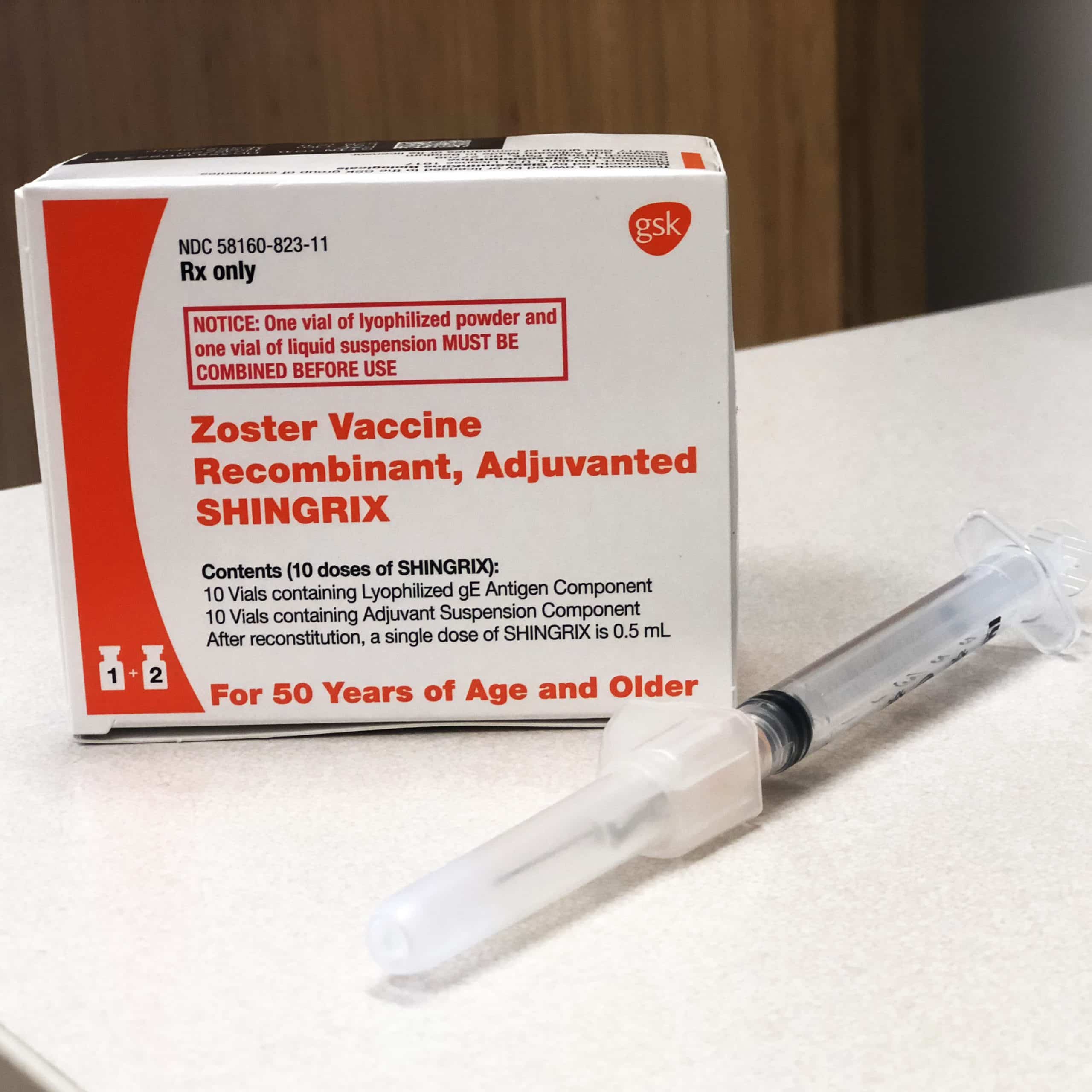
GSK Australia today announced that a new vaccine to help protect against shingles in adults aged 50 years and older is now available on the private market in Australia.
While most people fully recover from shingles , it can be a painful and potentially debilitating condition triggered by the reactivation of the chicken pox virus in adulthood. Shingles can affect up to 1 in 3 people at some stage in their lives, and this risk increases with age1. In Australia, it is estimated that 120,000 new cases of shingles occur each year and account for approximately one in 1000 of all GP visits2.
