Why Is It Still Important For Cancer Patients To Receive The Shingles Vaccine
People living with cancer and undergoing treatment for it are at a higher risk for developing shingles and complications. The recombinant shingles vaccine is both safe and effective for people with compromised immune systems, including cancer patients. Getting the vaccine will reduce the number of cases and reports of complications.
The timing of when you get the vaccine may be aligned with when your immune system is stronger.
For people with solid tumor cancers specifically, researchers have found that the vaccine produced an expected immune response, even in those who were undergoing chemotherapy. The immune response lasted even a year after getting the vaccine.
Stages Of Hodgkin Lymphoma
When testing is complete, it should be possible to determine the stage of your lymphoma. Staging means scoring the cancer by how far it’s spread.
The main stages of Hodgkin lymphoma are:
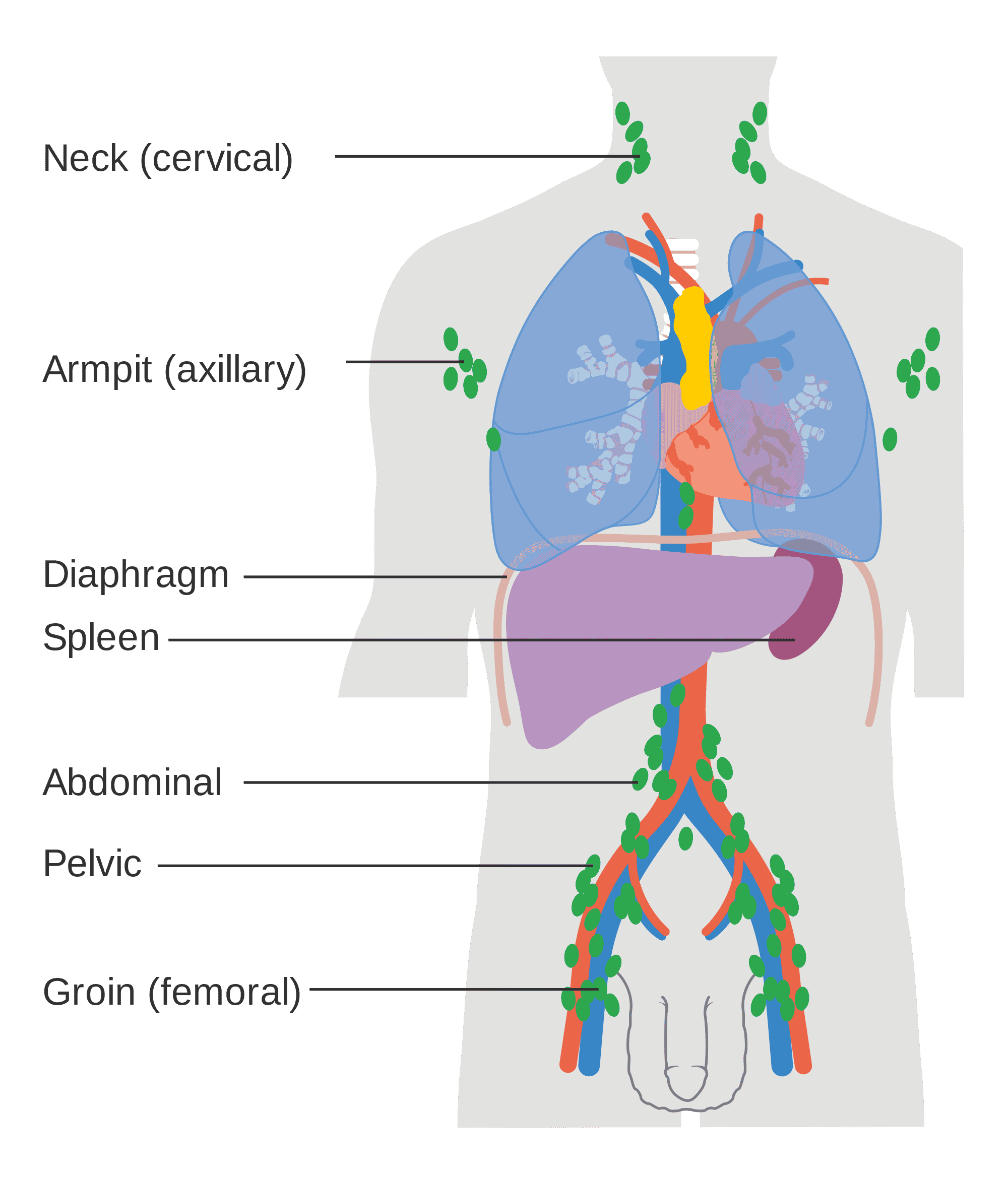
- stage 1 the cancer is limited to one group of lymph nodes, such as your neck or groin nodes either above or below your diaphragm
- stage 2 2 or more lymph node groups are affected, either above or below the diaphragm
- stage 3 the cancer has spread to lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm
- stage 4 the cancer has spread through the lymphatic system and is now present in organs or bone marrow
Health professionals also add the letters A or B to your stage, to indicate whether or not you have certain symptoms.
