How Cdc Monitors Vaccine Safety
CDC and FDA monitor the safety of vaccines after they are approved or authorized. If a problem is found with a vaccine, CDC and FDA will inform health officials, health care providers, and the public.
CDC uses 3 systems to monitor vaccine safety:
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System : an early warning system, co-managed by CDC and FDA, to monitor for potential vaccine safety problems. Anyone can report possible vaccine side effects to VAERS.
- The Vaccine Safety Datalink : a collaboration between CDC and 9 health care organizations that conducts vaccine safety monitoring and research.
- The Clinical Immunization Safety Assessment Project: a partnership between CDC and several medical research centers that provides expert consultation and conducts clinical research on vaccine-associated health risks.
Patient Reports Of Side Effects
During the first eight months of Shingrixs post-marketing use, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS, received 4,381 total reports of adverse events of these 130 were serious.
For every 100,000 doses distributed, the CDC found 136 complaints filed in the system. Approximately 3.2 million doses were distributed by GlaxoSmithKline during the eight-month period of reporting analyzed by the CDC.
Fever, chills and body aches and pain, swelling and redness in the arm receiving the shot were common side effects.
Yet seven patients died within six hours to six weeks of receiving Shingrix, the CDC said. The cause of four of these deaths was cardiovascular disease . Two were immunosuppressed patients who died of sepsis. And one 86-year-old woman died after a fall. v An eighth death after the use of Shingrix was also reported to VAERS, though this was not confirmed by the CDC.
Dr. Elisabeth M. Hesse, lead author of the report and a medical officer in the CDCs Office of Immunization Safety, wrote in an email that no information in medical documentation indicated the reported deaths were related to vaccination.
She noted that the Rotashield vaccine for infants was withdrawn from the market after reports to VAERS of bowel obstruction and an investigation that verified these claims.
What Are The Advantages Of Getting The Shingles Vaccine
The shingles vaccine reduces your risk of getting shingles. Shingles causes a painful rash that usually develops on one side of your body or face. Some people describe the pain as an intense burning or shooting sensation. The rash is often a single strip that wraps around one side of your body or is on one side of your face. It consists of blisters that normally crust over in seven to 10 days. The rash generally clears up within a month.
Some people with shingles also experience additional symptoms including fever, headache, chills or upset stomach.
For some people, the pain from the rash can last for months or even years after the rash goes away. This long-term pain is called postherpetic neuralgia , and it is the most common complication of shingles.
Also Check: What R The Symptoms Of Shingles
Should I Get A Vaccine
Doctors say most healthy people over 50 should get Shingrix, as well as anyone 19 or older who are immunocompromised. Itâs available at pharmacies as well as doctorsâ offices. Most people have been exposed to the chickenpox even if they didnât actually develop symptoms.
You should get the Shingrix vaccine unless:
- You are allergic to any part of the vaccine
- Had a blood test that proves you never had chicken pox
- Have shingles now
- Are breastfeeding or nursing.
What Are The Side Effects
Shingrix can make the area where you get the shot swell or feel sore. Other effects include:
- Many people who get the vaccine have muscle aches, headaches, or feel tired.
- About 1 in 4 people have a fever or an upset stomach.
Younger people are more likely to have these side effects, and they typically last 2 or 3 days.
Itâs also possible to have an allergic reaction to an ingredient in the vaccine. If you have problems breathing, feel your face or throat swelling, or feel weak or dizzy after the shot, call 911 and get medical help right away.
Don’t Miss: Can You Put Peroxide On Shingles
Long Term Side Effects
In rare cases, the live shingles vaccine, Zostavax, can cause a skin rash or shingles.
The rash that occurs with shingles can affect any area of the body, but it often appears as a line of blisters that wraps around the torso.
Within a few days the blisters cluster, and they continue to form for several more days. The blisters can take 2â3 weeks to heal, according to the American Academy of Dermatology.
Other common symptoms of shingles include:
two shingles vaccines for adults: the recombinant zoster vaccine and the zoster virus vaccine .
Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, zoster vaccine, inactivated may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking zoster vaccine, inactivated:
Rare
- Ankle, knee, or great toe joint pain
- fever greater than 39 degree Celsius
- joint stiffness or swelling
- lower back or side pain
- swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin
Incidence not known
- Hives, welts, or itching
- inability to move the arms and legs
- large, hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, throat, hands, legs, feet, or sex organs
- redness of the skin
- sudden numbness and weakness in the arms and legs
Don’t Miss: How To Care For Someone With Shingles
New Shingles Vaccine: What You Need To Know
Nov. 13, 2019 — Unlike some vaccines, thereâs been so much demand for the new shingles vaccineShingrix that itâs not always easy to find. It was approved in 2017, and the CDC recommends the vaccine for adults 50 and older to prevent this painful, blistering illness. It is being used in place of the previous vaccine, Zostavax.