According to infectious disease physician and clinical virologist Professor Tony Cunningham, the availability of additional options to help prevent shingles and associated complications are welcome.
Shingles can be very painful. The pain associated with shingles is often described as burning, shooting or stabbing. The acute pain can last for between 2 to 4 weeks, with some people potentially experiencing complications and chronic pain for months.
Doctors never like to see their patients in pain. Shingles can be difficult to treat once the symptoms break out, so vaccines can play an important role in helping reduce the impact of the infection here in Australia where up to 1 in 3 people experience the disease1 said Professor Cunningham.
Co Luu, Vaccines Medical Director at GSK Australia, says bringing innovative medicines and vaccines to Australia is a core focus.
| Hamish Walsh |
|
0400 773 733 |
Read Also: How Do You Determine If You Have Shingles
Im Living With Hiv Is It Safe For Me To Get Shingrix
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention hasnt made a recommendation about the use of Shingrix in people living with HIV.
However, one study looked at healthy adults ages 18 and older who were living with HIV and had an HIV dosing schedule that was customized to their needs. These people received the Shingrix vaccine, and the study results did not report any safety issues.
If youre living with HIV, talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of getting Shingrix.
How Long After Ive Received The Shingles Vaccine Am I Contagious
With the currently authorized shingles vaccine, Shingrix, you wont be contagious. The old vaccine, Zostavax, used a weakened form of the live varicella-zoster virus. Therefore, people worried about spreading the disease to the people around them.
Shingrix doesnt use a live version of the varicella-zoster virus. It is inactivated, which means it uses a dead version of the virus. Therefore, you have no risk of transmitting the disease to anyone.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
No one likes to get shots, especially for something youve already been vaccinated for. But the newer version of the shingles vaccine is one youll want to offer up your arm for. The Shingrix vaccine is more than 90% effective at helping you prevent shingles. Since most of us have had chickenpox in the past, the shingles vaccine is an easy way to prevent the dormant chickenpox virus from creeping up and hitting you again with shingles.
Read Also: How To Ease Nerve Pain From Shingles
What Does It Cost
Most insurances will cover the shingles vaccine, but the coverage varies. The vaccine can be administered at an OSF office under your medical benefits, but some plans, based on your age, will require the vaccine to be administered at a retail pharmacy under your pharmacy benefits.
Out-of-pocket costs will vary by plan and deductible but may be covered as a preventive care benefit. Check with your provider or insurance plan for more details.
Getting the shingles vaccine when you are eligible is the best way to protect yourself from shingles, Jason said. Even if you previously received Zostavax vaccine in the past , Shingrix can provide additional protection and is still recommended for vaccination.
Shingrix is in high demand, which has led to shortages at times. Call ahead to see if its available and ask to be added to the list if theres a wait. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about being vaccinated today.
How Can I Get The Shingles Vaccine
You can buy the shingles vaccine at most pharmacies and travel clinics. Shingrix® is given as a series of 2 doses, 2 to 6 months apart, and costs about $150/dose. Zostavax® II is given as 1 dose and costs about $200. Some health insurance plans may cover the cost of the vaccine check with your provider.
If you buy the vaccine at a travel clinic, a doctor or nurse on site will be able to immunize you. Most pharmacists in B.C. are also able to immunize.
If you want to be immunized by your doctor, find out if they have a supply of the shingles vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles From The New Vaccine
How Does The Shingles Vaccine Work
The vaccine recommended for most people is a live vaccine called Zostavax. It contains a weakened chickenpox virus . It’s similar, but not identical, to the chickenpox vaccine.
People with a weakened immune system cannot have live vaccines. They will be offered a non-live vaccine called Shingrix. It activates the immune system but also contains an ingredient called an adjuvant, which helps to boost the response to the vaccine.
Very occasionally, people develop chickenpox following shingles vaccination . Talk to a GP if this happens to you.
Are There Any Side Effects Of Taking The Shingles Vaccine
As with any medication or vaccine, the shingles vaccine has possible side effects. The shot helps your body develop an immune defense against shingles. Any side effects you might have are temporary and usually resolve within two to three days.
You might have side effects from the first shot, the second shot, or both shots. You can take an over-the-counter pain reliever like Advil or Tylenol .