A is put after your stage if you have no additional symptoms other than swollen lymph nodes. B is put after your stage if you have additional symptoms of weight loss, fever or night sweats.
What Does A Rash From Hodgkin Lymphoma Look Like
If youre experiencing a skin rash, you may be wondering whats causing it and whether it could be a sign of Hodgkin lymphoma. Although certain other types of lymphoma can cause skin irritation, this symptom is fairly uncommon with Hodgkin lymphoma, which sometimes produces pruritus without a rash. Researchers believe the itchiness is caused by cytokines, which are chemicals released by the bodys immune system in response to lymphoma. Cytokines can irritate nerve endings in the skin, which can in turn cause persistent itching. Many individuals experience this itchiness in their hands, lower legs or feet, while others feel it throughout their entire body. Patients often report that the itching tends to worsen while they are lying in bed at night.
You May Like: What Are The Beginning Signs Of Shingles
For Stem Cell Transplant Patients
The CDC and the American Society for Blood & Marrow Transplantation recommend flu shots for all bone marrow, stem cell and cord blood transplant survivors beginning one year post-transplant and continuing every year thereafter. The flu shot is also recommended for others living or working in the household. Although most transplant centers follow the current CDC guidelines regarding flu shots, some recommend flu shots even earlier than one year after the transplant.
For more information about the flu and special considerations for people who have cancer, visit the CDC’s Cancer and Flu page.
The Link Between Cancer And Shingles
Also called herpes zoster, shingles is a condition characterized by a painful rash on one side of the face or body. It’s caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus in the body .
People diagnosed with lung cancer and other solid tumor cancers are at a higher risk for developing shingles.
More specifically, the highest risk for shingles in people with solid tumor cancers includes those who:
- Have been recently diagnosed
- Are undergoing chemotherapy
The risk of developing shingles is also higher in people with blood-related cancers.
Both cancer and cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, impact your immune system and reduce your ability to fight off infections.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Certainteed Landmark Shingles
Stage 4 Lymphoma Prognosis
Lymphoma is not a cookie-cutter disease. Many factors may have an impact on your potential prognosis. Your response to treatment, age, and overall health all play a role. The number of lymph node areas or organs affected may also have an impact.
The data used to compute the five-year relative survival rate for stage 4 lymphoma are based on the experiences of people who were diagnosed five or more years ago. Since treatments are always improving, this data may not take into account new treatments and, so, may not be able to predict what will happen in your case.
These numbers are based on data maintained by the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database:
- Stage 4 non-Hodgkin’s diffuse large B-cell lymphoma has a five-year relative survival rate of 57%
- Stage 4 non-Hodgkin’s follicular lymphoma has a five-year relative survival rate of 86%
- Stage 4 Hodgkin’s lymphoma has a five-year relative survival rate of 82%
Diagnosing Stages Of Lymphoma
There are several diagnostic tests used to determine the lymphoma stage. Testing can also help determine how you’re responding to your current treatment for this disease. These tests vary, based on your symptoms.
Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes will be biopsied to confirm a diagnosis of Hodgkins or non-Hodgkins lymphoma. In many instances, the entire lymph node will be removed for laboratory testing. This ensures that enough tissue is available for analysis and diagnosis.
A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy will be done to determine if cancer has spread to the bones. Usually, the bone marrow is taken from the hip bone for this test.
A spinal tap to remove and test cerebrospinal fluid may be done if your doctor suspects that lymphoma has spread to the brain.
Sampling of pleural fluid or peritoneal fluid may be done to check for spread into the chest or stomach. Lymphoma can cause fluid buildup in these and other areas of the body. These tests use fluid extracted from the abdomen or chest to look for cancer cells.
Imaging tests will be done to identify enlarged lymph nodes and organs where cancer may have spread. They include:
- Computed tomography scan: A cross-sectional detailed X-ray study
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to produce images
- Magnetic resonance imaging scan: Uses magnetic fields
- Bone scan: Uses a radioactive tracer to look for bone damage and cancer
- Positron-emission tomography scan: Uses radioactive sugar to identify highly active cells
You May Like: How Often Do You Have The Shingles Shot
Signs And Symptoms Of Non
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can cause many different signs and symptoms, depending on the type of lymphoma and where it is in the body. Sometimes it might not cause any symptoms until it grows quite large.