More than a year later, doctors say they are learning more about how it works, its safety risks, and how it compares to Zostavax.
How effective is Shingrix?
âIt’s just remarkable,” says Wilbur Chen, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “It has performed better than I expected.”
In studies, Shingrix was more than 97% effective at preventing shingles in people 50 and older. It works just as well in older adults, who are at greater risk for a painful shingles complication called postherpetic neuralgia . “When 70- and 80-year-olds get shingles, it can be extremely debilitating,” Chen says.
By contrast, Zostavax cuts the risk of shingles by only 51% and PHN by 67%. It’s only about 38% effective in people over age 70.
How safe is Shingrix?
“So far so good,” Schaffner says. The main side effect is soreness in the arm where you get the shot.
Other side effects are mild and usually last for 2 to 3 days, including:
Who shouldn’t get Shingrix?
Can I get the Shingrix vaccine now?
What do doctors still need to learn about Shingrix?
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Its normal to have questions before you get a vaccine. Some common questions you may want to discuss with your healthcare provider include:
- When should I get the shingles vaccine?
- What side effects should I expect?
- How does the shingles vaccine work?
- When should I schedule each dose of the shingles vaccine?
- How effective is the shingles vaccine?
- Is there any reason I shouldnt get the shingles vaccine?
- What could happen if I dont get the shingles vaccine?
Read Also: How To Treat Pain After Shingles
How Can I Learn More
- Ask your health care provider.
- Visit the website of the Food and Drug Administration for vaccine package inserts and additional information at www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines.
- Contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention :
- Call 1-800-232-4636 or
- Visit CDCâs website at www.cdc.gov/vaccines.
Vaccine Information Statement
Side Effects Of Shingrix
Shingrix comes with one drawback, though, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Some of thecommon side effects, like arm pain, redness at the injection site, muscle pain and fevers became more common. They can last up to three days and be intense enough to limit your activity during that time.
Injection-site reactions during the clinical trial were common. Heres what patients experienced:
If you have pain or swelling at the injection site, Baker says, You can take Tylenol or ibuprofen. She adds that injection-site reactions like pain, redness and swelling expected and normal.
Systemic effects were also common, with 10% of people reporting that the symptoms were intense enough to limit their activity. Others reported the following:
- 17% gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea or diarrhea
If you are experiencing systemic symptoms after taking the vaccination, Baker says, Its certainly fine to take through the first two to three days when having symptoms. If the symptoms last longer than that, she says its time to call your healthcare provider.
The vaccine also may increase the risk of Guillain-Barre syndrome, a rare complication that can cause temporary paralysis.
As with any vaccine, anaphylactic shock is less likely, but a possible reaction. If you have hives, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing or an elevated heart rate within hours of receiving the vaccine, you should contact your healthcare provider right away.
Recommended Reading: Is It Possible To Have A Mild Case Of Shingles
What Vaccines Can Help Prevent Shingles
There is currently one vaccine available in the U.S. to prevent shingles. Shingrix was approved in 2017 and it is more than 90% effective in preventing shingles. With Shingrix, you get two shots between 2 and 6 months apart and protection lasts an estimated 4-5 years. Doctors recommend it for healthy people over 50 as well as those 19 years of age and older who are or will be immunodeficient or immunosuppressed due to disease or therapy..
An earlier vaccine called Zostavax was removed from the market in 2020. That vaccine used a weak form of the chickenpox virus to send your bodyâs immune system into action to fight the disease. Shingrix does not. If you received the Zostavax vaccine, it is recommended that you also receive Shingrix.