Common side effects can include:
- Redness and swelling at the shot site
- Sore arm and mild to moderate pain
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a nervous system disorder, is a condition that has reported as developing, although rarely, after Shingrix. However, the risk of developing GBS also is slightly elevated if you get shingles.
Talk with a healthcare provider about the shingles vaccines possible risks and side effects and what to do if you experience any.
Don’t Miss: What Does Shingles Rash Look Like At First
What Are The Benefits Of The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccines are the best way to protect you from getting shingles. The vaccines have been shown to reduce the risk of getting shingles by 50% for Zostavax® II, and to more than 90% for Shingrix®.
For those who still get shingles after being immunized, the vaccines can reduce pain, including the type of pain that lasts after shingles.
Why Is It Important To Receive A Vaccination Against Shingles
About 33% of adults in the U.S. will develop shingles at some point in their lives. Shingles can cause painful blisters, a rash, chills, and fever, among other symptoms. Many people who have shingles later develop PHN, which can cause long-lasting pain that is difficult to treat.
Getting the Shingrix vaccine can help individuals avoid shingles and PHN and help prevent shingles from spreading to vulnerable people.
Don’t Miss: Who Do You Get Shingles
New Shingles Vaccine Changes Recommendations For Adults
The pain associated with shingles can be unbearable. It can last for months and be so debilitating that even routine tasks become too difficult to bear. The single dose Zostavax® vaccine had been recommended since 2006, and it is about 50 percent effective at protecting against a shingles rash and about 75-80 percent effective at protecting against pain.
Fortunately, a new shingles vaccine, called Shingrix®, offers improved protection not only from developing the disease, but also against the severe pain associated with shingles. Shingrix is 95 percent effective at protecting against both the rash and associated pain. It is given as two doses separated by two to six months.
In this video, Dr. Offit discusses the differences between the two shingles vaccines and updated recommendations for adults. These include getting the vaccine at 50 years of age instead of 60 and being revaccinated if youve previously received the older version .
Are There Any Restrictions After A Shingles Shot
You should not receive the shingles vaccine if you are pregnant, if you have an active shingles infection, or if you previously had an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine. If youre eligible for the vaccine and receive the vaccination, there are no restrictions afterward and you can leave the doctors office or pharmacy as soon as the shot is complete.
Recommended Reading: What Shingles Vaccine Is Best
Administering And Storing Shingrix
- Adults 50 years and older should receive 2 doses of Shingrix. Give the second dose 2 to 6 months after the first.
- Administer Shingrix intramuscularly in the deltoid region of the upper arm with a 1- to 1.5-inch needle.
- Both vials of Shingrix must be refrigerated at a temperature of 36-46° F. Do not use if exposed to temperatures below 36° F.
Live Shingles Vaccine Vs Non
A live vaccine is one that contains a weakened form of a germ. Shingrix is not a live vaccine. Its an inactive vaccine, which is a vaccine thats made from a germ thats been killed.
Because Shingrix is inactive, more people can receive it. This includes people with a weakened immune system .
Zostavax was a shingles vaccine that was live.
People with weakened immune systems are typically advised against receiving live vaccines. This is because on very rare occasions, live vaccines can mutate back to the full-strength germ that causes a disease. If this happens, people with weakened immune systems would have a much higher risk for developing the disease that the vaccine is meant to prevent.
Read Also: What Does Shingles Look Like On Your Head
How Safe Is Shingrix
studies showed that Shingrix was safe and effective.
There have been concerns about ingredients, such as thimerosal, that may be added to vaccines. Thimerosal is a kind of preservative that contains mercury. Its added then taken out of some vaccines to keep other germs and bacteria from growing. The concern arose when early research connected thimerosal to autism. This link has since been found to be false. Shingrix doesnt contain thimerosal.
Who Needs A Shingles Vaccine
Shingrix is recommended for adults aged 50 or older. You should still get the vaccine even if youve had shingles in the past, as it is possible to get it again.
You can also get Shingrix if you received Zostavax in the past. This is important because studies have shown that the efficacy of Zostavax over time.
Don’t Miss: Is The Shingles Vaccine Free
Shingrix For Prevention Of Shingles
Shingrix is a vaccine thats used to prevent shingles . Its approved for use in people:
- ages 50 years and older
- ages 18 years and older who have an increased risk of shingles
People with an increased risk of shingles include those with a weakened immune system, such as people with HIV.