Having one or more symptoms doesnt mean you definitely have lymphoma. In fact, many of the symptoms listed here are more likely to be caused by other conditions, such as an infection. Still, if you have any of these symptoms, have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Feeling full after only a small amount of food
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath or cough
- Severe or frequent infections
Some people with Non-Hodgkin lymphoma have what are known as B symptoms:
- Fever without an infection
- Drenching night sweats
- Weight loss without trying
What Is The Outlook For People With Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is treatable. About 90% of people with early-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma are cured. Among people with more advanced disease, the cure rate is lower. Younger people respond to treatment better than older adults, and females tend to respond to treatment more successfully than males.
Sometimes, the treatments that cure Hodgkin’s lymphoma may cause health problems later in life, including an underactive thyroid, lung problems, heart disease, or other types of cancer, such as melanoma or breast cancer. Therefore, people whove had this type of cancer are advised to continue regular monitoring throughout the rest of their lives.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles On Your Breast
How Is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Diagnosed
Doctors may suspect Hodgkin’s lymphoma after hearing about the patients symptoms and doing a physical exam. They can confirm a diagnosis by doing a biopsy.
After learning about symptoms like fever or unintended weight loss, and checking for swollen lymph nodes, a doctor will want to know about their personal and family medical history. Its helpful to know that a first-degree relative may have had Hodgkin lymphoma.
To diagnose Hodgkin’s lymphoma, a doctor surgically removes some or all of an affected lymph node to biopsy it. After a biopsy, doctors look within the sample for abnormal cells known as Reed-Sternberg cells. Their presence confirms a diagnosis of Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Further testing is done to stage the cancer, which helps determine treatment. This may involve a PET scan, a CT scan, blood tests, and/or biopsy of the bone marrow, in some cases.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Anyone may get Hodgkin’s lymphoma, although its rare in young children. Its most common among:
- Adolescents and young adults in their teens, 20s, and 30s
- Adults older than 50 or 60
- People with a family history of Hodgkin lymphoma
- People with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Sjögren syndrome, or celiac disease
- People who have had EBV, including those who had mono as teens
- People with HIV, many of whom have had EBV
Read Also: Who Should Get The Shingles Vaccine
Ebv And Hodgkin Lymphoma
Recognition of an association of infectious mononucleosis with Hodgkin lymphoma predates the discovery of Epstein-Barr virus and the present understanding that the disease entity is a malignancy of B lineage cells. In the last several years, our understanding of that association has advanced considerably. There are new insights into infectious mononucleosis and perturbations in cellular immunity, new insights relating to the role that virus may play in the molecular pathogenesis of HL, an emerging appreciation of the increased incidence of HL in HIV and its relationship to immune suppression, and new approaches to clinical monitoring and therapy. The terminology used to describe the association between the ubiquitous virus, the symptomatic and asymptomatic primary infection, and virus-associated tumor is sometimes ambiguous. Please refer to Table for clarification of terms as they are used here.
Symptoms From Lymphoma In The Chest
When lymphoma starts in the thymus or lymph nodes in the chest, it may press on the nearby trachea , which can cause coughing, trouble breathing, or a feeling of chest pain or pressure.
The superior vena cava is the large vein that carries blood from the head and arms back to the heart. It passes near the thymus and lymph nodes inside the chest. Lymphomas in this area may push on the SVC, which can cause the blood to back up in the veins. This can lead to swelling in the head, arms, and upper chest. It can also cause trouble breathing and a change in consciousness if it affects the brain. This is called SVC syndrome. It can be life-threatening and must be treated right away.
You May Like: How Often To Get Shingle Shot
Inactivated Shingles Vaccine Now Available For People Who Cant Have Live Vaccines
An alternative to the live shingles vaccine is now available in the UK for people with lowered immunity.
This month, a shingles vaccine became available in the UK for people who cant have the live vaccine.Currently, shingles vaccination is recommended for people aged 70 to 79. However, until recently, the only vaccine available in the UK was based on a live but weakened version of varicella zoster virus . This is not suitable for people with low immune systems because it could cause shingles infection.From 1 September 2021, a vaccine called Shingrix® is available for people with lowered immunity. This contains a protein made by the varicella zoster virus but it does not contain the virus itself. It cannot cause shingles.People aged 70 to 79 who may be eligible for Shingrix® vaccine instead of the live vaccine include:
- people with Hodgkin lymphoma or high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma who are less than 12 months since achieving cure
Disseminated Herpes Zoster Infection Initially Presenting With Abdominal Pain In Patients With Lymphoma Undergoing Conventional Chemotherapy: A Report Of Three Cases
Copyright: ©Okumaet al. This is an open access article distributed under theterms of CreativeCommons Attribution License.