What Are The Common Side Effects Of The Shingles Vaccine
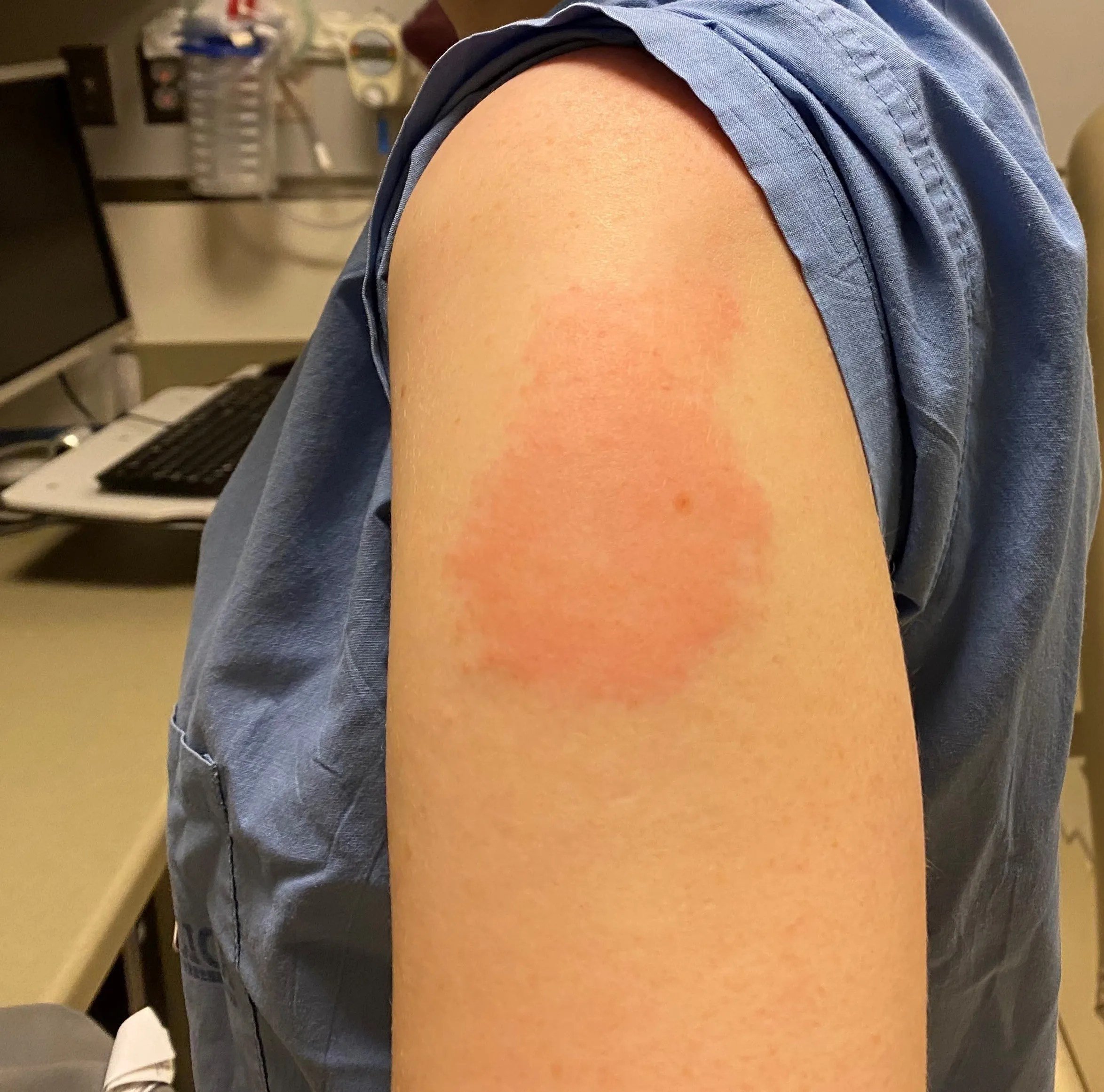
- You may feel sore, swollen, or itchy for a few days where the needle was given.
- You may feel unwell for a day or two with headaches, fatigue, fever, flu-like symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
- Tylenol® or ibuprofen may be taken afterwards, as directed, to reduce discomfort or fever.
- If a rash appears, please inform Public Health at 613-966-5500.
Also Check: How Do Adults Get Shingles
Who Is Eligible For The Vaccine
People aged 70 years of age are eligible for the vaccine.
The vaccine is also available for those previously eligible but who missed immunisation. For example, anyone in their 70s who has not yet had the vaccine.
You become eligible for the shingles vaccine as you turn 70 and remain eligible up to the age of 79.
People under 70 years of age are at lower risk of shingles but will become eligible for the vaccine when they turn 70. People aged 80 years and over are not eligible for the shingles vaccination because the vaccine becomes less effective as people get older. If you are worried about shingles speak to your GP.
You May Like: How Far Apart Should Shingles Shots Be
Risks Of A Vaccine Reaction
- A sore arm with mild or moderate pain is very common after recombinant shingles vaccine. Redness and swelling can also happen at the site of the injection.
- Tiredness, muscle pain, headache, shivering, fever, stomach pain, and nausea are common after recombinant shingles vaccine.
These side effects may temporarily prevent a vaccinated person from doing regular activities. Symptoms usually go away on their own in 2 to 3 days. You should still get the second dose of recombinant shingles vaccine even if you had one of these reactions after the first dose.
Guillain-Barré syndrome , a serious nervous system disorder, has been reported very rarely after recombinant zoster vaccine.
People sometimes faint after medical procedures, including vaccination. Tell your provider if you feel dizzy or have vision changes or ringing in the ears.