Shingrix is not meant for use in preventing chickenpox .
Effectiveness for prevention of shingles
Shingrix has been found to be effective in helping to prevent shingles. For details on how the drug performed in clinical studies, see Shingrixs
state that Shingrix is the preferred vaccine for shingles. They recommend it for:
- all adults ages 50 years and older
- adults ages 18 to 50 years with a weakened immune system
Dose Route Of Administration And Schedule
Live attenuated zoster vaccine
Dose
Each dose is 0.65 mL .
Route of administration
Each dose is 0.5 mL .
Route of administration
Intramuscular, into the deltoid region of the upper arm.
Administration of the RZV as a subcutaneous injection is a vaccine administration error and should be avoided. However, if Shingrix is inadvertently administered subcutaneously, that dose will be considered as valid in the vaccine series. The second dose will be given as per vaccine schedule.
For more information, refer to Vaccine Administration Practices in Part 1.
Schedule
2 doses, 2 to 6 months apart. A 0,12 months schedule may be considered for improved adherence to the 2nd dose .
Providers should consider different strategies to promote adherence to the two dose schedule for RZV .
Recommended Reading: Do You Need To See A Doctor For Shingles
How Long Does It Take To Work
It takes time for your body to make enough antibodies to fight off germs and protect you from certain diseases.
Results from clinical studies of Shingrix showed that the recommended dosing schedule for Shingrix does cause an immune response.
How long Shingrix takes to work may not be the same for everyone. The timing for you will depend on your body chemistry. In general, you should be protected from shingles soon after the second dose.
Studies in animals showed that there was no risk with Shingrix during pregnancy. However, animal studies dont always predict the way humans would respond.
If youre pregnant or planning to become pregnant, wait until after youve had your baby to get the Shingrix vaccine. Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
There havent been enough studies to show whether Shingrix appears in breast milk.
Until more is known, its best to wait until youve finished breastfeeding before getting Shingrix.
Simultaneous Administration With Other Vaccines
RZV and LZV may be administered concomitantly with other live vaccines given by the parenteral, oral, or intranasal routes. For concomitant parenteral injections, different injection sites and separate needles and syringes should be used.
In general, inactivated vaccines including RZV may be administered concomitantly with, or at any time before or after, other inactivated vaccines or live vaccines protecting against a different disease.
LZV may be given at any time before or after live oral or intranasal vaccines. If two live parenteral vaccines are not administered concomitantly, there should be a period of at least 4 weeks before the second live parenteral vaccine is given.
Concomitant administration of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine and LZV has not resulted in decreased efficacy and so the two vaccines can be given concomitantly.
For more information, refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1.
Also Check: How Do You Feel If You Have Shingles
What Is The Brand Name Of The Shingles Vaccine
There are 2 shingles vaccines used in the UK:
- Zostavax, a live vaccine given as 1 dose
- Shingrix, a non-live vaccine given as 2 doses, 2 months apart
Most people will have the Zostavax vaccine. The Shingrix vaccine is recommended if Zostavax is not suitable for you, for example if you have a condition that affects your immune system.
You can read more about the shingles vaccines in the patient information leaflets:
Who Should Not Receive The Live Zoster Vaccine
- Primary or acquired immunodeficiency
- Haematologic neoplasms: leukaemias, lymphomas myelodysplastic syndromes
- Post-transplant: solid organ , haematopoietic stem cell transplant
- Immunocompromised due to primary or acquired immunodeficiency
- Other significantly immunocompromising conditions
Before vaccinating people with Zostavax
Obtain medical history prior to vaccination with Zostavax, check contraindications of Zostavax in immunocompromised individuals.
In persons who are or have recently been immunocompromised, the safety of administering Zostavax should always be considered on a case-by-case basis. If there is uncertainty around the level of immunocompromise and when vaccine administration may be safe, vaccination should be withheld and expert advice sought from the treating physician and/or an immunisation specialist.
UPDATE: Denosumab has been removed from the list of immunosuppressive medications contraindicated with Zostavax as there is currently not enough evidence to suggest it is a contraindication to Zostavax.
Also Check: Does Insurance Cover Shingles Shots