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
Introduction
Case report
Case 1
A 61-year-old woman undergoing treatment for grade 2follicular lymphoma, clinical stage IV, with a low InternationalPrognostic Index score, presented at the National CancerCenter Hospital in December 2013, with severe upperabdominal pain that had lasted 3 days prior to admission. Thepatient had a long history of treatment for follicular lymphoma, asfollows: 6 cycles of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine andprednisone withrituximab 1 course of rituximab monotherapy consisting of 8cycles 1 cycle of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine andprednisone 5 cycles of bendamustine and 6 cycles of gemcitabine. The patient was on day 5of the second cycle of salvage C-MOPP prior to admission, and hadalso been taking 15 mg/day prednisolone for tumor fever since 4months prior to admission. The cluster of differentiation 4cell count was 118 cells/mm3 on admission, and had been< 200 cells/mm3 since 10 months prior . The serum immunoglobulin G level was 289 mg/dl and hadbeen < 400 mg/dl since 10 months prior .
Case 2
Case 3
Discussion
Table I. |
Table II. |
| C-MOPP withoutprocarbazine, 2 cycles | 20 |
| CHOP, 3 cycles andRT, 40 Gy | |
References
Related Articles
Also Check: Laminated Comp Shingle Rfg Without Felt
Shingles Vaccine Shows Promise In Lymphoma Patients
- Shingles Vaccine Shows Promise in Lymphoma Patients
Vaccines are often not effective in individuals with lymphoma, but a new study shows that it is possible for these patients to mount a potent immune response to the shingles vaccine.
Wilmot Cancer Institute researchers focused on this hard-to-vaccinate group and how best to prevent this particular illness because people with blood cancers are at higher risk of shingles and its complications, which can be fatal in this population. Shingles is a painful reactivation of the chicken pox virus. It is most common in older adults and can cause debilitating rashes and other health problems.
The shingles vaccine is standard care for everyone over age 50. In people with lymphoma, however, doctors have had two concerns about this vaccine in the past: That a weakened immune system due to B-cell blood cancer does not allow a person to make an effective immune response to the vaccine and that a common treatment for lymphoma, known as BTK inhibitors, might interrupt or prevent an immune response to the vaccine.
According to the Wilmot research published in the journal, Leukemia, 32 lymphoma patients who received a newer version of the shingles vaccine responded favorably. The new vaccine uses an inactivated virus and is safer for people with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms From Lymphoma In The Abdomen
Lymphomas that start or grow in the abdomen can cause swelling or pain in the abdomen. This could be from lymph nodes or organs such as the spleen or liver enlarging, but it can also be caused by the build-up of large amounts of fluid.
An enlarged spleen might press on the stomach, which can cause a loss of appetite and feeling full after only a small meal.
Lymphomas in the stomach or intestines can cause abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting.
Read Also: What Can Help With Shingles Pain
National Health Insurance Research Database
The data for this study were from the National Health Insurance Research Database , which is derived from the National Health Insurance of Taiwan and has been which was implemented since March 1st of 1995. This nationwide population-based database provided the most comprehensive information for this study.
For patients with certain severe illnesses, such as autoimmune diseases, end-stage renal disease and malignant diseases, the NHI has established a registration system . The patients who met the criteria for catastrophic illness are registered, and their responsibilities for all co-payments are waived. For patients with NHL, certificates of catastrophic illness are issued when the lymphoma pathologically proven.
Flu Shots And Immunizations
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends seasonal influenza shots for cancer patients and survivors and anyone who has contact with a cancer patient. Unless contraindicated by your oncologist, LLS encourages blood cancer patients and survivors to get their flu shot every year.
Cancer patients and survivors should get the flu shot, not the nasal mist form of the flu vaccine. Shots are safe for people with compromised immune systems because they’re made from inactivated virus the flu mist is made from a live but weakened virus.
The ideal time to be vaccinated for seasonal flu is in the fall as soon as the shot becomes available as it takes about two weeks for the vaccination to begin providing protection. Before you get the shot, let the person who is providing the vaccine know about any allergies you have and any previous reactions to a flu shot.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles Vaccine If You Had Shingles
Active Shingles Infection As Detected On 18f
- 1Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology, Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO, USA
- 2Department of Hematology/Oncology, Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO, USA
- 3Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology, St. Louis VA Medical Center, St. Louis, MO, USA
We present the case of a 56-year-old male with a history of recurrent follicular lymphoma undergoing chemotherapy with multiple 18F-FDG PET-CT studies at an outside facility. He developed a painful erythematous, pruritic rash in the left back requiring a visit to the emergency room. He was diagnosed and treated for Varicella zoster infection. He then presented to our imaging center 2 months later for a follow up 18F-FDG PET/CT study. Imaging demonstrated a cutaneous band of increased metabolic activity in the upper back following a dermatomal distribution. This was confirmed to be in the same area as the treated Varicella zoster eruption. A subsequent follow up 18F-FDG PET-CT scan 4 months later to confirm tumor resolution demonstrated the abnormal band of uptake in the back had resolved. This case illustrates the significance of being aware of this entity and to distinguish it from metastasis, especially in patients with a known history of malignancy.