As with any medicine, there is a very remote chance of a vaccine causing a severe allergic reaction, other serious injury, or death.
Recommended Reading: Post Shingles Fatigue And Joint Pain Symptoms
When Should I Get The Second Dose
The CDC recommends that adults ages 50 and older get a second dose of Shingrix two to six months after their first dose. If youve waited longer than six months since your first dose of Shingrix, its safe to get a second dose right away. Most people dont need to repeat the first dose.
Some immunocompromised adults may need a second dose within one to two months. If you have a disease or are taking medication that affects your immune system, talk to your healthcare provider about the best timeline for your two doses of the shingles vaccine.
How Effective Is The Shingles Vaccine In Preventing Shingles
The shingles vaccine can provide strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia , the most commonly occurring shingles complication.
The shingles vaccine is 97% effective in preventing shingles in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 91% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
In addition, the shingles vaccine is 91% effective in preventing PHN in people ages 50 to 69 years old. Its 89% effective in people ages 70 years and older.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Shingles And Not Have A Rash
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not receive Shingrix if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to inactivated zoster virus vaccine.
Tell your doctor if:
-
you have ever had an allergic reaction to any vaccine or
-
you have fainted after receiving an injection.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
More Information On Side Effects
Reactions listed under possible side effects or adverse events on vaccine product information sheets may not all be directly linked to the vaccine. See Vaccine side effects and adverse reactions for more information on why this is the case.
If you are concerned about any reactions that occur after vaccination, consult your doctor. In the UK you can report suspected vaccine side effects to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency through the Yellow Card Scheme . See more information on the Yellow Card scheme and monitoring of vaccine safety.
Read Also: Is Shingles A Sign Of Hiv
What Are The Possible Side Effects Of Shingles Immunisation
All medicines and vaccines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time theyre not.
For most people, the chance of having a serious side effect from a vaccine is much lower than the chance of serious harm if you caught the disease.
Talk to your doctor about possible side effects of shingles vaccines, or if you have possible side effects that worry you.
Common side effects of shingles vaccines include:
- pain, redness, swelling or itching where the needle went in
Serious reactions to immunisation are rare. With Zostavax® vaccination, very rarely a generalised chickenpox-like rash may occur around 24 weeks after vaccination. This may be associated with fever and feeling unwell. This rash may be a sign of a serious reaction to the virus in the vaccine. Seek medical attention and inform of recent Zostavax vaccination if you experience this reaction.
The Consumer Medicine Information links in How do you get immunised against shingles? list the side effects of each vaccine.
When Should You Get Immunised Against Shingles

Anyone aged 60 years and over who wants to protect themselves against shingles can talk to their doctor about getting immunised.
Shingles immunisation is recommended for:
- adults aged 60 years and over who have not previously received zoster vaccine
- adults aged 70 years to 79 years, for free under the National Immunisation Program
- adults aged 50 or over who live in the same household as someone who has a weakened immune system.
Recommended Reading: What Is The New Shingle Shot Called
Recommended Reading: What Does Shingles Start Out Looking Like
How Is Shingrix Given
Shingrix is given as an injection into a muscle. A healthcare provider will give you this injection.
Shingrix is usually given in a series of 2 shots:
-
the second shot may be given any time within 2 to 6 months after the first shot.
-
for people who have a weak immune system, the second shot may be given any time within 1 to 2 months after the first shot.
You may receive this vaccine at the same time that you get a flu shot.
Read all patient information, medication guides, and instruction sheets provided to you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
How Do Inactivated Viral Vaccines Work
Inactivated viralvaccines are sterile biologic products that provide immunity against viral infections. Inactivated viral vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to produce antibodies against specific types of viruses, and protect a person from becoming infected when exposed to these viruses.
In the case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes respiratory illness and has led to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines do not entirely prevent infection but protect vaccinated individuals from serious illness and hospitalization from the disease.
Inactivated viral vaccines contain particles of proteins or genetic material from viruses. Inactivated viral vaccines may also contain substances that preserve and stabilize the vaccine, and enhance immune response. Some viral vaccines are delivered in inactivated harmless viruses such as human adenovirus.
Inactivated viral vaccines may be made from:
- Surface proteins of the viruses enable the virus to hold on to a human cell, enter inside and replicate.
- Modified RNA particles from the virus can enter host cells and induce the production of viral antigen, which stimulates an immune response from the body.
- Recombined DNA material from multiple strains and subtypes of viruses, killed to eliminate disease-causing capability.
Currently, inactivated viral vaccines approved by the FDA protect against viral infectious diseases that include:
- Coronavirus disease , caused by SARS-Cov-2 virus
Adults
Read Also: How Long To Recover From Shingles